musl在1.2.x后发生了很大的变化。
数据结构
管理堆空间的最上层数据结构是malloc_context:
struct malloc_context {
uint64_t secret;
#ifndef PAGESIZE
size_t pagesize;
#endif
int init_done;
unsigned mmap_counter;
struct meta *free_meta_head;
struct meta *avail_meta;
size_t avail_meta_count, avail_meta_area_count, meta_alloc_shift;
struct meta_area *meta_area_head, *meta_area_tail;
unsigned char *avail_meta_areas;
struct meta *active[48];
size_t usage_by_class[48];
uint8_t unmap_seq[32], bounces[32];
uint8_t seq;
uintptr_t brk;
};
- secret:在每页的开头,用于校验,检查
meta_area的check - mmap_counter:mmap内存总数
- free_meta_head:freed meta组成的双向链表
- avail_meta:指向可用的meta数组
- active:正在使用的meta数组,将chunk按大小分为了48类
- usage_by_class:对应的大小使用了多少内存
- brk:使用brk开拓的heap的最高地址
struct meta_area {
uint64_t check;
struct meta_area *next;
int nslots;
struct meta slots[];
};
在最开始会使用brk申请一页的内存,页的开头存放meta_area用来管理meta,剩余部分都是meta,即slots[]。meta_area使用单向链表维护,在ctx中有指向头尾的指针。
- check:与secret相同
- next:下一个
meta_area结构 - nslots:当前使用的meta数量
- slots:meta部分
struct meta {
struct meta *prev, *next;
struct group *mem;
volatile int avail_mask, freed_mask;
uintptr_t last_idx:5;
uintptr_t freeable:1;
uintptr_t sizeclass:6;
uintptr_t maplen:8*sizeof(uintptr_t)-12;
};
meta使用双向链表维护。每个meta对应一个group,由mem指针指向。meta可以是brk分配的, 可以是mmap映射的,但是group只能是mmap映射的
- mem:该meta管理的group
- freed_mask:已经被释放的chunk的bitmap
- avail_mask:目前可用的bitmap
struct group {
struct meta *meta;
unsigned char active_idx:5;
char pad[UNIT - sizeof(struct meta *) - 1];
unsigned char storage[];
};
group用来管理分配给用户的内存,在mmap分配的页的开头。
- meta:指向管理该group的meta
- storage[]:分配给用户的内存
给用户的内存我们定义为chunk,但是musl并没有对应的结构体定义,所以这里我们自己定义一下:
struct chunk {
uint8_t res; // 保留 \x00
uint8_t idx:5; //前5bit作为idx表示这是group中第几个chunk, 高3bit作为reserved
uint8_t reserved:3; // 如果剩余大小>5,该段固定为101
uint16_t offset; //与第一个chunk的偏移
char user_data[]; // 最后一字节需要为\x00
char remain_data[]; // 剩余空间最后一字节需要为\x00
uint32_t remain_size; // chunk剩余size大小
};
如果剩余空间为0,则最后两个字段都可以被用户使用。用户使用的内存一般都是由mmap分配的,而除group外,所有的管理数据结构都在heap段,实现了管理与使用的分离。下面是大致的结构框图。
一个meta双向链表中的sizeclass相同,active对应idx指向链表其中一个。
size_to_class
#define IB 4
const uint16_t size_classes[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 12, 15,
18, 20, 25, 31,
36, 42, 50, 63,
72, 84, 102, 127,
146, 170, 204, 255,
292, 340, 409, 511,
584, 682, 818, 1023,
1169, 1364, 1637, 2047,
2340, 2730, 3276, 4095,
4680, 5460, 6552, 8191,
};
static inline int a_ctz_32(uint32_t x)
{
#ifdef a_clz_32
return 31-a_clz_32(x&-x);
#else
static const char debruijn32[32] = {
0, 1, 23, 2, 29, 24, 19, 3, 30, 27, 25, 11, 20, 8, 4, 13,
31, 22, 28, 18, 26, 10, 7, 12, 21, 17, 9, 6, 16, 5, 15, 14
};
return debruijn32[(x&-x)*0x076be629 >> 27];
#endif
}
static inline int a_clz_32(uint32_t x)
{
x >>= 1;
x |= x >> 1;
x |= x >> 2;
x |= x >> 4;
x |= x >> 8;
x |= x >> 16;
x++;
return 31-a_ctz_32(x);
}
static inline int size_to_class(size_t n)
{
n = (n+IB-1)>>4;
if (n<10) return n;
n++;
int i = (28-a_clz_32(n))*4 + 8;
if (n>size_classes[i+1]) i+=2;
if (n>size_classes[i]) i++;
return i;
}
将size转化为内部的类,musl把chunk大小分为48类,用size_to_class进行计算。与*active[48]对应
0x0 ~ 0xc ->0
0xd ~ 0x1c ->1
0x1d ~ 0x2c ->2
0x2d ~ 0x3c ->3
0x3d ~ 0x4c ->4
0x4d ~ 0x5c ->5
0x5d ~ 0x6c ->6
0x6d ~ 0x7c ->7
0x7d ~ 0x8c ->8
0x8d ~ 0x9c ->9
0x9d ~ 0xbc ->10
0xbd ~ 0xec ->11
0xed ~ 0x11c ->12
0x11d ~ 0x13c ->13
0x13d ~ 0x18c ->14
0x18d ~ 0x1ec ->15
0x1ed ~ 0x23c ->16
0x23d ~ 0x29c ->17
0x29d ~ 0x31c ->18
0x31d ~ 0x3ec ->19
0x3ed ~ 0x47c ->20
0x47d ~ 0x53c ->21
0x53d ~ 0x65c ->22
0x65d ~ 0x7ec ->23
0x7ed ~ 0x91c ->24
0x91d ~ 0xa9c ->25
0xa9d ~ 0xcbc ->26
0xcbd ~ 0xfec ->27
0xfed ~ 0x123c ->28
0x123d ~ 0x153c ->29
0x153d ~ 0x198c ->30
0x198d ~ 0x1fec ->31
0x1fed ~ 0x247c ->32
0x247d ~ 0x2a9c ->33
0x2a9d ~ 0x331c ->34
0x331d ~ 0x3fec ->35
0x3fed ~ 0x490c ->36
0x490d ~ 0x553c ->37
0x553d ~ 0x664c ->38
0x664d ~ 0x7fec ->39
0x7fed ~ 0x923c ->40
0x923d ~ 0xaa9c ->41
0xaa9d ~ 0xccbc ->42
0xccbd ~ 0xffec ->43
0xffed ~ 0x1247c ->44
0x1247d ~ 0x1553c ->45
0x1553d ~ 0x1997c ->46
malloc
void *malloc(size_t n)
{
if (size_overflows(n)) return 0;
struct meta *g;
uint32_t mask, first;
int sc;
int idx;
int ctr;
if (n >= MMAP_THRESHOLD) {
[...]
}
sc = size_to_class(n);
rdlock(); // 加锁
g = ctx.active[sc]; // 获取对应的meta
mmap部分略过
// use coarse size classes initially when there are not yet
// any groups of desired size. this allows counts of 2 or 3
// to be allocated at first rather than having to start with
// 7 or 5, the min counts for even size classes.
if (!g && sc>=4 && sc<32 && sc!=6 && !(sc&1) && !ctx.usage_by_class[sc]) {
size_t usage = ctx.usage_by_class[sc|1];
// if a new group may be allocated, count it toward
// usage in deciding if we can use coarse class.
if (!ctx.active[sc|1] || (!ctx.active[sc|1]->avail_mask
&& !ctx.active[sc|1]->freed_mask))
usage += 3;
if (usage <= 12)
sc |= 1;
g = ctx.active[sc];
}
如果对应meta为空,且 4<=sc<32 且 sc!=6 且 sc是偶数 且 这个大小的类还没使用过内存。这段逻辑很迷,个人感觉像是,如果第一次申请小内存,则会向后取更大类的meta。就像减少小内存的分配?
for (;;) {
mask = g ? g->avail_mask : 0; // 取 avail_mask
first = mask&-mask; // 取第一个可用的chunk
if (!first) break;
if (RDLOCK_IS_EXCLUSIVE || !MT)
g->avail_mask = mask-first; // 将对应的mask置位,下面将要取出它
else if (a_cas(&g->avail_mask, mask, mask-first)!=mask)
continue; // 无锁时使用原子操作保证 avail_mask 的更新
idx = a_ctz_32(first); // 取2的指数,计算在group的idx
goto success;
}
upgradelock();
// 到这里表明对应的 meta 没有可用的chunk,需要寻找新的 meta
// 也说明对应 active 的项没有可用的空间需要更新
idx = alloc_slot(sc, n);
if (idx < 0) {
unlock();
return 0;
}
g = ctx.active[sc]; // 更新 meta
success:
ctr = ctx.mmap_counter;
unlock();
return enframe(g, idx, n, ctr); // 设置头部字段并将内存返回给用户
}
alloc_slot
static int alloc_slot(int sc, size_t req)
{
uint32_t first = try_avail(&ctx.active[sc]); // 尝试在对应类的meta的链表寻找可分配的内存
if (first) return a_ctz_32(first);
struct meta *g = alloc_group(sc, req); // 找到了对应的meta,开始申请group
if (!g) return -1;
g->avail_mask--; // 第一个chunk被使用了
queue(&ctx.active[sc], g);
return 0;
}
try_avail
static uint32_t try_avail(struct meta **pm)
{
struct meta *m = *pm; // actvie剩余的部分当作一个数组
uint32_t first;
if (!m) return 0;
uint32_t mask = m->avail_mask;
if (!mask) { // 没有可用的chunk
if (!m) return 0;
if (!m->freed_mask) { // 没有被free的chunk,说明所有的chunk都被分配出去了
dequeue(pm, m); // 将当前meta从链表中取出,unlink操作,更新对应数组项
m = *pm; // 更新后的meta
if (!m) return 0; // 如果更新后的为null,直接返回
} else {
m = m->next; // 这里应该是优先使用下一个meta,这样链表中的meta都是循环使用的,减少了dequeue操作
*pm = m;
}
mask = m->freed_mask;
// skip fully-free group unless it's the only one
// or it's a permanently non-freeable group
// 如果当前meta中的chunk全被free,并且当前meta管理的内存可用被free
// 那么优先使用下一个,这里应该是为了将全被free的内存返回给系统,减少占用
if (mask == (2u<<m->last_idx)-1 && m->freeable) {
m = m->next;
*pm = m;
mask = m->freed_mask;
}
// activate more slots in a not-fully-active group
// if needed, but only as a last resort. prefer using
// any other group with free slots. this avoids
// touching & dirtying as-yet-unused pages.
// ((2u << m->mem->active_idx) - 1)建立一个掩码, 如果acctive_idx为3, 那么就是0b1111
// 如果这个group中有free的chunk,但不是已被激活的chunk
if (!(mask & ((2u<<m->mem->active_idx)-1))) {
if (m->next != m) { // 如果链表中还有其他meta则优先使用free的可使用的chunk
m = m->next;
*pm = m;
} else { // 到这里开始激活更多的chunk
int cnt = m->mem->active_idx + 2;
int size = size_classes[m->sizeclass]*UNIT;
int span = UNIT + size*cnt;
// activate up to next 4k boundary
while ((span^(span+size-1)) < 4096) { // 直到到达页边界
cnt++;
span += size;
}
if (cnt > m->last_idx+1)
cnt = m->last_idx+1;
m->mem->active_idx = cnt-1; // 更新active_idx
}
}
mask = activate_group(m); // 激活这个group, 把free的chunk转移到avail中,其实就是交换下bitmap的事
assert(mask); // 由于group中freed_mask非空, 拓展active后使freed chunk变为可用
decay_bounces(m->sizeclass);
}
first = mask&-mask;
m->avail_mask = mask-first;
return first; // 返回第一个可用的
}
这代码写的真迷。
经过前面的步骤,我们尝试了在对应类的meta链表中获取内存,甚至扩大active都没有成功,所以要申请新的meta以及对应的group。
alloc_group
static struct meta *alloc_group(int sc, size_t req)
{
size_t size = UNIT*size_classes[sc];
int i = 0, cnt;
unsigned char *p;
struct meta *m = alloc_meta(); // 获取一个 meta
if (!m) return 0;
size_t usage = ctx.usage_by_class[sc];
size_t pagesize = PGSZ;
int active_idx;
if (sc < 9) {
while (i<2 && 4*small_cnt_tab[sc][i] > usage)
i++;
cnt = small_cnt_tab[sc][i];
} else {
// lookup max number of slots fitting in power-of-two size
// from a table, along with number of factors of two we
// can divide out without a remainder or reaching 1.
cnt = med_cnt_tab[sc&3];
// reduce cnt to avoid excessive eagar allocation.
while (!(cnt&1) && 4*cnt > usage)
cnt >>= 1;
// data structures don't support groups whose slot offsets
// in units don't fit in 16 bits.
while (size*cnt >= 65536*UNIT)
cnt >>= 1;
}
// If we selected a count of 1 above but it's not sufficient to use
// mmap, increase to 2. Then it might be; if not it will nest.
// 如果在上面我们的cnt为1,但是不够使用mmap,将cnt增加到2可能就可以了
if (cnt==1 && size*cnt+UNIT <= pagesize/2) cnt = 2;
// All choices of size*cnt are "just below" a power of two, so anything
// larger than half the page size should be allocated as whole pages.
if (size*cnt+UNIT > pagesize/2) {
// check/update bounce counter to start/increase retention
// of freed maps, and inhibit use of low-count, odd-size
// small mappings and single-slot groups if activated.
int nosmall = is_bouncing(sc);
account_bounce(sc);
step_seq();
// since the following count reduction opportunities have
// an absolute memory usage cost, don't overdo them. count
// coarse usage as part of usage.
if (!(sc&1) && sc<32) usage += ctx.usage_by_class[sc+1];
// try to drop to a lower count if the one found above
// increases usage by more than 25%. these reduced counts
// roughly fill an integral number of pages, just not a
// power of two, limiting amount of unusable space.
if (4*cnt > usage && !nosmall) {
if (0);
else if ((sc&3)==1 && size*cnt>8*pagesize) cnt = 2;
else if ((sc&3)==2 && size*cnt>4*pagesize) cnt = 3;
else if ((sc&3)==0 && size*cnt>8*pagesize) cnt = 3;
else if ((sc&3)==0 && size*cnt>2*pagesize) cnt = 5;
}
size_t needed = size*cnt + UNIT;
needed += -needed & (pagesize-1);
// produce an individually-mmapped allocation if usage is low,
// bounce counter hasn't triggered, and either it saves memory
// or it avoids eagar slot allocation without wasting too much.
if (!nosmall && cnt<=7) {
req += IB + UNIT;
req += -req & (pagesize-1);
if (req<size+UNIT || (req>=4*pagesize && 2*cnt>usage)) {
cnt = 1;
needed = req;
}
}
上面做了一些size的调整。
p = mmap(0, needed, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANON, -1, 0);
if (p==MAP_FAILED) {
free_meta(m);
return 0;
}
m->maplen = needed>>12;
ctx.mmap_counter++; // mmap 申请的内存数量++
active_idx = (4096-UNIT)/size-1; // 计算active_idx 最多cnt-1
if (active_idx > cnt-1) active_idx = cnt-1;
if (active_idx < 0) active_idx = 0;
} else { // active_idx <= cnt -1,只要active_idx不小于0,这段是必须进行的
int j = size_to_class(UNIT+cnt*size-IB);
int idx = alloc_slot(j, UNIT+cnt*size-IB); // 从对应大小的meta_area中找到一个meta??
if (idx < 0) {
free_meta(m);
return 0;
}
struct meta *g = ctx.active[j];
p = enframe(g, idx, UNIT*size_classes[j]-IB, ctx.mmap_counter);
m->maplen = 0;
p[-3] = (p[-3]&31) | (6<<5);
for (int i=0; i<=cnt; i++)
p[UNIT+i*size-4] = 0;
active_idx = cnt-1;
}
ctx.usage_by_class[sc] += cnt;
m->avail_mask = (2u<<active_idx)-1;
m->freed_mask = (2u<<(cnt-1))-1 - m->avail_mask;
m->mem = (void *)p;
m->mem->meta = m;
m->mem->active_idx = active_idx;
m->last_idx = cnt-1;
m->freeable = 1;
m->sizeclass = sc;
return m;
}
到这里我们就应该得到了内存,如果又失败则是内存不足。
alloc_meta
struct meta *alloc_meta(void)
{
struct meta *m;
unsigned char *p;
if (!ctx.init_done) { // 如果没有初始化先初始化
#ifndef PAGESIZE
ctx.pagesize = get_page_size();
#endif
ctx.secret = get_random_secret();
ctx.init_done = 1;
}
size_t pagesize = PGSZ;
if (pagesize < 4096) pagesize = 4096;
if ((m = dequeue_head(&ctx.free_meta_head))) return m; // 从free的meta链表头取一个meta,如果取到了直接返回这个meta即可
if (!ctx.avail_meta_count) { // 没有可用的meta
int need_unprotect = 1;
if (!ctx.avail_meta_area_count && ctx.brk!=-1) { // 没有可用的meta_area,并且上一次brk没有失败(也可能是还没有使用brk开辟堆空间)
uintptr_t new = ctx.brk + pagesize;
int need_guard = 0;
if (!ctx.brk) { // 还未开辟堆空间
need_guard = 1;
ctx.brk = brk(0); // brk(0)获取heap的初始地址
// some ancient kernels returned _ebss
// instead of next page as initial brk.
ctx.brk += -ctx.brk & (pagesize-1); // 按页进行对齐
new = ctx.brk + 2*pagesize; // 第一次开辟heap,开辟两个页
}
if (brk(new) != new) { // brk失败
ctx.brk = -1;
} else { // brk成功,更新ctx中的各种信息
if (need_guard) mmap((void *)ctx.brk, pagesize,
PROT_NONE, MAP_ANON|MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED, -1, 0); // 不知道这个guard什么意思,与heap的第一页有关
ctx.brk = new;
ctx.avail_meta_areas = (void *)(new - pagesize); // 从第二页的开头开始使用
ctx.avail_meta_area_count = pagesize>>12; // 一个meta_area管理一个页
need_unprotect = 0;
}
}
if (!ctx.avail_meta_area_count) { // 没有可用的meta_area且无法brk的情况
size_t n = 2UL << ctx.meta_alloc_shift; // 申请2,4,8...页指数增加
p = mmap(0, n*pagesize, PROT_NONE, // 使用mmap进行映射
MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANON, -1, 0);
if (p==MAP_FAILED) return 0;
ctx.avail_meta_areas = p + pagesize;
ctx.avail_meta_area_count = (n-1)*(pagesize>>12); // 每次申请的第一个页都不能使用???
ctx.meta_alloc_shift++;
}
p = ctx.avail_meta_areas;
if ((uintptr_t)p & (pagesize-1)) need_unprotect = 0; // 如果页对齐了,则为0
if (need_unprotect)
if (mprotect(p, pagesize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE) // 没有对齐则不需要保护??
&& errno != ENOSYS)
return 0;
ctx.avail_meta_area_count--; // 第一个meta_area将被使用
ctx.avail_meta_areas = p + 4096;
if (ctx.meta_area_tail) {
ctx.meta_area_tail->next = (void *)p;
} else {
ctx.meta_area_head = (void *)p;
}
ctx.meta_area_tail = (void *)p;
ctx.meta_area_tail->check = ctx.secret;
ctx.avail_meta_count = ctx.meta_area_tail->nslots
= (4096-sizeof(struct meta_area))/sizeof *m;
ctx.avail_meta = ctx.meta_area_tail->slots;
}
ctx.avail_meta_count--; // 第一个meta被使用
m = ctx.avail_meta++; //
m->prev = m->next = 0;
return m;
}
这样看,在初始化时会申请两个页,第一个页无法使用作为guard,第二个页作为meta_area使用,剩余内存都会用做meta。
frame set
static inline void set_size(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *end, size_t n)
{
int reserved = end-p-n;
if (reserved) end[-reserved] = 0;
if (reserved >= 5) {
*(uint32_t *)(end-4) = reserved;
end[-5] = 0;
reserved = 5;
}
p[-3] = (p[-3]&31) + (reserved<<5);
}
static inline void *enframe(struct meta *g, int idx, size_t n, int ctr)
{
size_t stride = get_stride(g);
size_t slack = (stride-IB-n)/UNIT;
unsigned char *p = g->mem->storage + stride*idx;
unsigned char *end = p+stride-IB;
// cycle offset within slot to increase interval to address
// reuse, facilitate trapping double-free.
int off = (p[-3] ? *(uint16_t *)(p-2) + 1 : ctr) & 255;
assert(!p[-4]);
if (off > slack) {
size_t m = slack;
m |= m>>1; m |= m>>2; m |= m>>4;
off &= m;
if (off > slack) off -= slack+1;
assert(off <= slack);
}
if (off) {
// store offset in unused header at offset zero
// if enframing at non-zero offset.
*(uint16_t *)(p-2) = off;
p[-3] = 7<<5;
p += UNIT*off;
// for nonzero offset there is no permanent check
// byte, so make one.
p[-4] = 0;
}
*(uint16_t *)(p-2) = (size_t)(p-g->mem->storage)/UNIT;
p[-3] = idx;
set_size(p, end, n);
return p;
}
这两个函数设置了chunk的头部与尾部的控制字段。
free
void free(void *p)
{
if (!p) return;
struct meta *g = get_meta(p); // 获取对应的meta
int idx = get_slot_index(p); // 获取在group中的idx,p[-3]&31,五位的idx说明一个最多32个chunk
size_t stride = get_stride(g); // 获取group中一个chunk的大小,步幅
unsigned char *start = g->mem->storage + stride*idx; // chunk的起始地址
unsigned char *end = start + stride - IB; // chunk的结尾地址,减去一个chunk的头部大小
get_nominal_size(p, end); // 检查用户使用的大小是否溢出
uint32_t self = 1u<<idx, all = (2u<<g->last_idx)-1;
// idx字段置为0xff,offset置为0
((unsigned char *)p)[-3] = 255;
// invalidate offset to group header, and cycle offset of
// used region within slot if current offset is zero.
*(uint16_t *)((char *)p-2) = 0;
// release any whole pages contained in the slot to be freed
// unless it's a single-slot group that will be unmapped.
// 如果该group中的chunk比页大,并且包含多个chunk,则将group到这个chunk的这段空间交给操作系统处置,程序提出建议free。madvise的操作不再赘述
if (((uintptr_t)(start-1) ^ (uintptr_t)end) >= 2*PGSZ && g->last_idx) {
unsigned char *base = start + (-(uintptr_t)start & (PGSZ-1));
size_t len = (end-base) & -PGSZ;
if (len) madvise(base, len, MADV_FREE);
}
// atomic free without locking if this is neither first or last slot
for (;;) { // 设置对应的mask,但是free的chunk并不会马上avail
uint32_t freed = g->freed_mask;
uint32_t avail = g->avail_mask;
uint32_t mask = freed | avail;
assert(!(mask&self));
if (!freed || mask+self==all) break; // 如果当前chunk被free后,这个group中的chunk都处于avail或free,跳出由nontrivial_free处理
if (!MT)
g->freed_mask = freed+self;
else if (a_cas(&g->freed_mask, freed, freed+self)!=freed)
continue;
return;
}
wrlock();
struct mapinfo mi = nontrivial_free(g, idx);
unlock();
if (mi.len) munmap(mi.base, mi.len);
}
get_meta
static inline struct meta *get_meta(const unsigned char *p)
{
assert(!((uintptr_t)p & 15)); // 16自己对齐检查
int offset = *(const uint16_t *)(p - 2);
int index = get_slot_index(p);
if (p[-4]) { // 如果头部第一字节不为0,这个chunk只能是第一个chunk
assert(!offset);
offset = *(uint32_t *)(p - 8);
assert(offset > 0xffff);
}
const struct group *base = (const void *)(p - UNIT*offset - UNIT);
const struct meta *meta = base->meta;
assert(meta->mem == base); // group与meta的对应检查
assert(index <= meta->last_idx); // idx未超出范围检查
assert(!(meta->avail_mask & (1u<<index))); // 当前chunk是被分配的
assert(!(meta->freed_mask & (1u<<index))); // 当前chunk是未free
const struct meta_area *area = (void *)((uintptr_t)meta & -4096);
assert(area->check == ctx.secret); // secret检查
if (meta->sizeclass < 48) { // size偏移检查
assert(offset >= size_classes[meta->sizeclass]*index);
assert(offset < size_classes[meta->sizeclass]*(index+1));
} else {
assert(meta->sizeclass == 63);
}
if (meta->maplen) {
assert(offset <= meta->maplen*4096UL/UNIT - 1);
}
return (struct meta *)meta;
}
get_nominal_size
static inline size_t get_nominal_size(const unsigned char *p, const unsigned char *end)
{
size_t reserved = p[-3] >> 5; // 保留字段,猜测是标识该chunk已被active,5<<5=0xa
if (reserved >= 5) {
assert(reserved == 5);
reserved = *(const uint32_t *)(end-4); // 取了尾部的四个字节
assert(reserved >= 5);
assert(!end[-5]);
}
assert(reserved <= end-p);
assert(!*(end-reserved));
// also check the slot's overflow byte
assert(!*end);
return end-reserved-p;
}
在尾部的四个字节记录了该chunk所占用的大小减去用户申请的大小所剩的字节。例如,malloc(0x10),程序会分配sizeclass=0x1的chunk,chunk大小0x20,减去头部四个字节0x20-0x4=0x1c,再减去用户申请0x1c-0x10=12=0xc。get_nominal_size中检测了剩余size字段的前一个字节是否被修改(要求为0)。且这个size大小满足5 <= remain_size <= chunk_size。函数中还检测了用户是否超出所申请的大小,进一步防止溢出。
nontrivial_free
static struct mapinfo nontrivial_free(struct meta *g, int i)
{
uint32_t self = 1u<<i;
int sc = g->sizeclass;
uint32_t mask = g->freed_mask | g->avail_mask;
// 如果当前chunk被free后,这个group中的chunk都处于avail或free
if (mask+self == (2u<<g->last_idx)-1 && okay_to_free(g)) {
// any multi-slot group is necessarily on an active list
// here, but single-slot groups might or might not be.
if (g->next) { // 如果它在链表中且sc<48,从链表中取出它,再激活,将free的转化为可用的
assert(sc < 48);
int activate_new = (ctx.active[sc]==g);
dequeue(&ctx.active[sc], g);
if (activate_new && ctx.active[sc])
activate_group(ctx.active[sc]);
}
return free_group(g); // free掉这个group,也会free掉对应的meta将其加入free_meta链表
} else if (!mask) { // 所有内存都是分配状态,这里与上一个函数有对应
assert(sc < 48);
// might still be active if there were no allocations
// after last available slot was taken.
if (ctx.active[sc] != g) { // 将其加入对应链表,因为当前有一个chunk被free了
queue(&ctx.active[sc], g);
}
}
a_or(&g->freed_mask, self); // 更新mask
return (struct mapinfo){ 0 };
}
Debug Details
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
void *p1, *p2, *p3;
p1 = malloc(0x10);
malloc(0x10);
malloc(0x10);
p2 = malloc(0x30);
malloc(0x30);
malloc(0x30);
p3 = malloc(0x50);
malloc(0x50);
malloc(0x50);
free(p1);
free(p2);
free(p3);
return 0;
}
首先,申请三个0x10的chunk
gef➤ p __malloc_context
$1 = {
secret = 0xb64bf19b04a64b1a,
init_done = 0x1,
mmap_counter = 0x0,
free_meta_head = 0x0,
avail_meta = 0x55555555a1f8,
avail_meta_count = 0x59,
avail_meta_area_count = 0x0,
meta_alloc_shift = 0x0,
meta_area_head = 0x55555555a000,
meta_area_tail = 0x55555555a000,
avail_meta_areas = 0x55555555b000 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x55555555b000>,
active = {0x0, 0x55555555a1d0, 0x0, 0x55555555a0e0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x55555555a0b8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x55555555a090, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x55555555a158, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x55555555a040, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x55555555a018, 0x0 <repeats 24 times>},
usage_by_class = {0x0, 0xf, 0x0 <repeats 46 times>},
unmap_seq = '\000' <repeats 31 times>,
bounces = '\000' <repeats 31 times>,
seq = 0x0,
brk = 0x55555555b000
}
现在申请了一个meta_area,avail_meta_areas指向下一个可用的meta_area与当前的brk相同。
gef➤ p *(struct meta_area*)0x55555555a000
$2 = {
check = 0xb64bf19b04a64b1a,
next = 0x0,
nslots = 0x65,
slots = 0x55555555a018
}
可以看到check与secret相同,next指向null。当前区域最多0x65个meta。
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x55555555a1d0
$3 = {
prev = 0x55555555a1d0,
next = 0x55555555a1d0,
mem = 0x7ffff7ffecb0, // 指向group
avail_mask = 0x7ff8, // 0b111 1111 1111 1000 我们申请了三个chunk,前三个不可用
freed_mask = 0x0, // 目前没有chunk被free
last_idx = 0xe, // 最后一个chunk的下标为0xe,与总共15个chunk对应
freeable = 0x1, // 当前meta可被free
sizeclass = 0x1, // 用户空间由0x1这个group管理
maplen = 0x0
}
gef➤ p *(struct group*)0x7ffff7ffecb0
$4 = {
meta = 0x55555555a1d0,
active_idx = 0xe, // 与之前的`last_idx`对应了
pad = "\000\000\000\000\240\000",
storage = 0x7ffff7ffecc0 "" // 用户使用空间的开始
}
一个chunk的头部只有四字节,再向前的四字节由前面的chunk使用。0xa0,0xa1,0xa2表示这个是group的第0,1,2的chunk。再向前一字节,0x00和0x02代表当前chunk与第一个chunk的偏移,以0x10为单位。0xc代表剩余的字节。
free(p1)
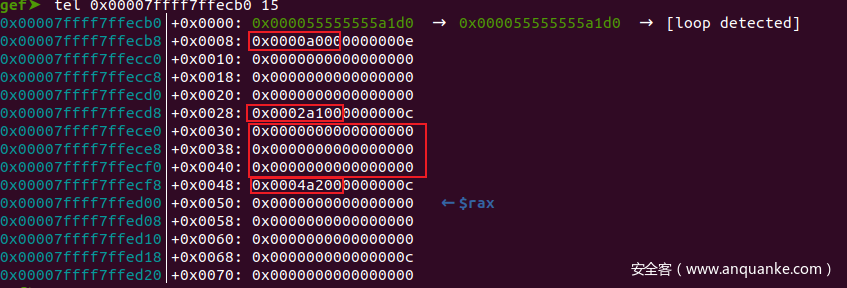
gef➤ tel 0x00007ffff7ffecb0 15
0x00007ffff7ffecb0│+0x0000: 0x000055555555a1d0 → 0x000055555555a1d0 → [loop detected]
0x00007ffff7ffecb8│+0x0008: 0x0000ff000000000e
0x00007ffff7ffecc0│+0x0010: 0x0000000000000000 ← $r9
0x00007ffff7ffecc8│+0x0018: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffecd0│+0x0020: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffecd8│+0x0028: 0x0002a1000000000c
0x00007ffff7ffece0│+0x0030: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffece8│+0x0038: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffecf0│+0x0040: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffecf8│+0x0048: 0x0004a2000000000c
0x00007ffff7ffed00│+0x0050: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffed08│+0x0058: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffed10│+0x0060: 0x0000000000000000
0x00007ffff7ffed18│+0x0068: 0x000000000000000c
0x00007ffff7ffed20│+0x0070: 0x0000000000000000
gef➤ p *(struct meta*)0x55555555a1d0
$18 = {
prev = 0x55555555a1d0,
next = 0x55555555a1d0,
mem = 0x7ffff7ffecb0,
avail_mask = 0x7ff8,
freed_mask = 0x1,
last_idx = 0xe,
freeable = 0x1,
sizeclass = 0x1,
maplen = 0x0
}
avail_mask没有发生变化,被free的chunk不会马上可用。freed_mask变成1,说明当前第一个chunk被free了。
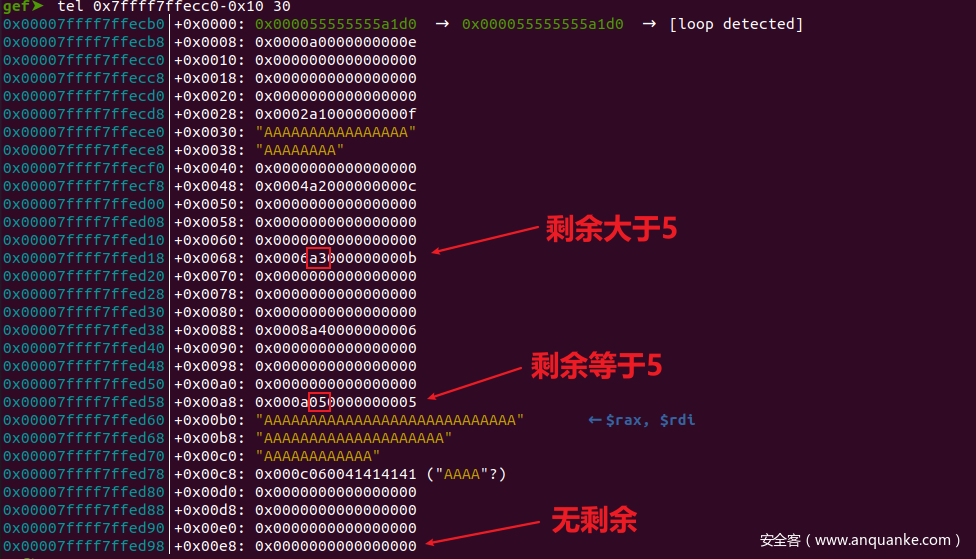
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
void *p1, *p2, *p3, *p4;
void *buf;
p1 = malloc(0xd);
p2 = malloc(0x10);
memset(p2,'A',0x10);
p3 = malloc(0x11);
malloc(0x1c-6);
malloc(0x1c-5);
buf = malloc(0x1c);
malloc(0x1c);
memset(buf,'A',0x1c);
p4 = malloc(0x1d);
exit(0);
}
再用这个例子验证chunk的结构
再申请一个p4(0x1d)
p3与p4已经不在一个group中了。
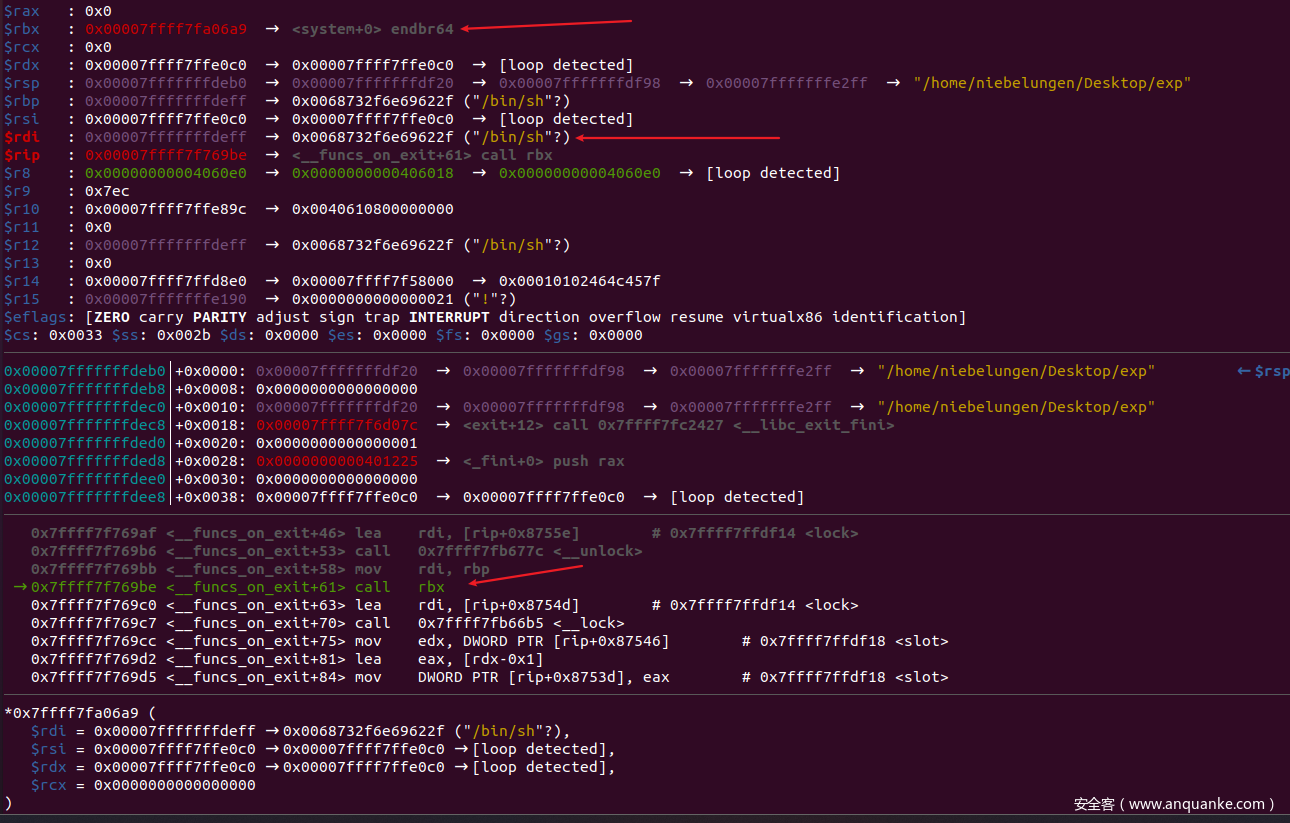
如果溢出一字节
memset(p2,'A',0x11);
free(p2);
niebelungen@pwn:~/Desktop$ /usr/local/musl/bin/musl-gcc -g ./exp.c -o exp
niebelungen@pwn:~/Desktop$ ./exp
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
我之前介绍过exit劫持的方法在1.2.x中还是可以使用。博客指路:https://niebelungen-d.top/2021/08/22/Musl-libc-Pwn-Learning/
At last
源码的view差不多就这样。通过调试可以对其chunk的结构有更深的了解不然代码部分很难看懂。











发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录