V8是chrome核心组件,重要程度不用多言。本系列文章,讲解V8源码,力求做到全面覆盖知识点、有理论高度,做到细致讲解代码、有实践依据。
本篇内容
本次是第二篇,主要内容是从宏观上概述V8的运行过程,包括:初始化、编译代码、运行、退出。面对V8这个庞大的系统工程,本文尽力为读者构建一个全面的大局观,从程序源码的角度揭示V8代码的主要脉络,达到快速入手的目的。本文想给读者的“大局观”是:知道V8是怎么运行的,了解V8运行过程中的几个重要中间阶段、重要中间结果、以及相应的重要数据结构。为此,本文从Javascript代码的两个主要阶段编译和执行的知识点出发,以V8源码中的重要数据结构抽象语法树(AST)和字节表(Bytecode)为抓手展开全面、宏观的讲解。
1 V8运行过程
以v8\samples\hello-world.c为例,这个例子我曾反复说过,它是运行V8功能的最小代码集合,只包含了V8的最重要最基本的功能,适合入门。例如,徒增学习难度的优化编译功能,在这个例子中就没出现,优化编译是V8最重要的部分,是提升性能的关键,但对初学者并没有用,所以说只有基础功能的hello-world最适合入门。
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Initialize V8.
v8::V8::InitializeICUDefaultLocation(argv[0]);
v8::V8::InitializeExternalStartupData(argv[0]);
std::unique_ptr<v8::Platform> platform = v8::platform::NewDefaultPlatform();
v8::V8::InitializePlatform(platform.get());
v8::V8::Initialize();
// Create a new Isolate and make it the current one.
v8::Isolate::CreateParams create_params;
create_params.array_buffer_allocator =
v8::ArrayBuffer::Allocator::NewDefaultAllocator();
v8::Isolate* isolate = v8::Isolate::New(create_params);
{
v8::Isolate::Scope isolate_scope(isolate);
// Create a stack-allocated handle scope.
v8::HandleScope handle_scope(isolate);
// Create a new context.
v8::Local<v8::Context> context = v8::Context::New(isolate);
// Enter the context for compiling and running the hello world script.
v8::Context::Scope context_scope(context);
{
// Create a string containing the JavaScript source code.
v8::Local<v8::String> source =
v8::String::NewFromUtf8Literal(isolate, "'Hello' + ', World!'");
// Compile the source code.
v8::Local<v8::Script> script =
v8::Script::Compile(context, source).ToLocalChecked();
// Run the script to get the result.
v8::Local<v8::Value> result = script->Run(context).ToLocalChecked();
//...
//省略部分代码
//...
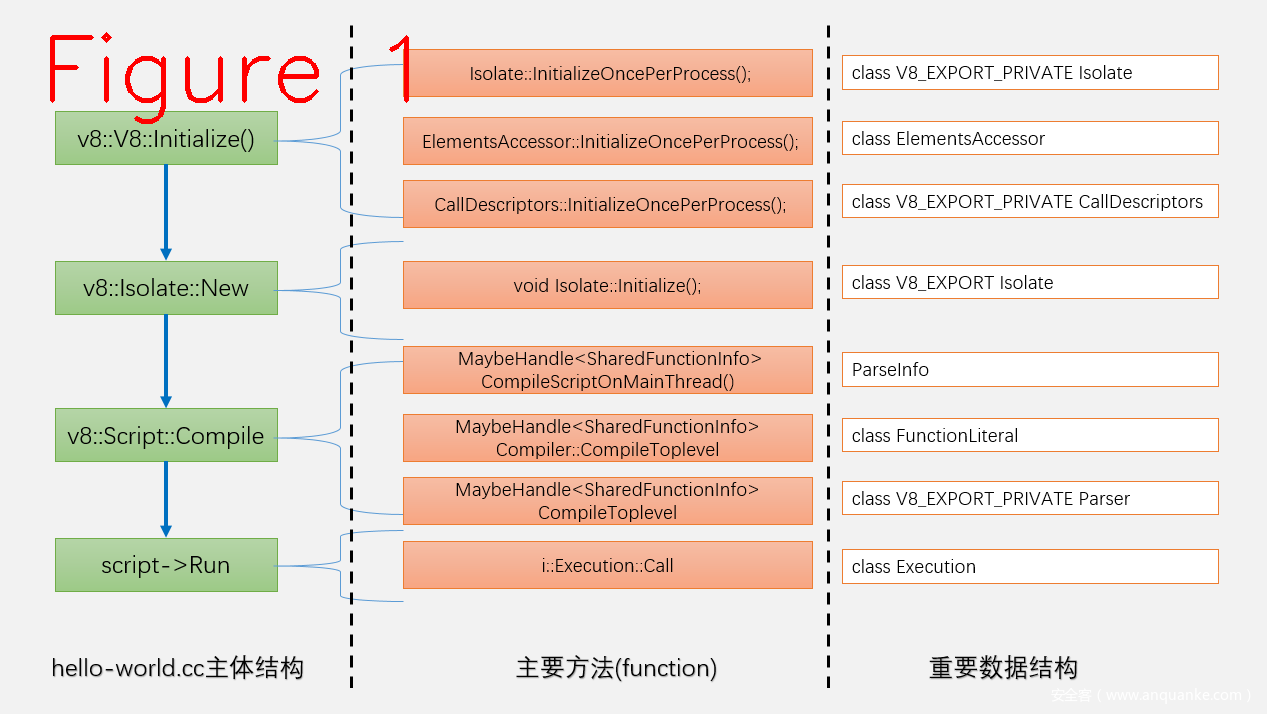
上面这段代码是hello-world.cc中最重要的部分,V8的初始化是v8::V8::Initialize(),Isolate的创建v8::Isolate::New,编译v8::Script::Compile,执行script->Run。handle和context没有提及,因为对初学者不重要。图1说明了每个阶段的重要数据结构,读者可以利用VS2019的debug跟踪查看详细过程(跟踪方法见上一篇文章)。
图1中可以看到hello-world.cc程序的主要主体结构(工作流程),还有与之对应的方法和数据结构。V8代码量很大,通过重要数据结构和中间结果入手学习,可以很好地抓住V8的主线功能,把主线功能理解透彻之后,再学习旁支功能可达到事半功倍的效果。接下来,以图1中主要方法为主,结合主要数据结构进行单独讲解。
2 V8启动时的内存申请
InitReservation负责为V8申请内存,代码位置src\utils\allocation.cc。
// Reserve a region of twice the size so that there is an aligned address
// within it that's usable as the cage base.
VirtualMemory padded_reservation(params.page_allocator,
params.reservation_size * 2,
reinterpret_cast<void*>(hint));
Address address =
VirtualMemoryCageStart(padded_reservation.address(), params);
...省略了很多行代码...
// Now free the padded reservation and immediately try to reserve an
// exact region at aligned address. We have to do this dancing because
// the reservation address requirement is more complex than just a
// certain alignment and not all operating systems support freeing parts
// of reserved address space regions.
padded_reservation.Free();
VirtualMemory reservation(params.page_allocator,
params.reservation_size,
reinterpret_cast<void*>(address));
申请内存时为了保证内存对齐,它的做法是先申请两倍的内存,然后从中找一个适合做内存对齐的地址,再把两倍内存释放,从刚找到的地址申请需要的4G大小。具体做法是:padded_reservation申请一个两倍大小的内存(8G),再利用padded_reservation.Free()释放,再用reservation申请的4G内存则是V8真正的内存。下面讲解V8管理内存的主要数据结构:VirtualMemoryCage。V8向操作系统申请4G内存,用于后续的所有工作,例如创新Isolate,等等。V8的内存方式采用的段页式,和操作系统(OS)的方法类似,但不像OS有多个段,V8只有一个段,但有很多页。VirtualMemeoryCage的定义在allocation.h中,我们对它的结构进行说明。
// +------------+-----------+----------- ~~~ -+
// | ... | ... | ... |
// +------------+-----------+------------ ~~~ -+
// ^ ^ ^
// start cage base allocatable base
//
// <------------> <------------------->
// base bias size allocatable size
// <-------------------------------------------->
// reservation size
“a VirtualMemory reservation”是V8源码中的叫法,reservation size是4G,也就是v8申请内存的总大小,start是这个内存的基址,cage base是v8用于管理的基址,可以先理解为cage base是页表位置,allocatable开始是v8可以分配的,用于创新isolate。VirtualMemoryCage中的成员reservation_负责指向这个4G内存。另一个重要的结构是ReservationParams,申请内存大小(4G),对齐方式,指针压缩等参数都在这个结构中定义。
3 Isolate
Isolate是一个完整的V8实例,有着完整的堆栈和Heap。V8是虚拟机,isolate才是运行javascript的宿主。一个Isolate是一个独立的运行环境, 包括但不限于堆管理器(heap)、垃圾回收器(gc)等。在一个时间,有且只有一个线程能在isolate中运行代码,也就是说同一时刻,只有一个线程能进入isolate,多个线程可以通过切换来共享同一个isolate。
/**
* Isolate represents an isolated instance of the V8 engine. V8 isolates have
* completely separate states. Objects from one isolate must not be used in
* other isolates. The embedder can create multiple isolates and use them in
* parallel in multiple threads. An isolate can be entered by at most one
* thread at any given time. The Locker/Unlocker API must be used to
* synchronize.
*/
class V8_EXPORT Isolate {
public:
/**
* Initial configuration parameters for a new Isolate.
*/
struct V8_EXPORT CreateParams {
CreateParams();
~CreateParams();
/**
* Allows the host application to provide the address of a function that is
* notified each time code is added, moved or removed.
*/
JitCodeEventHandler code_event_handler = nullptr;
/**
* ResourceConstraints to use for the new Isolate.
*/
ResourceConstraints constraints;
/**
* Explicitly specify a startup snapshot blob. The embedder owns the blob.
*/
StartupData* snapshot_blob = nullptr;
/**
* Enables the host application to provide a mechanism for recording
* statistics counters.
*/
CounterLookupCallback counter_lookup_callback = nullptr;
//.....
//省略多行
//.....
上面这段代码是isolate对外(export)提供的接口,方便其它程序的使用。 这个isolate可以理解为javascript的运行单元,多个线程也就是多个任务可以共享一个运行单元,这种共享类似操作系统中的调度机制,涉及到几个重要的概念:任务切换(亦称任务调度)、中断、上下文(context)的切换方法,由此我们引出V8中几个重要的概念。
a.Context:上下文,所有的JS代码都是在某个V8 Context中运行的。
b.Handle,一个指定JS对象的索引,它指向此JS对象在V8堆中的位置。
c.Handle Scope,包含很多handle的集合,用于对多个handle进行统一管理,当Scope被移出堆时,它所管理的handle集合也就被释放了。
其它的重要概念,本文不涉及,暂不深究。
Isolate还有一个对内的isolate数据结构,代码如下。它可以与对外接口进行无差别转换,在转换过程中,数据不会丢失。
class V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE Isolate final : private HiddenFactory {
// These forward declarations are required to make the friend declarations in
// PerIsolateThreadData work on some older versions of gcc.
class ThreadDataTable;
class EntryStackItem;
public:
Isolate(const Isolate&) = delete;
Isolate& operator=(const Isolate&) = delete;
using HandleScopeType = HandleScope;
void* operator new(size_t) = delete;
void operator delete(void*) = delete;
// A thread has a PerIsolateThreadData instance for each isolate that it has
// entered. That instance is allocated when the isolate is initially entered
// and reused on subsequent entries.
class PerIsolateThreadData {
public:
PerIsolateThreadData(Isolate* isolate, ThreadId thread_id)
: isolate_(isolate),
thread_id_(thread_id),
stack_limit_(0),
thread_state_(nullptr)
//省略很多代码...
这个isolate是V8内部使用的,不对外开放。这个结构贯穿了V8虚拟机的始终,是我们必须要掌握的,从入门的角度来讲,这个结构不是我们最先需要掌握的,我们只需要知道它,用到相关的成员再来查找,下文讲解的几个重要结构,其实都是i::isolate的成员。
3 编译
编译涉及到的概念包括:词法分析,用来生成token字;语法分析(parse),最后生成抽象语法树(AST)。下面介绍重要的数据结构
// A container for the inputs, configuration options, and outputs of parsing.
class V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE ParseInfo {
public:
ParseInfo(Isolate* isolate, const UnoptimizedCompileFlags flags,
UnoptimizedCompileState* state);
// Creates a new parse info based on parent top-level |outer_parse_info| for
// function |literal|.
static std::unique_ptr<ParseInfo> ForToplevelFunction(
const UnoptimizedCompileFlags flags,
UnoptimizedCompileState* compile_state, const FunctionLiteral* literal,
const AstRawString* function_name);
~ParseInfo();
template <typename IsolateT>
EXPORT_TEMPLATE_DECLARE(V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE)
Handle<Script> CreateScript(IsolateT* isolate, Handle<String> source,
MaybeHandle<FixedArray> maybe_wrapped_arguments,
ScriptOriginOptions origin_options,
NativesFlag natives = NOT_NATIVES_CODE);
// Either returns the ast-value-factory associcated with this ParseInfo, or
// creates and returns a new factory if none exists.
AstValueFactory* GetOrCreateAstValueFactory();
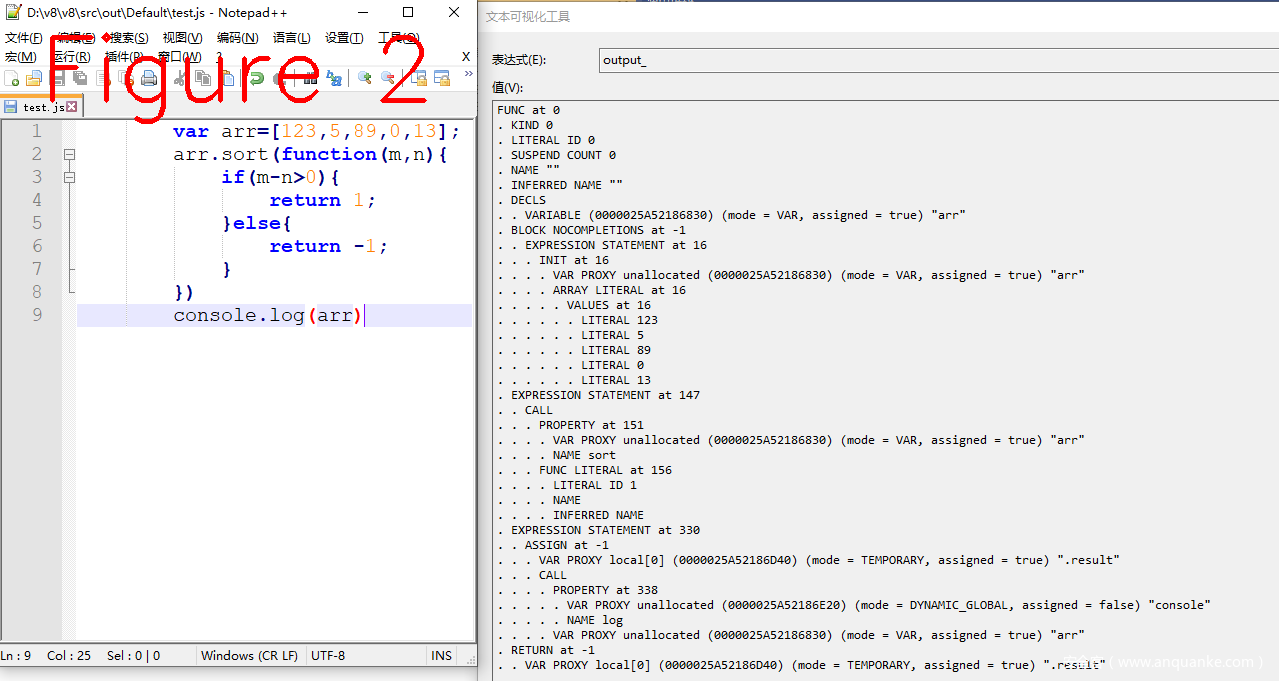
这个结构的作用是接收javascript源码(U16格式),输出就是AST,在它输出AST过程中,会临时生成Token,AST生成后销毁,不做永久保存,生成token过程中还用到了缓存(cache)机制来提高效率。下面先来看一段JS的AST语法树,如图2。
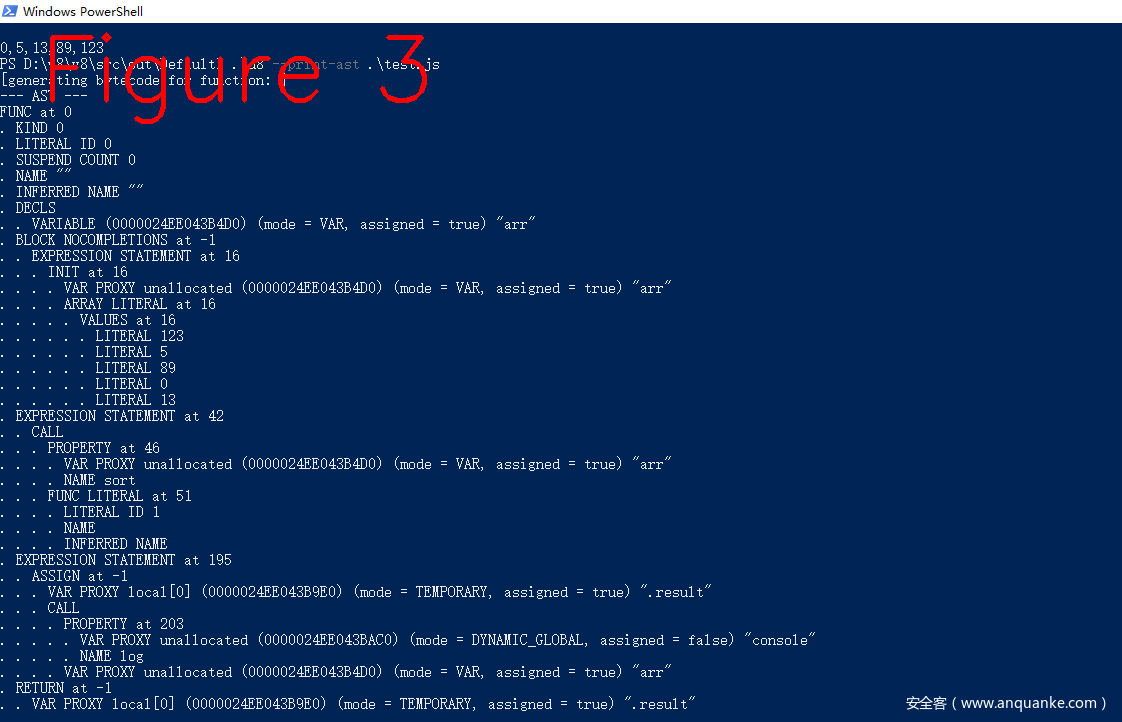
图2左侧是js源码,右侧是通过VS2019的调试工具看到的AST树,借助d8工具也能打印AST树,如图3所示,一屏显示不全,只截取了部分。
下面是AST树的主要数据结构。
class FunctionLiteral final : public Expression {
public:
enum ParameterFlag : uint8_t {
kNoDuplicateParameters,
kHasDuplicateParameters
};
enum EagerCompileHint : uint8_t { kShouldEagerCompile, kShouldLazyCompile };
// Empty handle means that the function does not have a shared name (i.e.
// the name will be set dynamically after creation of the function closure).
template <typename IsolateT>
MaybeHandle<String> GetName(IsolateT* isolate) const {
return raw_name_ ? raw_name_->AllocateFlat(isolate) : MaybeHandle<String>();
}
bool has_shared_name() const { return raw_name_ != nullptr; }
const AstConsString* raw_name() const { return raw_name_; }
void set_raw_name(const AstConsString* name) { raw_name_ = name; }
DeclarationScope* scope() const { return scope_; }
ZonePtrList<Statement>* body() { return &body_; }
void set_function_token_position(int pos) { function_token_position_ = pos; }
int function_token_position() const { return function_token_position_; }
int start_position() const;
int end_position() const;
bool is_anonymous_expression() const {
return syntax_kind() == FunctionSyntaxKind::kAnonymousExpression;
}
//省略很多代码... ...
Abstract Syntax Tree抽象语法树(AST)是精简版的解析树(parse tree),在编译过程中,解析树是包含javascript源码所有语法信息的树型表示结构,它是代码在编译阶段的等价表示。抽象语法树概念是相对于解析树而言,对解析树进行裁剪,去掉一些语法信息和一些不重要的细节,所以叫抽象语法树。
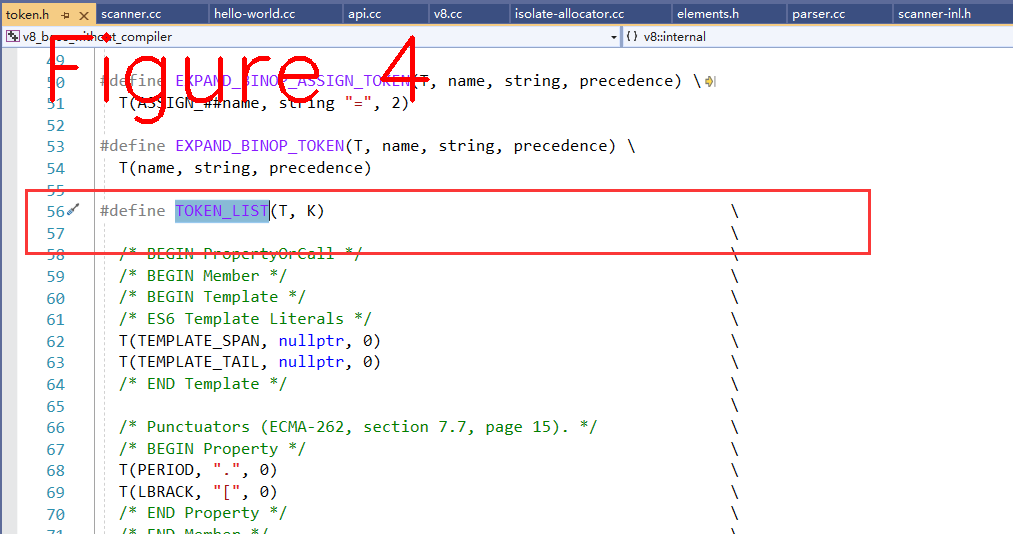
V8编译的第一个阶段是扫描(scanner)js源代码文本,把文本拆成一些单词,再传入分词器,经过一系列的类型识别,根据词的类型识别单词的含义,进而产生token序列,单词识别过程有一个预先定义好的识别器类型模板,如图4。
图4中只截取了部分,读者可根据文件名自行查阅。
4 代码执行
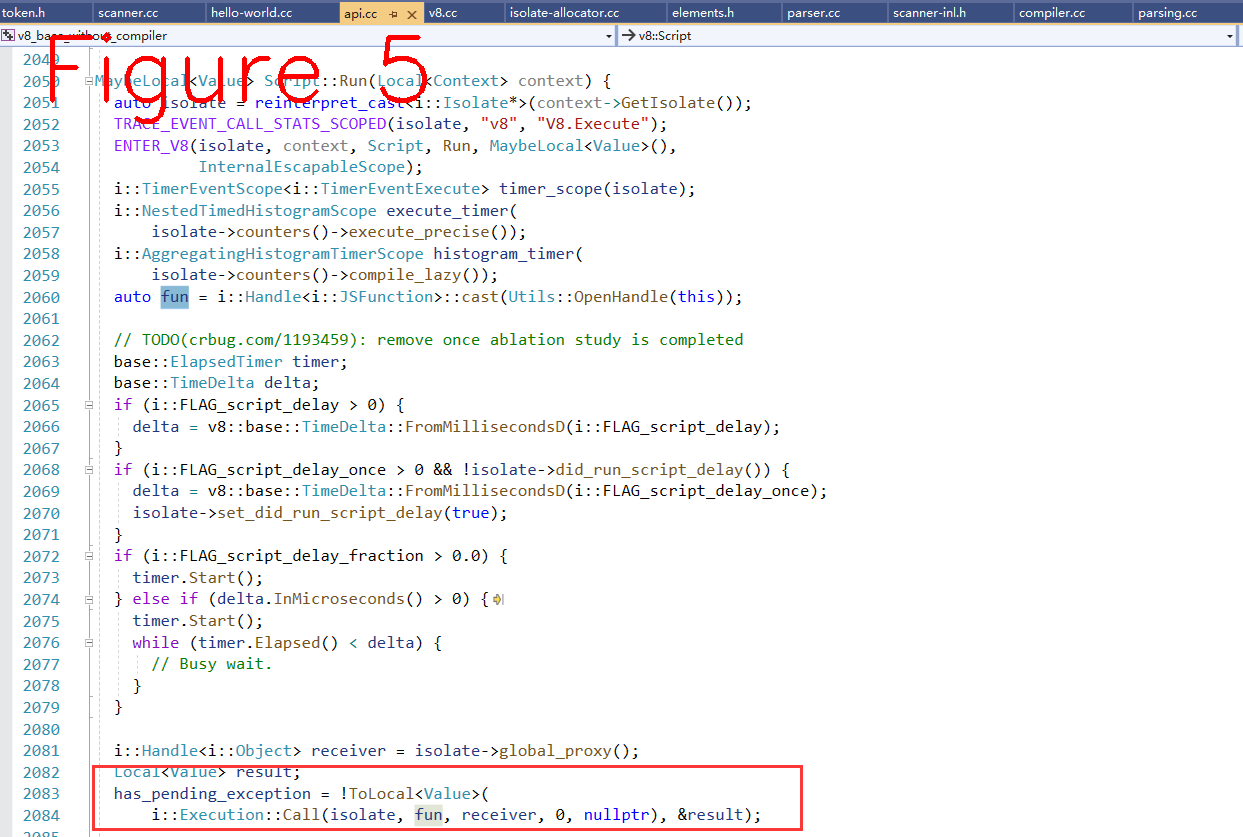
图5中给出来了执行Javascript代码的关键位置,从此处debug跟踪,将最终进入字节码(bytecode)的执行过程。
下面来看Exectuion这个数据结构,这个结构承载着运行过程前后的相关信息。
class Execution final : public AllStatic {
public:
// Whether to report pending messages, or keep them pending on the isolate.
enum class MessageHandling { kReport, kKeepPending };
enum class Target { kCallable, kRunMicrotasks };
// Call a function, the caller supplies a receiver and an array
// of arguments.
//
// When the function called is not in strict mode, receiver is
// converted to an object.
//
V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE V8_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT static MaybeHandle<Object> Call(
Isolate* isolate, Handle<Object> callable, Handle<Object> receiver,
int argc, Handle<Object> argv[]);
//省略很多
从图5中标记的位置跟踪进入能看到执行的细节,目前我们还没提到AST如何生成字节码,但已基本梳理了v8从启动到运行的关建过程,和关键的数据结构。我们已经能看到Javascript源码对应的AST树是什么样子,它在执行期时的字节码又是什么样。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流学习 邮箱:v8blink@outlook.com








发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录