一、简介
看 fuzz 的结构感知 时遇到了 protobuf,觉得很有意思,于是尝试使用 protobuf 来进行快速简易的 CTF fuzz。
以下以 TCTF2021-babyheap2021 为例,来简单说明一下自动化步骤。
这里主要用到以下项目:
- AFL++,其中的 qemu mode + qasan
- afl-libprotobuf-mutator
需要注意的是,该 fuzz 目前处于实验性版本,可能不太稳定,仅作为学习研究使用。
二、操作流程
1. 下载依赖
git clone 下 AFL++ 和 afl-libprotobuf-mutator (链接在上面)即可。
2. 配置 afl-libprotobuf-mutator
- 首先,用 ida64 打开 babyheap2021, F5阅读伪代码并总结其输入模板,最后用 protobuf 描述输入结构:
这类菜单题的输入模板大体上比较固定,下面的代码随便改改就能换一道题目用用。
代码编写完成后,覆盖保存至
afl-libprotobuf-mutator/gen/out.proto。注意路径必须完成一致,若遇到重名文件 out.proto 则直接替换。如果不会写 protobuf 描述的话,可以看看这个 Protocol Buffers Tutorials。
// out.proto syntax = "proto2"; package menuctf; message AllocChoice { required int32 choice_id = 1 [default=1]; required int32 size = 2; required string content = 3; } message UpdateChoice { required int32 choice_id = 1 [default=2]; required int32 idx = 2; required int32 size = 3; required string content = 4; } message DeleteChoice { required int32 choice_id = 1 [default=3]; required int32 idx = 2; } message ViewChoice { required int32 choice_id = 1 [default=4]; required int32 idx = 2; } message ExitChoice { required int32 choice_id = 1 [default=5]; } // Our address book file is just one of these. message ChoiceList { message Choice { oneof the_choice{ AllocChoice alloc_choice = 1; UpdateChoice update_choice = 2; DeleteChoice delete_choice = 3; ViewChoice view_choice = 4; ExitChoice exit_choice = 5; } } repeated Choice choice = 1; } - 到了这里,我们需要理一理思路。对于CTF题来说,大多都是直接从 stdin 中获取输入的文本数据。因此首先,我们需要编写
Protobuf::Message转常规输入字符串的代码:void ProtoToDataHelper(std::stringstream &out, const google::protobuf::Message &msg) { const google::protobuf::Descriptor *desc = msg.GetDescriptor(); const google::protobuf::Reflection *refl = msg.GetReflection(); const unsigned fields = desc->field_count(); // std::cout << msg.DebugString() << std::endl; for (unsigned i = 0; i < fields; ++i) { const google::protobuf::FieldDescriptor *field = desc->field(i); // 对于单个 choice if (field->cpp_type() == google::protobuf::FieldDescriptor::CPPTYPE_MESSAGE) { // 如果当前是 choice list if (field->is_repeated()) { const google::protobuf::RepeatedFieldRef<google::protobuf::Message> &ptr = refl->GetRepeatedFieldRef<google::protobuf::Message>(msg, field); // 将每个 choice 打出来 for (const auto &child : ptr) { ProtoToDataHelper(out, child); out << "\n"; } // 如果当前是某个子 choice } else if (refl->HasField(msg, field)) { const google::protobuf::Message &child = refl->GetMessage(msg, field); ProtoToDataHelper(out, child); } } // 对于单个 field else if (field->cpp_type() == google::protobuf::FieldDescriptor::CPPTYPE_INT32) { out << refl->GetInt32(msg, field); if(i < fields - 1) out << " "; } else if (field->cpp_type() == google::protobuf::FieldDescriptor::CPPTYPE_STRING) { out << refl->GetString(msg, field); if(i < fields - 1) out << " "; } else { abort(); } } } - 之后,参照 AFL++ 的 Custom Mutators in AFL++,完成一些必要的 custom mutate 函数。这里我们需要完成以下几种函数:
-
void *afl_custom_init(void *afl, unsigned int seed):在执行 custom mutate 前需要执行的初始化操作,这里只需初始化一下随机种子。 -
size_t afl_custom_fuzz(void *data, unsigned char *buf, size_t buf_size, unsigned char **out_buf, unsigned char *add_buf, size_t add_buf_size, size_t max_size):变异逻辑,在该代码中编写自己的变异逻辑。 -
size_t afl_custom_post_process(void* data, uint8_t *buf, size_t buf_size, uint8_t **out_buf):将 protobuf::Message 格式的二进制数据转换成 target 可读的数据。 -
void afl_custom_deinit(void *data):变异完成后需要做的事情,目前没有什么事情需要在这里进行处理。 -
int32_t afl_custom_init_trim(void *data, uint8_t *buf, size_t buf_size):自定义 trim 逻辑的初始化。为了防止 trim 逻辑破坏 protobuf::Message 的二进制数据,影响正常的 Parse 过程,这里可以让该函数直接返回0,跳过每次的 trim 阶段。 -
size_t afl_custom_trim(void *data, uint8_t **out_buf):自定义 trim 逻辑。由于afl_custom_init_trim函数返回0,因此实际上该函数不会被调用,但我们仍然必须声明该函数以启用自定义 trim 逻辑。
需要注意的是,这一整个
extern "C"的代码以及内部用到的ProtoToDataHelper函数的代码,必须全部放在afl-libprotobuf-mutator/src/mutate.cc中。由于 afl-libprotobuf-mutator 较为久远,因此大部分 AFL++ 相关的接口需要修改亿下。
// AFLPlusPlus interface extern "C" { static std::default_random_engine engine_pro; static std::uniform_int_distribution<unsigned int> dis(0, UINT32_MAX); void *afl_custom_init(void *afl, unsigned int seed) { #pragma unused (afl) engine_pro.seed(seed); return nullptr; } void afl_custom_deinit(void *data) { assert(!data); } // afl_custom_fuzz size_t afl_custom_fuzz(void *data, unsigned char *buf, size_t buf_size, unsigned char **out_buf, unsigned char *add_buf, size_t add_buf_size, size_t max_size) { #pragma unused (data) #pragma unused (add_buf) #pragma unused (add_buf_size) static uint8_t *saved_buf = nullptr; assert(buf_size <= max_size); uint8_t *new_buf = (uint8_t *) realloc((void *)saved_buf, max_size); if (!new_buf) { *out_buf = buf; return buf_size; } saved_buf = new_buf; memcpy(new_buf, buf, buf_size); size_t new_size = LLVMFuzzerCustomMutator( new_buf, buf_size, max_size, dis(engine_pro) ); *out_buf = new_buf; return new_size; } size_t afl_custom_post_process(void* data, uint8_t *buf, size_t buf_size, uint8_t **out_buf) { #pragma unused (data) // new_data is never free'd by pre_save_handler // I prefer a slow but clearer implementation for now static uint8_t *saved_buf = NULL; menuctf::ChoiceList msg; std::stringstream stream; // 如果加载成功 if (protobuf_mutator::libfuzzer::LoadProtoInput(true, buf, buf_size, &msg)) { ProtoToDataHelper(stream, msg); } else { // printf("[afl_custom_post_process] LoadProtoInput Error\n"); // std::ofstream err_bin("err.bin"); // err_bin.write((char*)buf, buf_size); // abort(); // 如果加载失败,则返回 Exit Choice /// NOTE: 错误的变异 + 错误的 trim 将会导致 post process 加载失败,尤其是 trim 逻辑。 /// TODO: 由于默认的 trim 会破坏样例,因此需要手动实现一个 trim,这里实现了一个空 trim,不进行任何操作 ProtoToDataHelper(stream, menuctf::ExitChoice()); } const std::string str = stream.str(); uint8_t *new_buf = (uint8_t *) realloc((void *)saved_buf, str.size()); if (!new_buf) { *out_buf = buf; return buf_size; } *out_buf = saved_buf = new_buf; memcpy((void *)new_buf, str.c_str(), str.size()); return str.size(); } int32_t afl_custom_init_trim(void *data, uint8_t *buf, size_t buf_size) { /// NOTE: disable trim return 0; } size_t afl_custom_trim(void *data, uint8_t **out_buf) { /// NOTE: unreachable return 0; } } -
- 当然,编写上面的代码需要做一次又一次的测试,这里放上笔者的测试代码片段。这部分测试代码位于
afl-libprotobuf-mutator/src/dump.cc。inline std::string slurp(const std::string& path) { std::ostringstream buf; std::ifstream input (path.c_str()); buf << input.rdbuf(); return buf.str(); } extern "C" { void *afl_custom_init(void *afl, unsigned int seed); size_t afl_custom_fuzz(void *data, unsigned char *buf, size_t buf_size, unsigned char **out_buf, unsigned char *add_buf, size_t add_buf_size, size_t max_size); size_t afl_custom_post_process(void* data, uint8_t *buf, size_t buf_size, uint8_t **out_buf); void afl_custom_deinit(void *data); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { menuctf::ChoiceList msg; if (argc == 2) { std::string data = slurp(argv[1]); if(!protobuf_mutator::libfuzzer::LoadProtoInput(true, (const uint8_t *)data.c_str(), data.size(), &msg)) { printf("[afl_custom_post_process] LoadProtoInput Error\n"); abort(); } // 测试变异逻辑 void* init_data = afl_custom_init(nullptr, time(NULL)); for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { uint8_t *out_buf = nullptr; size_t new_size = afl_custom_fuzz(init_data, (uint8_t*)data.c_str(), data.size(), &out_buf, nullptr, 0, data.size() + 100); uint8_t *new_str = nullptr; size_t new_str_size = afl_custom_post_process(init_data, out_buf, new_size, &new_str); std::string new_str_str((char*)new_str, new_str_size); std::cout << i << ": " << new_str_str << std::endl; } afl_custom_deinit(init_data); } else { // alloc 12 "[menuctf::AllocChoice]" { auto choice = new menuctf::AllocChoice(); choice->set_size(12); choice->set_content("[menuctf::AllocChoice]"); msg.add_choice()->set_allocated_alloc_choice(choice); } // update 2 20 "[menuctf::UpdateChoice]" { auto choice = new menuctf::UpdateChoice(); choice->set_idx(2); choice->set_size(20); choice->set_content("[menuctf::UpdateChoice]"); msg.add_choice()->set_allocated_update_choice(choice); } // DeleteChoice 3 { auto choice = new menuctf::DeleteChoice(); choice->set_idx(3); msg.add_choice()->set_allocated_delete_choice(choice); } // ViewChoice 4 { auto choice = new menuctf::ViewChoice(); choice->set_idx(4); msg.add_choice()->set_allocated_view_choice(choice); } // ExitChoice { auto choice = new menuctf::ExitChoice(); msg.add_choice()->set_allocated_exit_choice(choice); } std::ofstream output_file("output.bin", std::ios::binary); // 这里保存的 Serialize 必须使用 Partial 保存, msg.SerializePartialToOstream(&output_file); output_file.close(); } // std::cout << "msg DebugString: " << msg.DebugString() << std::endl; std::stringstream stream; ProtoToDataHelper(stream, msg); std::cout << stream.str() << std::endl; return 0; } - 接下来只需在
afl-libprotobuf-mutator文件夹下执行./build.sh && make即可,完成后,在当前工作路径下将会生成dumper、libmutator.so以及mutator三个文件。我们可以利用 dumper 对上面的代码进行测试,libmutator.so 用于 afl++ 中的自定义变异。
3. 配置 AFL++
现在压力来到了 AFL++ 这里(笑),我们先试试看能不能马上跑起来。
尝试执行以下命令来构建 AFL++:
# 构建 AFLplusplus
# 1. 安装依赖项
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ninja-build build-essential python3-dev automake git flex bison libglib2.0-dev libpixman-1-dev python3-setuptools
# try to install llvm 11 and install the distro default if that fails
sudo apt-get install -y lld-11 llvm-11 llvm-11-dev clang-11 || sudo apt-get install -y lld llvm llvm-dev clang
sudo apt-get install -y gcc-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/.* //'|sed 's/\..*//')-plugin-dev libstdc++-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/.* //'|sed 's/\..*//')-dev
# 2. 开始构建
cd AFLplusplus
make distrib # 这一步要等一段时间
# sudo make install # 将 AFL++ 安装至本机
# 如果不需要了可以使用 sudo make uninstall 卸载
4. 运行
执行以下命令运行 AFL++:
# AFL++ 构建完成后,进入 workdir 配置语料
mkdir workdir
[配置语料等等...]
# 设置相关环境变量
export AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY=1 # 禁用除自定义 mutator 以外的其他自带 mutator
export AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY=../afl-libprotobuf-mutator/libmutator.so # 指定自定义路径
export AFL_USE_QASAN=1 # 启用 QASAN
# 运行 AFL++
AFLplusplus/afl-fuzz -i workdir/fuzz_input -o workdir/fuzz_output -Q -- ./babyheap
别忘记在 workdir 中放点输入语料,语料可以通过 afl-libprotobuf-mutator/dumper 来随便生成一点。
运行时如果遇到 afl-quemu-trace 不存在,则单独执行AFLplusplus/qemu_mode/build_qemu_support.sh 构建即可。
三、源代码
相关源代码以及构建方式已开源至 github 上。
重申一下,该 fuzz 目前处于实验性版本,可能有亿点点不太稳定(笑)。
四、可改进的地方
- libprotobuf-mutator 的变异效果一般,最好手动改进一下
- 需要实现一下 trim 逻辑,空的 trim 逻辑可能会产生 样例爆炸
五、一些需要注意的点
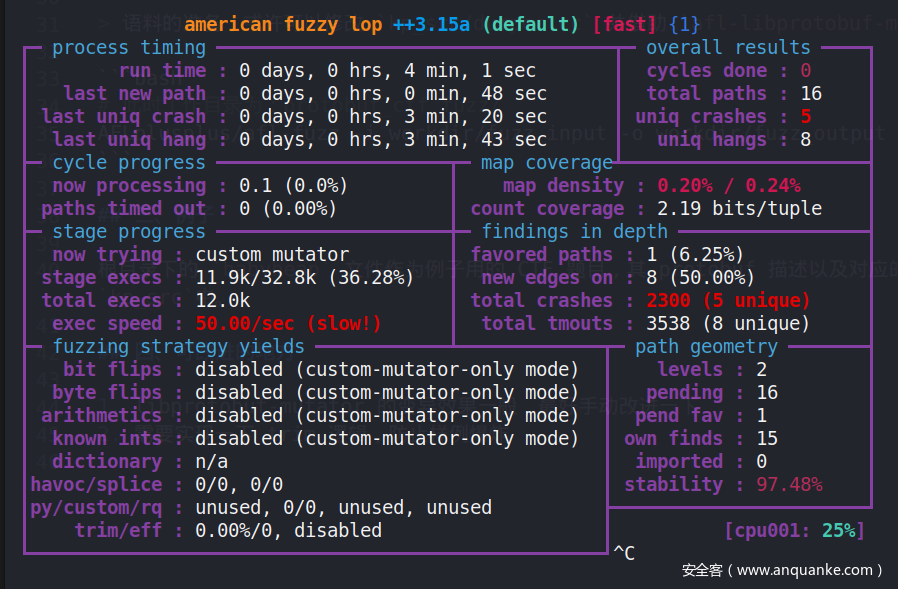
如果在运行 AFL++ 后,发现 fuzz 始终无法发现新路径,即路径始终只有一个,那么就必须考虑目标CTF文件是否可执行。以当前的 babyheap2021 为例,笔者在测试时初始 AFL++ 状态如下:
尝试直接执行 babyheap,发现 Permission Denied无法执行。但即便赋以 excutable 权限,仍然无法执行,报错 no such file or directory:
这一看,要么是架构问题,要么是 libc.so / ld.so 的问题。因此执行以下命令以更新 babyheap 所使用的 libc.so & ld.so,之后便可以正常执行。
patchelf --set-interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 ./babyheap
patchelf --replace-needed libc.so libc.so.6 ./babyheap
跑起来效果,还行?(不是很懂.jpg)










发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录