1.摘要
本次是第五篇,剖析V8语法分析(parser)的源码和工作流程,讲解V8语法分析的核心源码、主要工作流程以及重要数据结构。本文将沿用第四篇文章的“测试样例代码”。
2.语法分析概述
语法分析是词法分析(scanner)的下一阶段,词法分析输出(out)的token字是语法分析的输入(in),语法分析在工作时会频繁使用词法分析器生成token。本文把词法分析器当作黑盒功能使用,直接给出词法分析的token字结果,词法分析器原理参见第四篇文章。
3.源码分析
以function和JsPrint为例详细剖析V8语法分析器的实现原理,从语法分析器的入口函数DoParseProgram()入手做起,讲解用户自义函数JsPrint的语法分析过程,之后对延迟分析技术(parse lazily)进行说明。
3.1 语法分析
下面这段代码是语法分析的入口函数。
FunctionLiteral* Parser::DoParseProgram(Isolate* isolate, ParseInfo* info) {
DCHECK_EQ(parsing_on_main_thread_, isolate != nullptr);
DCHECK_NULL(scope_);
ParsingModeScope mode(this, allow_lazy_ ? PARSE_LAZILY : PARSE_EAGERLY);
ResetFunctionLiteralId();
FunctionLiteral* result = nullptr;
{
Scope* outer = original_scope_;
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(outer);
if (flags().is_eval()) {
outer = NewEvalScope(outer);
} else if (flags().is_module()) {
DCHECK_EQ(outer, info->script_scope());
outer = NewModuleScope(info->script_scope());
}
DeclarationScope* scope = outer->AsDeclarationScope();
scope->set_start_position(0);
FunctionState function_state(&function_state_, &scope_, scope);
ScopedPtrList<Statement> body(pointer_buffer());
int beg_pos = scanner()->location().beg_pos;
if (flags().is_module()) {
DCHECK(flags().is_module());
PrepareGeneratorVariables();
Expression* initial_yield =
BuildInitialYield(kNoSourcePosition, kGeneratorFunction);
body.Add(
factory()->NewExpressionStatement(initial_yield, kNoSourcePosition));
if (flags().allow_harmony_top_level_await()) {
BlockT block = impl()->NullBlock();
{
StatementListT statements(pointer_buffer());
ParseModuleItemList(&statements);
if (function_state.suspend_count() > 1) {
scope->set_is_async_module();
block = factory()->NewBlock(true, statements);
} else {
statements.MergeInto(&body);
}
}
if (IsAsyncModule(scope->function_kind())) {
impl()->RewriteAsyncFunctionBody(
&body, block, factory()->NewUndefinedLiteral(kNoSourcePosition));
}
} else {
ParseModuleItemList(&body);
}
if (!has_error() &&
!module()->Validate(this->scope()->AsModuleScope(),
pending_error_handler(), zone())) {
scanner()->set_parser_error();
}
} else if (info->is_wrapped_as_function()) {
DCHECK(parsing_on_main_thread_);
ParseWrapped(isolate, info, &body, scope, zone());
} else if (flags().is_repl_mode()) {
ParseREPLProgram(info, &body, scope);
} else {
this->scope()->SetLanguageMode(info->language_mode());
ParseStatementList(&body, Token::EOS);
}
scope->set_end_position(peek_position());
if (is_strict(language_mode())) {
CheckStrictOctalLiteral(beg_pos, end_position());
}
if (is_sloppy(language_mode())) {
InsertSloppyBlockFunctionVarBindings(scope);
}
if (flags().is_eval()) {
DCHECK(parsing_on_main_thread_);
info->ast_value_factory()->Internalize(isolate);
}
CheckConflictingVarDeclarations(scope);
if (flags().parse_restriction() == ONLY_SINGLE_FUNCTION_LITERAL) {
if (body.length() != 1 || !body.at(0)->IsExpressionStatement() ||
!body.at(0)
->AsExpressionStatement()
->expression()
->IsFunctionLiteral()) {
ReportMessage(MessageTemplate::kSingleFunctionLiteral);
}
}
int parameter_count = 0;
result = factory()->NewScriptOrEvalFunctionLiteral(
scope, body, function_state.expected_property_count(), parameter_count);
result->set_suspend_count(function_state.suspend_count());
}
info->set_max_function_literal_id(GetLastFunctionLiteralId());
if (has_error()) return nullptr;
RecordFunctionLiteralSourceRange(result);
return result;
}
DoParseProgram()是语法分析的开始,FunctionLiteral* result = nullptr;这条语句定义了一个result,它是语法分析结束时生成的抽象语法树(AST),result目前为空值,DoParseProgram()执行完,AST也就生成了。调试样例代码,进入下面这个方法。
void ParserBase<Impl>::ParseStatementList(StatementListT* body,
Token::Value end_token) {
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(body);
while (peek() == Token::STRING) {
bool use_strict = false;
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
bool use_asm = false;
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
Scanner::Location token_loc = scanner()->peek_location();
if (scanner()->NextLiteralExactlyEquals("use strict")) {
use_strict = true;
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
} else if (scanner()->NextLiteralExactlyEquals("use asm")) {
use_asm = true;
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
}
StatementT stat = ParseStatementListItem();
if (impl()->IsNull(stat)) return;
body->Add(stat);
if (!impl()->IsStringLiteral(stat)) break;
if (use_strict) {
RaiseLanguageMode(LanguageMode::kStrict);
if (!scope()->HasSimpleParameters()) {
impl()->ReportMessageAt(token_loc,
MessageTemplate::kIllegalLanguageModeDirective,
"use strict");
return;
}
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
} else if (use_asm) {
impl()->SetAsmModule();
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
} else {
RaiseLanguageMode(LanguageMode::kSloppy);
}
}
while (peek() != end_token) {
StatementT stat = ParseStatementListItem();
if (impl()->IsNull(stat)) return;
if (stat->IsEmptyStatement()) continue;
body->Add(stat);
}
}
上一个方法是语法分析的入口,而ParseStatementList()是开始分析程序语句。while (peek() == Token::STRING)这条语句,peek是取得token字的类型,这里取来的token是Token::FUNCTION,所以值为假,进入while (peek() != end_token)循环,执行ParseStatementListItem()方法,在这个方法中进入Token::FUNCTION对应的分析功能,代码如下:
ParserBase<Impl>::ParseHoistableDeclaration(
ZonePtrList<const AstRawString>* names, bool default_export) {
Consume(Token::FUNCTION);//cache机制
int pos = position();
ParseFunctionFlags flags = ParseFunctionFlag::kIsNormal;
if (Check(Token::MUL)) {
flags |= ParseFunctionFlag::kIsGenerator;
}
return ParseHoistableDeclaration(pos, flags, names, default_export);
}
Consume()是第三篇文章中提到的“token字缓存”机制的具体实现,从缓存中取出一个token开始分析,如果缓存缺失(cache miss),则驱动词法分析器(Scanner)开始工作。从Consume取token的方法原理是使Scanner类中的current成员指向next成员,再利用next_next判断是否扫描下一个token字,请读者自行查阅代码。
取出token字function、类型函数(Token::FUNCTION),接下来判断该函数属于哪种类型(FunctionKind),FunctionKind的具体代码如下:
enum FunctionKind : uint8_t {
// BEGIN constructable functions
kNormalFunction,
kModule,
kAsyncModule,
//.................................
//省略了很多代码
//.................................
// END concise methods 1
kAsyncGeneratorFunction,
// END async functions
kGeneratorFunction,
// BEGIN concise methods 2
kConciseGeneratorMethod,
kStaticConciseGeneratorMethod,
// END generators
kConciseMethod,
kStaticConciseMethod,
kClassMembersInitializerFunction,
kClassStaticInitializerFunction,
// END concise methods 2
kInvalid,
kLastFunctionKind = kClassStaticInitializerFunction,
};
不要混淆FunctionKind和Token::FUNCTION的概念,它们属于不同技术领域,Token属于编译技术,FunctionKind属于ECMA规范。在样例代码中,Token字function的FunctionKind是KnormalFunction,所以下一步是分析这个函数的名字(Token::IDENTIFIER),代码如下:
const AstRawString* Scanner::CurrentSymbol(
AstValueFactory* ast_value_factory) const {
if (is_literal_one_byte()) {
return ast_value_factory->GetOneByteString(literal_one_byte_string());
}
return ast_value_factory->GetTwoByteString(literal_two_byte_string());
}
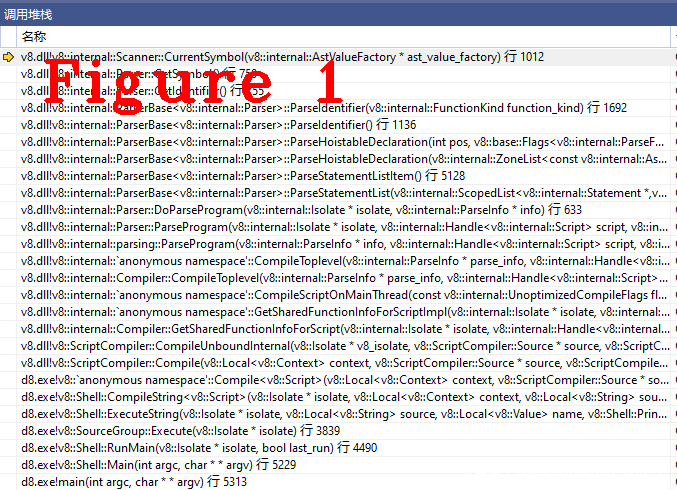
在CurrentSymbol()方法中,进行one_byte判断,JsPrint是one_byte类型,if语句为真,返回标识符。图1给出了CurrentSymbol()方法的函数调用堆栈,方便读者复现代码执行过程。
至此,两个Token字function和JsPrint语法分析完成,通俗概述以上代码的工作流程如下:
(1): 在Javascript源码中,当看到’function’这个字符时,后面应该是一个函数;
(2): 判断这个函数类型(FunctionKind),是异步或其它等等,样例代码是kNormalFunction;
(3): 是kNormalFunction,去获取函数的名字。
3.2 延迟分析
什么是延迟分析,延迟分析是V8中一种性能优化技术,即非立即执行的代码先不分析,执行时再做分析。众所周知,一个程序中,代码执行是有先后顺序的,也并不是所有代码都会执行,基于这一点,V8内部实现了延迟分析、延迟编译技术,达到提高效率的目的。下面讲解样例代码为什么会触发延迟分析。
JsPrint是一个常规(kNormalFunction)方法,取得函数名之后,开始分析函数内容,代码如下:
FunctionLiteral* Parser::ParseFunctionLiteral(
const AstRawString* function_name, Scanner::Location function_name_location,
FunctionNameValidity function_name_validity, FunctionKind kind,
int function_token_pos, FunctionSyntaxKind function_syntax_kind,
LanguageMode language_mode,
ZonePtrList<const AstRawString>* arguments_for_wrapped_function) {
bool is_wrapped = function_syntax_kind == FunctionSyntaxKind::kWrapped;
DCHECK_EQ(is_wrapped, arguments_for_wrapped_function != nullptr);
int pos = function_token_pos == kNoSourcePosition ? peek_position()
: function_token_pos;
DCHECK_NE(kNoSourcePosition, pos);
bool should_infer_name = function_name == nullptr;
if (should_infer_name) {
function_name = ast_value_factory()->empty_string();
}
FunctionLiteral::EagerCompileHint eager_compile_hint =
function_state_->next_function_is_likely_called() || is_wrapped
? FunctionLiteral::kShouldEagerCompile
: default_eager_compile_hint();
DCHECK_IMPLIES(parse_lazily(), info()->flags().allow_lazy_compile());
DCHECK_IMPLIES(parse_lazily(), has_error() || allow_lazy_);
DCHECK_IMPLIES(parse_lazily(), extension() == nullptr);
const bool is_lazy =
eager_compile_hint == FunctionLiteral::kShouldLazyCompile;
const bool is_top_level = AllowsLazyParsingWithoutUnresolvedVariables();
const bool is_eager_top_level_function = !is_lazy && is_top_level;
const bool is_lazy_top_level_function = is_lazy && is_top_level;
const bool is_lazy_inner_function = is_lazy && !is_top_level;
RCS_SCOPE(runtime_call_stats_, RuntimeCallCounterId::kParseFunctionLiteral,
RuntimeCallStats::kThreadSpecific);
base::ElapsedTimer timer;
if (V8_UNLIKELY(FLAG_log_function_events)) timer.Start();
const bool should_preparse_inner = parse_lazily() && is_lazy_inner_function;
bool should_post_parallel_task =
parse_lazily() && is_eager_top_level_function &&
FLAG_parallel_compile_tasks && info()->parallel_tasks() &&
scanner()->stream()->can_be_cloned_for_parallel_access();
// This may be modified later to reflect preparsing decision taken
bool should_preparse = (parse_lazily() && is_lazy_top_level_function) ||
should_preparse_inner || should_post_parallel_task;
ScopedPtrList<Statement> body(pointer_buffer());
int expected_property_count = 0;
int suspend_count = -1;
int num_parameters = -1;
int function_length = -1;
bool has_duplicate_parameters = false;
int function_literal_id = GetNextFunctionLiteralId();
ProducedPreparseData* produced_preparse_data = nullptr;
Zone* parse_zone = should_preparse ? &preparser_zone_ : zone();
DeclarationScope* scope = NewFunctionScope(kind, parse_zone);
SetLanguageMode(scope, language_mode);
#ifdef DEBUG
scope->SetScopeName(function_name);
#endif
if (!is_wrapped && V8_UNLIKELY(!Check(Token::LPAREN))) {
ReportUnexpectedToken(Next());
return nullptr;
}
scope->set_start_position(position());
bool did_preparse_successfully =
should_preparse &&
SkipFunction(function_name, kind, function_syntax_kind, scope,
&num_parameters, &function_length, &produced_preparse_data);
if (!did_preparse_successfully) {
if (should_preparse) Consume(Token::LPAREN);
should_post_parallel_task = false;
ParseFunction(&body, function_name, pos, kind, function_syntax_kind, scope,
&num_parameters, &function_length, &has_duplicate_parameters,
&expected_property_count, &suspend_count,
arguments_for_wrapped_function);
}
if (V8_UNLIKELY(FLAG_log_function_events)) {
double ms = timer.Elapsed().InMillisecondsF();
const char* event_name =
should_preparse
? (is_top_level ? "preparse-no-resolution" : "preparse-resolution")
: "full-parse";
logger_->FunctionEvent(
event_name, flags().script_id(), ms, scope->start_position(),
scope->end_position(),
reinterpret_cast<const char*>(function_name->raw_data()),
function_name->byte_length(), function_name->is_one_byte());
}
#ifdef V8_RUNTIME_CALL_STATS
if (did_preparse_successfully && runtime_call_stats_ &&
V8_UNLIKELY(TracingFlags::is_runtime_stats_enabled())) {
runtime_call_stats_->CorrectCurrentCounterId(
RuntimeCallCounterId::kPreParseWithVariableResolution,
RuntimeCallStats::kThreadSpecific);
}
#endif // V8_RUNTIME_CALL_STATS
language_mode = scope->language_mode();
CheckFunctionName(language_mode, function_name, function_name_validity,
function_name_location);
if (is_strict(language_mode)) {
CheckStrictOctalLiteral(scope->start_position(), scope->end_position());
}
FunctionLiteral::ParameterFlag duplicate_parameters =
has_duplicate_parameters ? FunctionLiteral::kHasDuplicateParameters
: FunctionLiteral::kNoDuplicateParameters;
FunctionLiteral* function_literal = factory()->NewFunctionLiteral(
function_name, scope, body, expected_property_count, num_parameters,
function_length, duplicate_parameters, function_syntax_kind,
eager_compile_hint, pos, true, function_literal_id,
produced_preparse_data);
function_literal->set_function_token_position(function_token_pos);
function_literal->set_suspend_count(suspend_count);
RecordFunctionLiteralSourceRange(function_literal);
if (should_post_parallel_task) {
// Start a parallel parse / compile task on the compiler dispatcher.
info()->parallel_tasks()->Enqueue(info(), function_name, function_literal);
}
if (should_infer_name) {
fni_.AddFunction(function_literal);
}
return function_literal;
}
ParseFunctionLiteral(),这个方法名字表明了它的主要功能是对函数内容进行语议分析。名字JsPrint分析完成后,进入这个方法分析JsPrint函数的内容,先判断这个方法是否符合延迟分析条件。
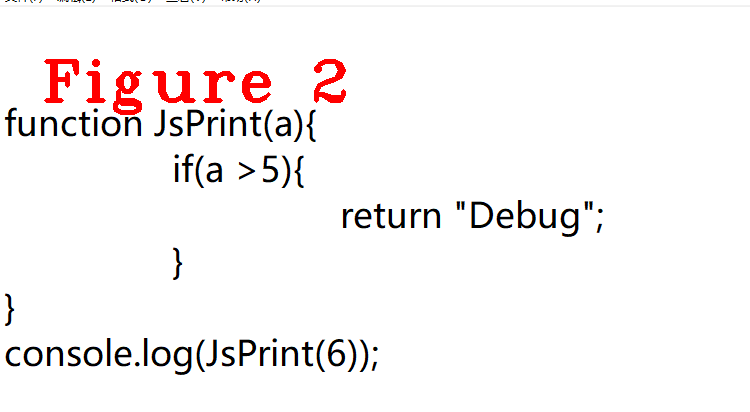
图2是样例代码,可以看出JsPrint不会马上执行,并且它是最外部的顶层方法,满足延迟分析条件。从Javascript的执行顺序也可以得到同样的结论:定义JsPrint函数,但代码执行时最先执行的是console.log(),console.log()执行时需要先计算参数并压栈,所以说JsPrint不是立即执行的,而console.log()执行时调用了JsPrint,所以它满足延迟分析条件。
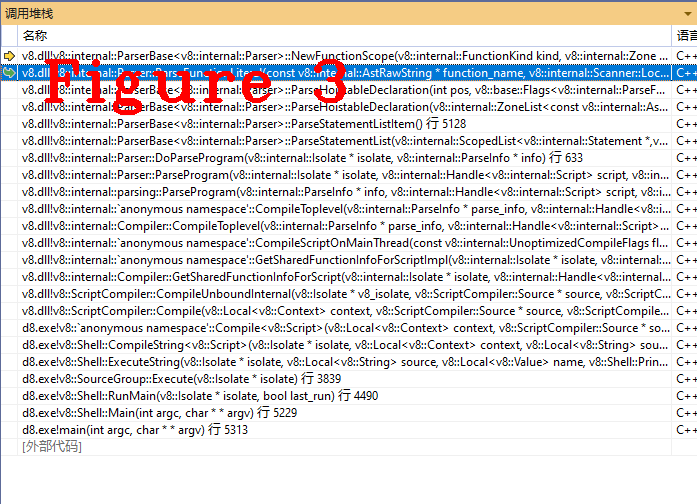
调试程序是最有效的验证手段,从代码的角度验证上述结论是否正确, 请读者跟踪ParseFunctionLiteral()方法,并查看is_lazy和is_top_level成员的值,看到这两个成员的值为真,上述结论正确无误,图3给出ParseFunctionLiteral()的调用堆栈,便于读者复现代码执行过程。
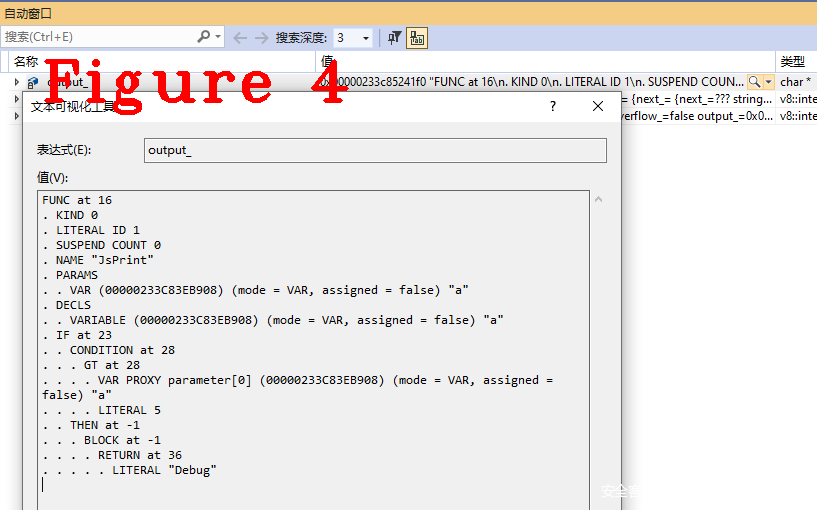
下面给出JsPrint()的抽象语法图,供读者分析学习,如图4。
总结,语法分析器代码逻辑十分复杂,分析代码时做好堆栈记录,有助于在跟踪代码中发生“跟错、跟丢”问题时快速帮你找到最近的正确位置,提高学习效率。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流 邮箱:v8blink@outlook.com








发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录