一、前言
本文基于如下环境:
- Kernel Version:5.11.0
- Debugging Env:Ubuntu 20.04.02 x64(Kernel Version—5.11.0)
近来笔者计划从脏牛漏洞入手,分析Linux内核漏洞,故在开始之前学习了Linux内核中内存管理部分相关内容,下文权当笔者学习过程整理的笔记。如有不当之处,望读者不吝赐教。
二、层次组织
0x01 Node
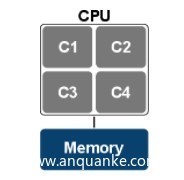
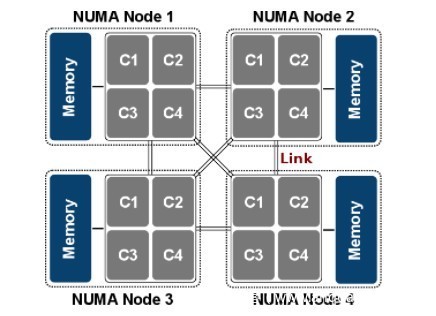
UMA——Uniform Memory Access,NUMA——Non-uniform memory access:
可进一步阅读Non-uniform memory access—Wikipedia。Linux为每个节点定义了一个类型为pg_data_t的描述符:
/*
* On NUMA machines, each NUMA node would have a pg_data_t to describe
* it's memory layout. On UMA machines there is a single pglist_data which
* describes the whole memory.
*
* Memory statistics and page replacement data structures are maintained on a
* per-zone basis.
*/
typedef struct pglist_data {
/*
* node_zones contains just the zones for THIS node. Not all of the
* zones may be populated, but it is the full list. It is referenced by
* this node's node_zonelists as well as other node's node_zonelists.
*/
struct zone node_zones[MAX_NR_ZONES];
/*
* node_zonelists contains references to all zones in all nodes.
* Generally the first zones will be references to this node's
* node_zones.
*/
struct zonelist node_zonelists[MAX_ZONELISTS];
int nr_zones; /* number of populated zones in this node */
#ifdef CONFIG_FLAT_NODE_MEM_MAP /* means !SPARSEMEM */
struct page *node_mem_map;
#ifdef CONFIG_PAGE_EXTENSION
struct page_ext *node_page_ext;
#endif
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG) || defined(CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT)
/*
* Must be held any time you expect node_start_pfn,
* node_present_pages, node_spanned_pages or nr_zones to stay constant.
* Also synchronizes pgdat->first_deferred_pfn during deferred page
* init.
*
* pgdat_resize_lock() and pgdat_resize_unlock() are provided to
* manipulate node_size_lock without checking for CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG
* or CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT.
*
* Nests above zone->lock and zone->span_seqlock
*/
spinlock_t node_size_lock;
#endif
unsigned long node_start_pfn;
unsigned long node_present_pages; /* total number of physical pages */
unsigned long node_spanned_pages; /* total size of physical page
range, including holes */
int node_id;
wait_queue_head_t kswapd_wait;
wait_queue_head_t pfmemalloc_wait;
struct task_struct *kswapd; /* Protected by
mem_hotplug_begin/end() */
int kswapd_order;
enum zone_type kswapd_highest_zoneidx;
int kswapd_failures; /* Number of 'reclaimed == 0' runs */
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPACTION
int kcompactd_max_order;
enum zone_type kcompactd_highest_zoneidx;
wait_queue_head_t kcompactd_wait;
struct task_struct *kcompactd;
#endif
/*
* This is a per-node reserve of pages that are not available
* to userspace allocations.
*/
unsigned long totalreserve_pages;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
/*
* node reclaim becomes active if more unmapped pages exist.
*/
unsigned long min_unmapped_pages;
unsigned long min_slab_pages;
#endif /* CONFIG_NUMA */
/* Write-intensive fields used by page reclaim */
ZONE_PADDING(_pad1_)
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
/*
* If memory initialisation on large machines is deferred then this
* is the first PFN that needs to be initialised.
*/
unsigned long first_deferred_pfn;
#endif /* CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT */
#ifdef CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE
struct deferred_split deferred_split_queue;
#endif
/* Fields commonly accessed by the page reclaim scanner */
/*
* NOTE: THIS IS UNUSED IF MEMCG IS ENABLED.
*
* Use mem_cgroup_lruvec() to look up lruvecs.
*/
struct lruvec __lruvec;
unsigned long flags;
ZONE_PADDING(_pad2_)
/* Per-node vmstats */
struct per_cpu_nodestat __percpu *per_cpu_nodestats;
atomic_long_t vm_stat[NR_VM_NODE_STAT_ITEMS];
} pg_data_t;
而每个节点又可以划分为数个内存管理区——ZONE,与之相关的字段如下:
struct zone node_zones[MAX_NR_ZONES]; //内存管理区描述符数组
struct zonelist node_zonelists[MAX_ZONELISTS]; //引用所有节点中内存管理区
int nr_zones; //当前节点中内存管理区数量
与当前节点相关字段:
unsigned long node_start_pfn; //节点第一个页框的PFN
unsigned long node_present_pages; /* total number of physical pages */
unsigned long node_spanned_pages; /* total size of physical page
range, including holes */
int node_id; //节点标识符
与kswapd内核线程相关字段:
wait_queue_head_t kswapd_wait;
wait_queue_head_t pfmemalloc_wait;
struct task_struct *kswapd; /* Protected by
mem_hotplug_begin/end() */
int kswapd_order;
enum zone_type kswapd_highest_zoneidx;
int kswapd_failures; /* Number of 'reclaimed == 0' runs */
0x02 Zone
内存管理区描述符定义如下:
struct zone {
/* Read-mostly fields */
/* zone watermarks, access with *_wmark_pages(zone) macros */
unsigned long _watermark[NR_WMARK];
unsigned long watermark_boost;
unsigned long nr_reserved_highatomic;
/*
* We don't know if the memory that we're going to allocate will be
* freeable or/and it will be released eventually, so to avoid totally
* wasting several GB of ram we must reserve some of the lower zone
* memory (otherwise we risk to run OOM on the lower zones despite
* there being tons of freeable ram on the higher zones). This array is
* recalculated at runtime if the sysctl_lowmem_reserve_ratio sysctl
* changes.
*/
long lowmem_reserve[MAX_NR_ZONES];
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
int node;
#endif
struct pglist_data *zone_pgdat;
struct per_cpu_pageset __percpu *pageset;
/*
* the high and batch values are copied to individual pagesets for
* faster access
*/
int pageset_high;
int pageset_batch;
#ifndef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM
/*
* Flags for a pageblock_nr_pages block. See pageblock-flags.h.
* In SPARSEMEM, this map is stored in struct mem_section
*/
unsigned long *pageblock_flags;
#endif /* CONFIG_SPARSEMEM */
/* zone_start_pfn == zone_start_paddr >> PAGE_SHIFT */
unsigned long zone_start_pfn;
/*
* spanned_pages is the total pages spanned by the zone, including
* holes, which is calculated as:
* spanned_pages = zone_end_pfn - zone_start_pfn;
*
* present_pages is physical pages existing within the zone, which
* is calculated as:
* present_pages = spanned_pages - absent_pages(pages in holes);
*
* managed_pages is present pages managed by the buddy system, which
* is calculated as (reserved_pages includes pages allocated by the
* bootmem allocator):
* managed_pages = present_pages - reserved_pages;
*
* So present_pages may be used by memory hotplug or memory power
* management logic to figure out unmanaged pages by checking
* (present_pages - managed_pages). And managed_pages should be used
* by page allocator and vm scanner to calculate all kinds of watermarks
* and thresholds.
*
* Locking rules:
*
* zone_start_pfn and spanned_pages are protected by span_seqlock.
* It is a seqlock because it has to be read outside of zone->lock,
* and it is done in the main allocator path. But, it is written
* quite infrequently.
*
* The span_seq lock is declared along with zone->lock because it is
* frequently read in proximity to zone->lock. It's good to
* give them a chance of being in the same cacheline.
*
* Write access to present_pages at runtime should be protected by
* mem_hotplug_begin/end(). Any reader who can't tolerant drift of
* present_pages should get_online_mems() to get a stable value.
*/
atomic_long_t managed_pages;
unsigned long spanned_pages;
unsigned long present_pages;
const char *name;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION
/*
* Number of isolated pageblock. It is used to solve incorrect
* freepage counting problem due to racy retrieving migratetype
* of pageblock. Protected by zone->lock.
*/
unsigned long nr_isolate_pageblock;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG
/* see spanned/present_pages for more description */
seqlock_t span_seqlock;
#endif
int initialized;
/* Write-intensive fields used from the page allocator */
ZONE_PADDING(_pad1_)
/* free areas of different sizes */
struct free_area free_area[MAX_ORDER];
/* zone flags, see below */
unsigned long flags;
/* Primarily protects free_area */
spinlock_t lock;
/* Write-intensive fields used by compaction and vmstats. */
ZONE_PADDING(_pad2_)
/*
* When free pages are below this point, additional steps are taken
* when reading the number of free pages to avoid per-cpu counter
* drift allowing watermarks to be breached
*/
unsigned long percpu_drift_mark;
#if defined CONFIG_COMPACTION || defined CONFIG_CMA
/* pfn where compaction free scanner should start */
unsigned long compact_cached_free_pfn;
/* pfn where compaction migration scanner should start */
unsigned long compact_cached_migrate_pfn[ASYNC_AND_SYNC];
unsigned long compact_init_migrate_pfn;
unsigned long compact_init_free_pfn;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPACTION
/*
* On compaction failure, 1<<compact_defer_shift compactions
* are skipped before trying again. The number attempted since
* last failure is tracked with compact_considered.
* compact_order_failed is the minimum compaction failed order.
*/
unsigned int compact_considered;
unsigned int compact_defer_shift;
int compact_order_failed;
#endif
#if defined CONFIG_COMPACTION || defined CONFIG_CMA
/* Set to true when the PG_migrate_skip bits should be cleared */
bool compact_blockskip_flush;
#endif
bool contiguous;
ZONE_PADDING(_pad3_)
/* Zone statistics */
atomic_long_t vm_stat[NR_VM_ZONE_STAT_ITEMS];
atomic_long_t vm_numa_stat[NR_VM_NUMA_STAT_ITEMS];
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
内存管理区第一个页框由zone_start_pfn字段标识,内存管理区名称保存在name字段中——不同类型其名称不同,类型定义如下:
enum zone_type {
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
ZONE_DMA,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA32
ZONE_DMA32,
#endif
ZONE_NORMAL,
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
ZONE_HIGHMEM,
#endif
ZONE_MOVABLE,
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DEVICE
ZONE_DEVICE,
#endif
__MAX_NR_ZONES
};
关于ZONE_HIGHMEM,值得说明的是在x86-64体系中没有该类型内存管理区。而在x86体系中存在该类型内存管理区,其原因是高端内存无法永久映射到内核地址空间中(关于高端内存这里不作展开,可阅读Linux内核高端内存一文)。注意,Linux内核对内存管理区的划分是针对物理内存空间,而非虚拟内存空间。可通过/proc/zoneinfo文件查看相关信息:
free_area字段标识内存管理区中不同大小空闲页框块,用于伙伴系统。关于managed_pages,spanned_pages,present_pages三个字段在注释中已经解释,这里不再赘述。每个内存管理区的zone_end_pfn可通过如下函数计算:
static inline unsigned long zone_end_pfn(const struct zone *zone)
{
return zone->zone_start_pfn + zone->spanned_pages;
}
0x03 Page
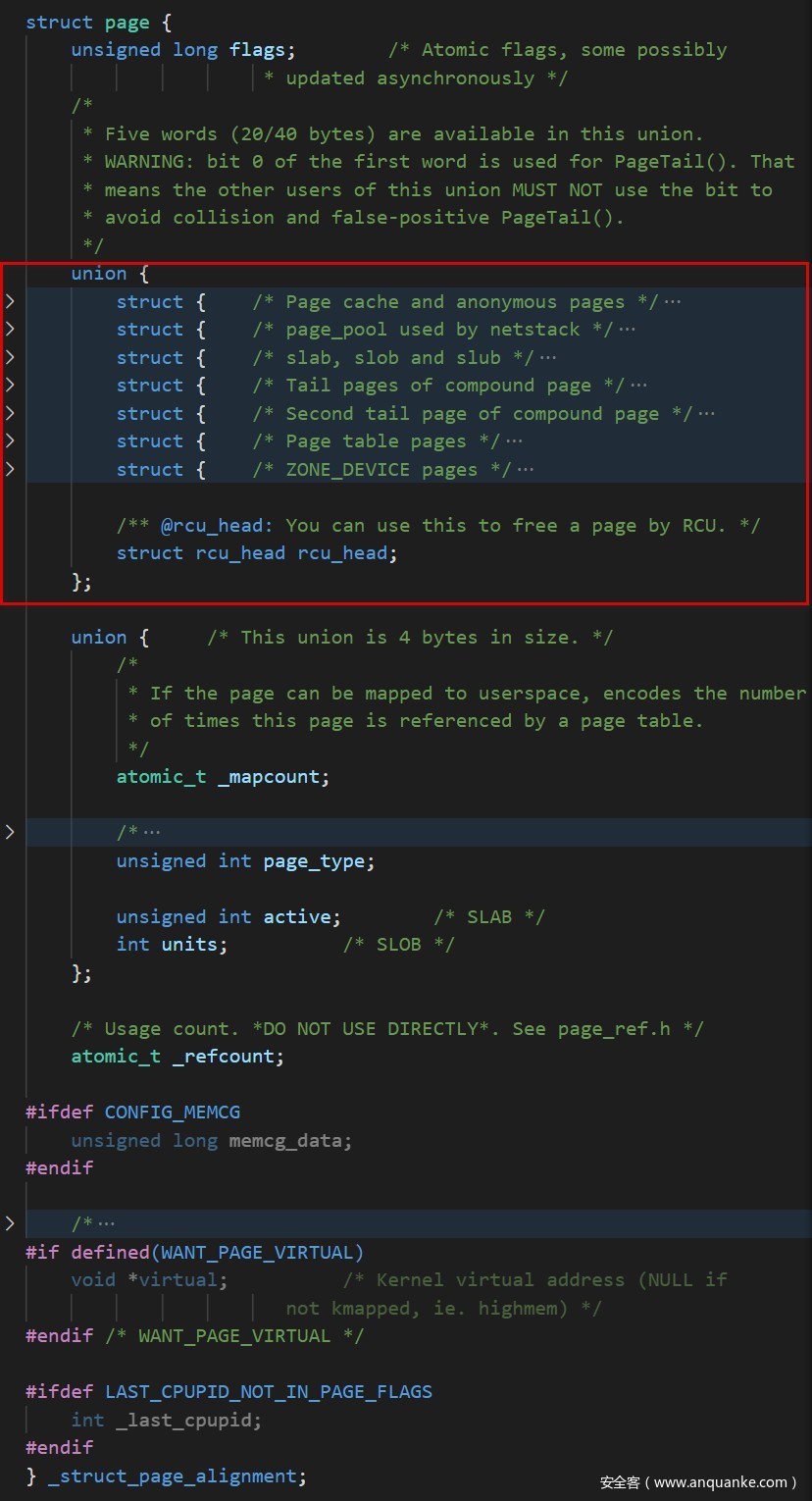
每个页框由page类型描述符定义,该结构定义位于include/linux/mm_types.h中(代码量稍大,读者可自行查看):
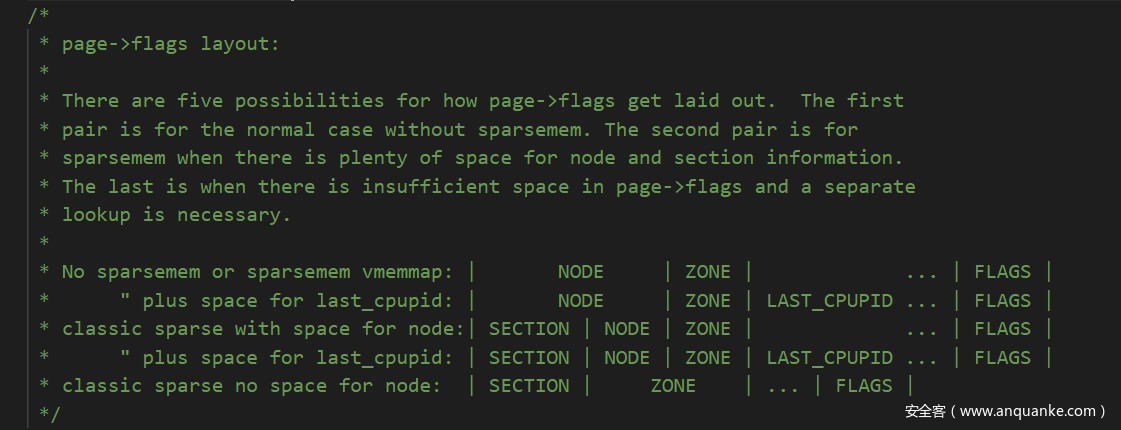
flags字段可定义值见include/linux/page-flags.h文件,其布局不同形式由include/linux/page-flags-layout.h定义:
_mapcount字段标识该页框被页表引用次数。
三、伙伴系统
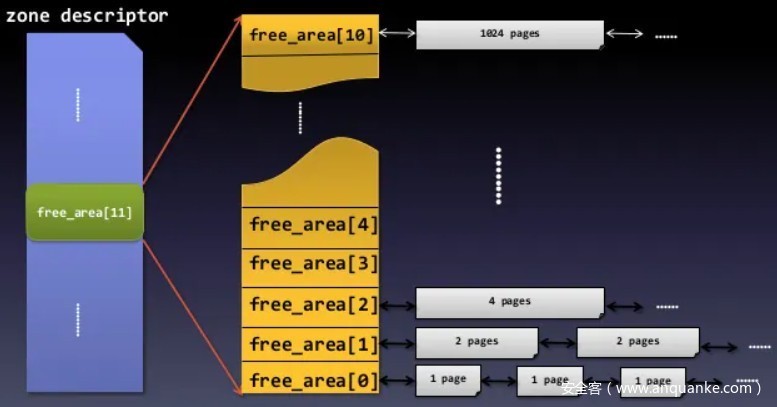
在zone描述符中,free_area字段用来保存该内存管理区内空闲页框,其定义如下:
/* free areas of different sizes */
struct free_area free_area[MAX_ORDER];
free_area数组中每个元素保存有相应2的指数大小空闲页框块,MAX_ORDER是2的指数最大值加1——通常定义为11:
#ifndef CONFIG_FORCE_MAX_ZONEORDER
#define MAX_ORDER 11
#else
#define MAX_ORDER CONFIG_FORCE_MAX_ZONEORDER
#endif
free_area类型定义如下:
struct free_area {
struct list_head free_list[MIGRATE_TYPES];
unsigned long nr_free;
};
其中free_list定义为不同类型空闲页框块的链表,nr_free是空闲页框块数量。
0x01 alloc_pages
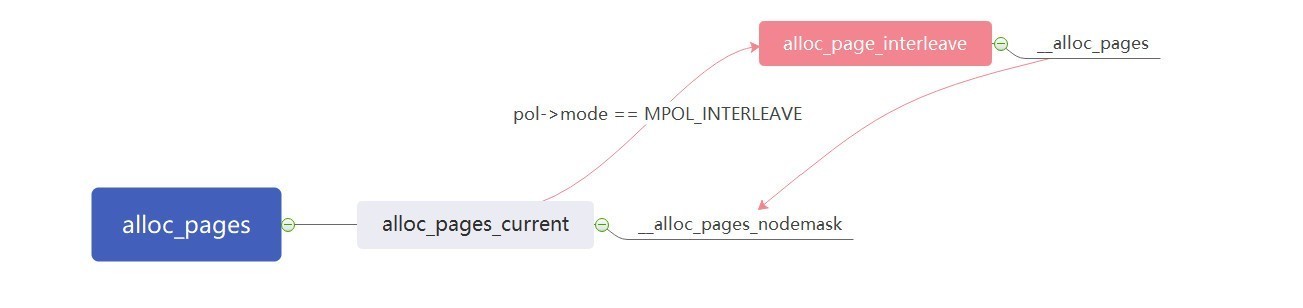
启用CONFIG_NUMA选项,该函数调用关系如下:
可以看到关键函数是__alloc_pages_nodemask。上面调用关系是启用CONFIG_NUMA之后的:
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
extern struct page *alloc_pages_current(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned order);
static inline struct page *
alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
return alloc_pages_current(gfp_mask, order);
}
extern struct page *alloc_pages_vma(gfp_t gfp_mask, int order,
struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long addr,
int node, bool hugepage);
#define alloc_hugepage_vma(gfp_mask, vma, addr, order) \
alloc_pages_vma(gfp_mask, order, vma, addr, numa_node_id(), true)
#else
static inline struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
return alloc_pages_node(numa_node_id(), gfp_mask, order);
}
若未启用该选项,调用关系如下:
alloc_pages
->alloc_pages_node
->__alloc_pages_node
->__alloc_pages
->__alloc_pages_nodemask
alloc_pages_current函数定义如下:
struct page *alloc_pages_current(gfp_t gfp, unsigned order)
{
struct mempolicy *pol = &default_policy;
struct page *page;
if (!in_interrupt() && !(gfp & __GFP_THISNODE))
pol = get_task_policy(current);
/*
* No reference counting needed for current->mempolicy
* nor system default_policy
*/
if (pol->mode == MPOL_INTERLEAVE)
page = alloc_page_interleave(gfp, order, interleave_nodes(pol));
else
page = __alloc_pages_nodemask(gfp, order,
policy_node(gfp, pol, numa_node_id()),
policy_nodemask(gfp, pol));
return page;
}
参数gfp定义了请求页框标志值,order定义了请求页框大小——2<sup>order</sup>个连续页框。标志值定义位于gfp.h文件:
#define GFP_ATOMIC (__GFP_HIGH|__GFP_ATOMIC|__GFP_KSWAPD_RECLAIM)
#define GFP_KERNEL (__GFP_RECLAIM | __GFP_IO | __GFP_FS)
#define GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT (GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_ACCOUNT)
#define GFP_NOWAIT (__GFP_KSWAPD_RECLAIM)
#define GFP_NOIO (__GFP_RECLAIM)
#define GFP_NOFS (__GFP_RECLAIM | __GFP_IO)
#define GFP_USER (__GFP_RECLAIM | __GFP_IO | __GFP_FS | __GFP_HARDWALL)
#define GFP_DMA __GFP_DMA
#define GFP_DMA32 __GFP_DMA32
#define GFP_HIGHUSER (GFP_USER | __GFP_HIGHMEM)
#define GFP_HIGHUSER_MOVABLE (GFP_HIGHUSER | __GFP_MOVABLE)
#define GFP_TRANSHUGE_LIGHT ((GFP_HIGHUSER_MOVABLE | __GFP_COMP | \
__GFP_NOMEMALLOC | __GFP_NOWARN) & ~__GFP_RECLAIM)
#define GFP_TRANSHUGE (GFP_TRANSHUGE_LIGHT | __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM)
/* Convert GFP flags to their corresponding migrate type */
#define GFP_MOVABLE_MASK (__GFP_RECLAIMABLE|__GFP_MOVABLE)
#define GFP_MOVABLE_SHIFT 3
alloc_pages_current函数首先获取默认mempolicy,该结构mode字段值可以有以下几种:
enum {
MPOL_DEFAULT,
MPOL_PREFERRED,
MPOL_BIND,
MPOL_INTERLEAVE,
MPOL_LOCAL,
MPOL_MAX, /* always last member of enum */
};
不同取值含义可参阅set_mempolicy(2) — Linux manual page。default_policy中mode定义为MPOL_PREFERRED:
static struct mempolicy default_policy = {
.refcnt = ATOMIC_INIT(1), /* never free it */
.mode = MPOL_PREFERRED,
.flags = MPOL_F_LOCAL,
};
若gfp标志中置__GFP_THISNODE位或位于中断时采用默认mempolicy,下面将以此种情况进行展开。policy_node根据mempolicy返回Node id,policy_nodemask会返回NULL:
nodemask_t *policy_nodemask(gfp_t gfp, struct mempolicy *policy)
{
/* Lower zones don't get a nodemask applied for MPOL_BIND */
if (unlikely(policy->mode == MPOL_BIND) &&
apply_policy_zone(policy, gfp_zone(gfp)) &&
cpuset_nodemask_valid_mems_allowed(&policy->v.nodes))
return &policy->v.nodes;
return NULL;
}
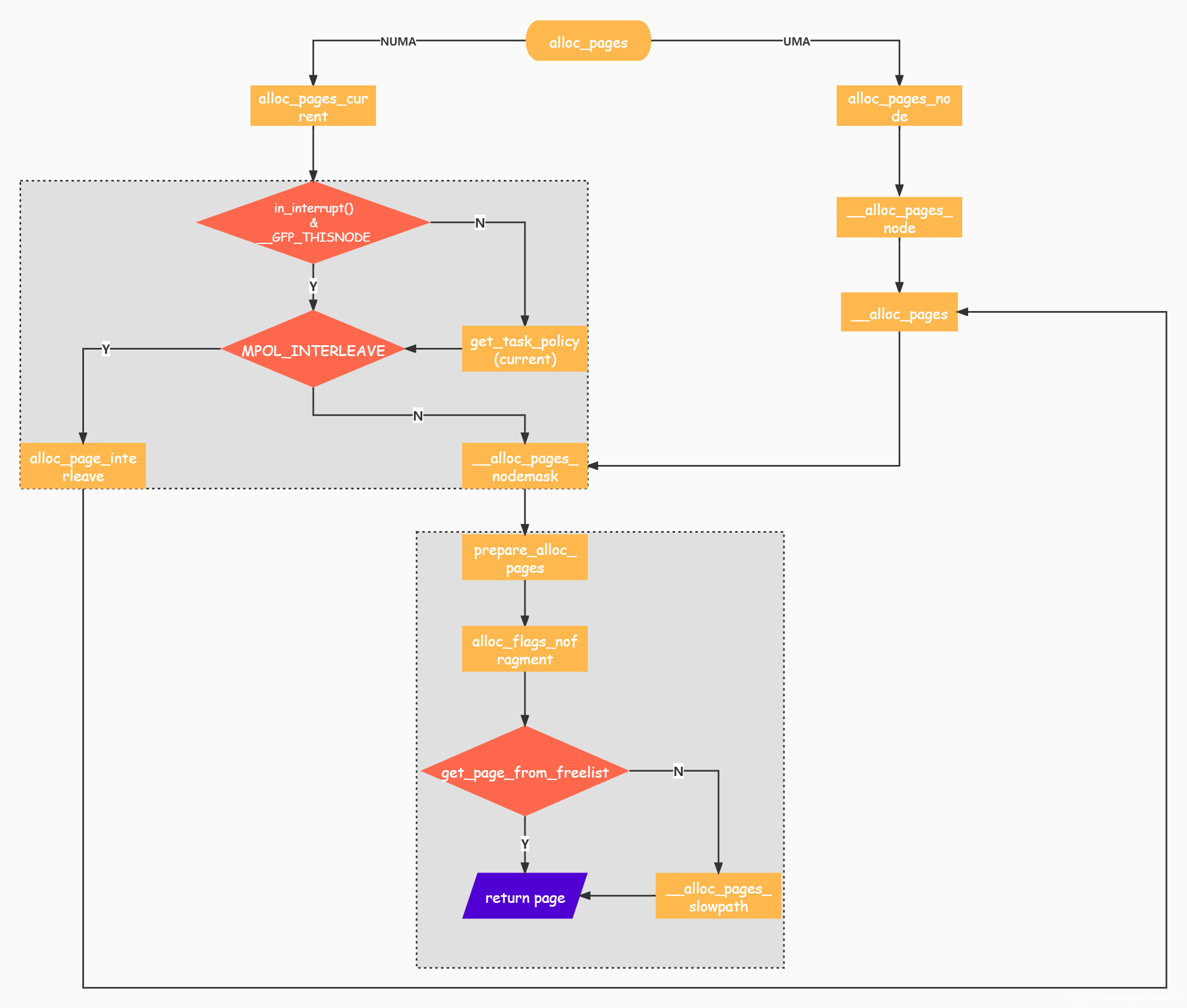
用一张图概括上文提及函数及下文将阐述函数的调用关系:
函数定义如下:
/*
* This is the 'heart' of the zoned buddy allocator.
*/
struct page *
__alloc_pages_nodemask(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int preferred_nid,
nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
struct page *page;
unsigned int alloc_flags = ALLOC_WMARK_LOW;
gfp_t alloc_mask; /* The gfp_t that was actually used for allocation */
struct alloc_context ac = { };
/*
* There are several places where we assume that the order value is sane
* so bail out early if the request is out of bound.
*/
if (unlikely(order >= MAX_ORDER)) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp_mask & __GFP_NOWARN));
return NULL;
}
gfp_mask &= gfp_allowed_mask;
alloc_mask = gfp_mask;
if (!prepare_alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order, preferred_nid, nodemask, &ac, &alloc_mask, &alloc_flags))
return NULL;
/*
* Forbid the first pass from falling back to types that fragment
* memory until all local zones are considered.
*/
alloc_flags |= alloc_flags_nofragment(ac.preferred_zoneref->zone, gfp_mask);
/* First allocation attempt */
page = get_page_from_freelist(alloc_mask, order, alloc_flags, &ac);
if (likely(page))
goto out;
/*
* Apply scoped allocation constraints. This is mainly about GFP_NOFS
* resp. GFP_NOIO which has to be inherited for all allocation requests
* from a particular context which has been marked by
* memalloc_no{fs,io}_{save,restore}.
*/
alloc_mask = current_gfp_context(gfp_mask);
ac.spread_dirty_pages = false;
/*
* Restore the original nodemask if it was potentially replaced with
* &cpuset_current_mems_allowed to optimize the fast-path attempt.
*/
ac.nodemask = nodemask;
page = __alloc_pages_slowpath(alloc_mask, order, &ac);
out:
if (memcg_kmem_enabled() && (gfp_mask & __GFP_ACCOUNT) && page &&
unlikely(__memcg_kmem_charge_page(page, gfp_mask, order) != 0)) {
__free_pages(page, order);
page = NULL;
}
trace_mm_page_alloc(page, order, alloc_mask, ac.migratetype);
return page;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__alloc_pages_nodemask);
首先是判断order大小是否超过MAX_ORDER:
if (unlikely(order >= MAX_ORDER)) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp_mask & __GFP_NOWARN));
return NULL;
}
之后执行prepare_alloc_pages,该函数主要是初始化ac变量——类型为alloc_context结构体(该结构及其字段含义见注释,不再赘述):
/*
* Structure for holding the mostly immutable allocation parameters passed
* between functions involved in allocations, including the alloc_pages*
* family of functions.
*
* nodemask, migratetype and highest_zoneidx are initialized only once in
* __alloc_pages_nodemask() and then never change.
*
* zonelist, preferred_zone and highest_zoneidx are set first in
* __alloc_pages_nodemask() for the fast path, and might be later changed
* in __alloc_pages_slowpath(). All other functions pass the whole structure
* by a const pointer.
*/
struct alloc_context {
struct zonelist *zonelist;
nodemask_t *nodemask;
struct zoneref *preferred_zoneref;
int migratetype;
/*
* highest_zoneidx represents highest usable zone index of
* the allocation request. Due to the nature of the zone,
* memory on lower zone than the highest_zoneidx will be
* protected by lowmem_reserve[highest_zoneidx].
*
* highest_zoneidx is also used by reclaim/compaction to limit
* the target zone since higher zone than this index cannot be
* usable for this allocation request.
*/
enum zone_type highest_zoneidx;
bool spread_dirty_pages;
};
函数执行操作如下:
static inline bool prepare_alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
int preferred_nid, nodemask_t *nodemask,
struct alloc_context *ac, gfp_t *alloc_mask,
unsigned int *alloc_flags)
{
ac->highest_zoneidx = gfp_zone(gfp_mask);
ac->zonelist = node_zonelist(preferred_nid, gfp_mask);
ac->nodemask = nodemask;
ac->migratetype = gfp_migratetype(gfp_mask);
if (cpusets_enabled()) {
*alloc_mask |= __GFP_HARDWALL;
/*
* When we are in the interrupt context, it is irrelevant
* to the current task context. It means that any node ok.
*/
if (!in_interrupt() && !ac->nodemask)
ac->nodemask = &cpuset_current_mems_allowed;
else
*alloc_flags |= ALLOC_CPUSET;
}
fs_reclaim_acquire(gfp_mask);
fs_reclaim_release(gfp_mask);
might_sleep_if(gfp_mask & __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM);
if (should_fail_alloc_page(gfp_mask, order))
return false;
*alloc_flags = current_alloc_flags(gfp_mask, *alloc_flags);
/* Dirty zone balancing only done in the fast path */
ac->spread_dirty_pages = (gfp_mask & __GFP_WRITE);
/*
* The preferred zone is used for statistics but crucially it is
* also used as the starting point for the zonelist iterator. It
* may get reset for allocations that ignore memory policies.
*/
ac->preferred_zoneref = first_zones_zonelist(ac->zonelist,
ac->highest_zoneidx, ac->nodemask);
return true;
}
其中gfp_zone函数根据gfp_mask计算出Zone(该函数返回值类型定义见0x01.2节):
static inline enum zone_type gfp_zone(gfp_t flags)
{
enum zone_type z;
int bit = (__force int) (flags & GFP_ZONEMASK);
z = (GFP_ZONE_TABLE >> (bit * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT)) &
((1 << GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) - 1);
VM_BUG_ON((GFP_ZONE_BAD >> bit) & 1);
return z;
}
其中GFP_ZONEMASK定义如下——即0x0F(gfp_mask低四位表示进行分配的Zone):
#define ___GFP_DMA 0x01u
#define ___GFP_HIGHMEM 0x02u
#define ___GFP_DMA32 0x04u
#define ___GFP_MOVABLE 0x08u
......
#define __GFP_DMA ((__force gfp_t)___GFP_DMA)
#define __GFP_HIGHMEM ((__force gfp_t)___GFP_HIGHMEM)
#define __GFP_DMA32 ((__force gfp_t)___GFP_DMA32)
#define __GFP_MOVABLE ((__force gfp_t)___GFP_MOVABLE) /* ZONE_MOVABLE allowed */
#define GFP_ZONEMASK (__GFP_DMA|__GFP_HIGHMEM|__GFP_DMA32|__GFP_MOVABLE)
不同位置1结果如下:
* bit result
* =================
* 0x0 => NORMAL
* 0x1 => DMA or NORMAL
* 0x2 => HIGHMEM or NORMAL
* 0x3 => BAD (DMA+HIGHMEM)
* 0x4 => DMA32 or NORMAL
* 0x5 => BAD (DMA+DMA32)
* 0x6 => BAD (HIGHMEM+DMA32)
* 0x7 => BAD (HIGHMEM+DMA32+DMA)
* 0x8 => NORMAL (MOVABLE+0)
* 0x9 => DMA or NORMAL (MOVABLE+DMA)
* 0xa => MOVABLE (Movable is valid only if HIGHMEM is set too)
* 0xb => BAD (MOVABLE+HIGHMEM+DMA)
* 0xc => DMA32 or NORMAL (MOVABLE+DMA32)
* 0xd => BAD (MOVABLE+DMA32+DMA)
* 0xe => BAD (MOVABLE+DMA32+HIGHMEM)
* 0xf => BAD (MOVABLE+DMA32+HIGHMEM+DMA)
GFP_ZONE_TABLE及GFP_ZONES_SHIFT定义如下:
#if MAX_NR_ZONES < 2
#define ZONES_SHIFT 0
#elif MAX_NR_ZONES <= 2
#define ZONES_SHIFT 1
#elif MAX_NR_ZONES <= 4
#define ZONES_SHIFT 2
#elif MAX_NR_ZONES <= 8
#define ZONES_SHIFT 3
#else
#error ZONES_SHIFT -- too many zones configured adjust calculation
#endif
......
#if defined(CONFIG_ZONE_DEVICE) && (MAX_NR_ZONES-1) <= 4
/* ZONE_DEVICE is not a valid GFP zone specifier */
#define GFP_ZONES_SHIFT 2
#else
#define GFP_ZONES_SHIFT ZONES_SHIFT
#endif
......
#define GFP_ZONE_TABLE ( \
(ZONE_NORMAL << 0 * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (OPT_ZONE_DMA << ___GFP_DMA * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (OPT_ZONE_HIGHMEM << ___GFP_HIGHMEM * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (OPT_ZONE_DMA32 << ___GFP_DMA32 * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (ZONE_NORMAL << ___GFP_MOVABLE * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (OPT_ZONE_DMA << (___GFP_MOVABLE | ___GFP_DMA) * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT) \
| (ZONE_MOVABLE << (___GFP_MOVABLE | ___GFP_HIGHMEM) * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT)\
| (OPT_ZONE_DMA32 << (___GFP_MOVABLE | ___GFP_DMA32) * GFP_ZONES_SHIFT)\
)
node_zonelist函数用于获取对应Node的zonelists。0x01.1节在介绍Node时,其中pglist_data结构包含有node_zonelists字段:
/*
* node_zonelists contains references to all zones in all nodes.
* Generally the first zones will be references to this node's
* node_zones.
*/
struct zonelist node_zonelists[MAX_ZONELISTS];
MAX_ZONELISTS值取决是否启用CONFIG_NUMA选项:
enum {
ZONELIST_FALLBACK, /* zonelist with fallback */
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
/*
* The NUMA zonelists are doubled because we need zonelists that
* restrict the allocations to a single node for __GFP_THISNODE.
*/
ZONELIST_NOFALLBACK, /* zonelist without fallback (__GFP_THISNODE) */
#endif
MAX_ZONELISTS
};
zonelist结构定义如下:
/* Maximum number of zones on a zonelist */
#define MAX_ZONES_PER_ZONELIST (MAX_NUMNODES * MAX_NR_ZONES)
......
struct zoneref {
struct zone *zone; /* Pointer to actual zone */
int zone_idx; /* zone_idx(zoneref->zone) */
};
/*
* One allocation request operates on a zonelist. A zonelist
* is a list of zones, the first one is the 'goal' of the
* allocation, the other zones are fallback zones, in decreasing
* priority.
*
* To speed the reading of the zonelist, the zonerefs contain the zone index
* of the entry being read. Helper functions to access information given
* a struct zoneref are
*
* zonelist_zone() - Return the struct zone * for an entry in _zonerefs
* zonelist_zone_idx() - Return the index of the zone for an entry
* zonelist_node_idx() - Return the index of the node for an entry
*/
struct zonelist {
struct zoneref _zonerefs[MAX_ZONES_PER_ZONELIST + 1];
};
node_zonelist函数定义如下:
#define ___GFP_THISNODE 0x200000u
......
static inline int gfp_zonelist(gfp_t flags)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
if (unlikely(flags & __GFP_THISNODE))
return ZONELIST_NOFALLBACK;
#endif
return ZONELIST_FALLBACK;
}
......
static inline struct zonelist *node_zonelist(int nid, gfp_t flags)
{
return NODE_DATA(nid)->node_zonelists + gfp_zonelist(flags);
}
gfp_migratetype函数根据gfp_flags返回内存迁移类型,内存迁移用以缓解内存碎片,可参阅Linux Kernel vs. Memory Fragmentation (Part I):
#define ___GFP_RECLAIMABLE 0x10u
......
#define __GFP_RECLAIMABLE ((__force gfp_t)___GFP_RECLAIMABLE)
......
/* Convert GFP flags to their corresponding migrate type */
#define GFP_MOVABLE_MASK (__GFP_RECLAIMABLE|__GFP_MOVABLE)
#define GFP_MOVABLE_SHIFT 3
static inline int gfp_migratetype(const gfp_t gfp_flags)
{
VM_WARN_ON((gfp_flags & GFP_MOVABLE_MASK) == GFP_MOVABLE_MASK);
BUILD_BUG_ON((1UL << GFP_MOVABLE_SHIFT) != ___GFP_MOVABLE);
BUILD_BUG_ON((___GFP_MOVABLE >> GFP_MOVABLE_SHIFT) != MIGRATE_MOVABLE);
if (unlikely(page_group_by_mobility_disabled))
return MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE;
/* Group based on mobility */
return (gfp_flags & GFP_MOVABLE_MASK) >> GFP_MOVABLE_SHIFT;
}
下面代码块执行与否取决于是否启用cpuset功能(CONFIG_CPUSETS配置选项):
if (cpusets_enabled()) {
*alloc_mask |= __GFP_HARDWALL;
/*
* When we are in the interrupt context, it is irrelevant
* to the current task context. It means that any node ok.
*/
if (!in_interrupt() && !ac->nodemask)
ac->nodemask = &cpuset_current_mems_allowed;
else
*alloc_flags |= ALLOC_CPUSET;
}
若未配置CONFIG_FAIL_PAGE_ALLOC选项,should_fail_alloc_page直接返回false:
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIL_PAGE_ALLOC
......
#else /* CONFIG_FAIL_PAGE_ALLOC */
static inline bool __should_fail_alloc_page(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
return false;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_FAIL_PAGE_ALLOC */
noinline bool should_fail_alloc_page(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
return __should_fail_alloc_page(gfp_mask, order);
}
若未配置CONFIG_CMA选项,current_alloc_flags直接返回alloc_flags:
static inline unsigned int current_alloc_flags(gfp_t gfp_mask,
unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
unsigned int pflags = current->flags;
if (!(pflags & PF_MEMALLOC_NOCMA) &&
gfp_migratetype(gfp_mask) == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)
alloc_flags |= ALLOC_CMA;
#endif
return alloc_flags;
}
first_zones_zonelist函数定义如下,其返回不大于highest_zoneidx的第一个Zone:
/* Returns the next zone at or below highest_zoneidx in a zonelist */
struct zoneref *__next_zones_zonelist(struct zoneref *z,
enum zone_type highest_zoneidx,
nodemask_t *nodes)
{
/*
* Find the next suitable zone to use for the allocation.
* Only filter based on nodemask if it's set
*/
if (unlikely(nodes == NULL))
while (zonelist_zone_idx(z) > highest_zoneidx)
z++;
else
while (zonelist_zone_idx(z) > highest_zoneidx ||
(z->zone && !zref_in_nodemask(z, nodes)))
z++;
return z;
}
......
static __always_inline struct zoneref *next_zones_zonelist(struct zoneref *z,
enum zone_type highest_zoneidx,
nodemask_t *nodes)
{
if (likely(!nodes && zonelist_zone_idx(z) <= highest_zoneidx))
return z;
return __next_zones_zonelist(z, highest_zoneidx, nodes);
}
......
static inline struct zoneref *first_zones_zonelist(struct zonelist *zonelist,
enum zone_type highest_zoneidx,
nodemask_t *nodes)
{
return next_zones_zonelist(zonelist->_zonerefs,
highest_zoneidx, nodes);
}
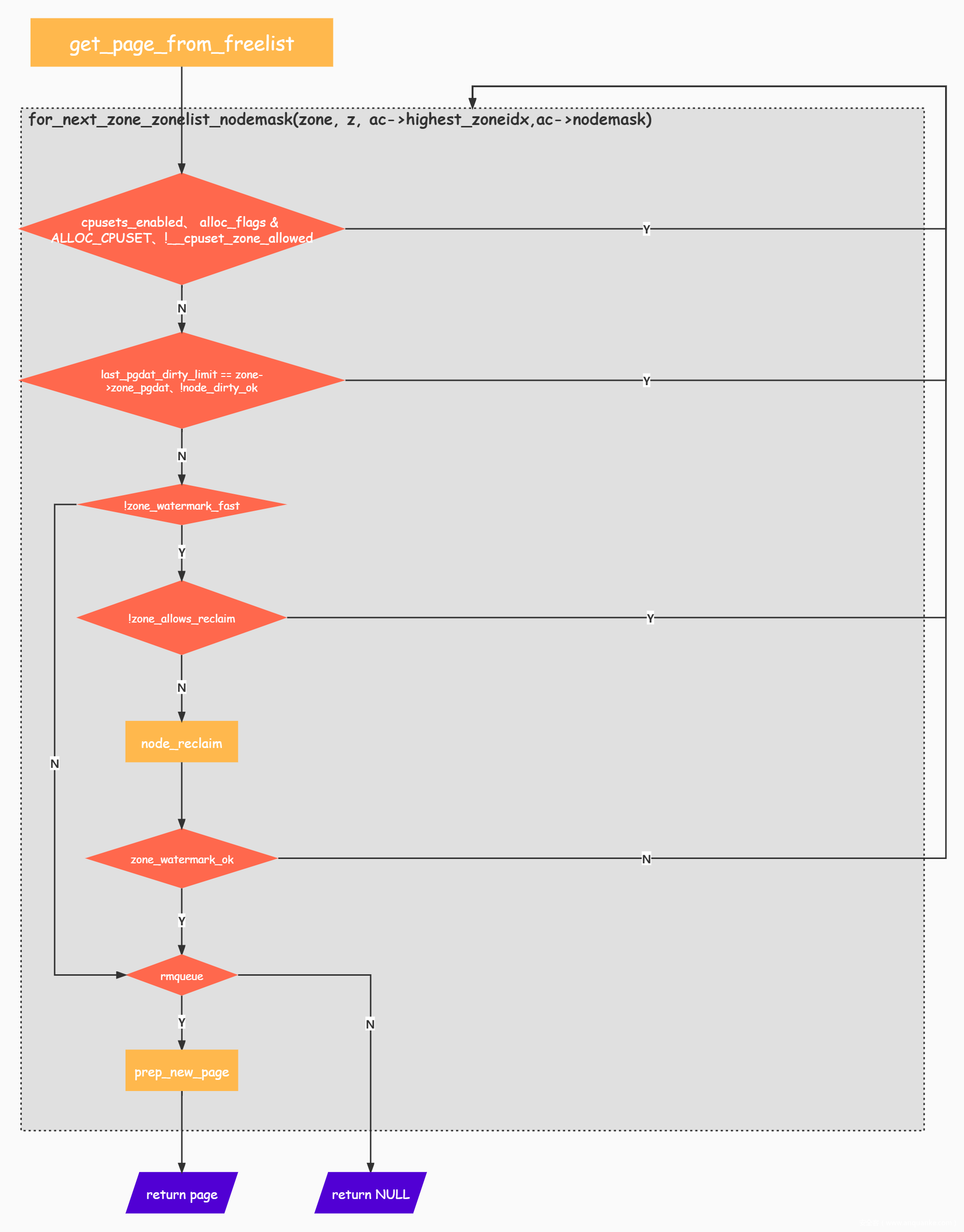
准备工作完成后,下面执行get_page_from_freelist函数——即fastpath:
/*
* get_page_from_freelist goes through the zonelist trying to allocate
* a page.
*/
static struct page *
get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags,
const struct alloc_context *ac)
{
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
struct pglist_data *last_pgdat_dirty_limit = NULL;
bool no_fallback;
retry:
/*
* Scan zonelist, looking for a zone with enough free.
* See also __cpuset_node_allowed() comment in kernel/cpuset.c.
*/
no_fallback = alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
z = ac->preferred_zoneref;
for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->highest_zoneidx,
ac->nodemask) {
struct page *page;
unsigned long mark;
if (cpusets_enabled() &&
(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&
!__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))
continue;
if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {
if (last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat)
continue;
if (!node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat)) {
last_pgdat_dirty_limit = zone->zone_pgdat;
continue;
}
}
if (no_fallback && nr_online_nodes > 1 &&
zone != ac->preferred_zoneref->zone) {
int local_nid;
/*
* If moving to a remote node, retry but allow
* fragmenting fallbacks. Locality is more important
* than fragmentation avoidance.
*/
local_nid = zone_to_nid(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone);
if (zone_to_nid(zone) != local_nid) {
alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
goto retry;
}
}
mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,
ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,
gfp_mask)) {
int ret;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
/*
* Watermark failed for this zone, but see if we can
* grow this zone if it contains deferred pages.
*/
if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {
if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
goto try_this_zone;
}
#endif
/* Checked here to keep the fast path fast */
BUILD_BUG_ON(ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS < NR_WMARK);
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)
goto try_this_zone;
if (node_reclaim_mode == 0 ||
!zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))
continue;
ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);
switch (ret) {
case NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:
/* did not scan */
continue;
case NODE_RECLAIM_FULL:
/* scanned but unreclaimable */
continue;
default:
/* did we reclaim enough */
if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, mark,
ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags))
goto try_this_zone;
continue;
}
}
try_this_zone:
page = rmqueue(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone, order,
gfp_mask, alloc_flags, ac->migratetype);
if (page) {
prep_new_page(page, order, gfp_mask, alloc_flags);
/*
* If this is a high-order atomic allocation then check
* if the pageblock should be reserved for the future
*/
if (unlikely(order && (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER)))
reserve_highatomic_pageblock(page, zone, order);
return page;
} else {
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
/* Try again if zone has deferred pages */
if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {
if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
goto try_this_zone;
}
#endif
}
}
/*
* It's possible on a UMA machine to get through all zones that are
* fragmented. If avoiding fragmentation, reset and try again.
*/
if (no_fallback) {
alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
goto retry;
}
return NULL;
}
for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask宏展开如下:
#define for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, highidx, nodemask) \
for (zone = z->zone; \
zone; \
z = next_zones_zonelist(++z, highidx, nodemask), \
zone = zonelist_zone(z))
依次执行cpusets_enabled、alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET、__cpuset_zone_allowed与last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat、node_dirty_ok及zone_watermark_fast函数进行检查,如未通过检查则进行下一次循环。关于watermark,在此暂不作展开。若alloc_flags置ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS位或是zone_watermark_ok返回True,直接跳转到try_this_zone——伙伴系统核心部分:
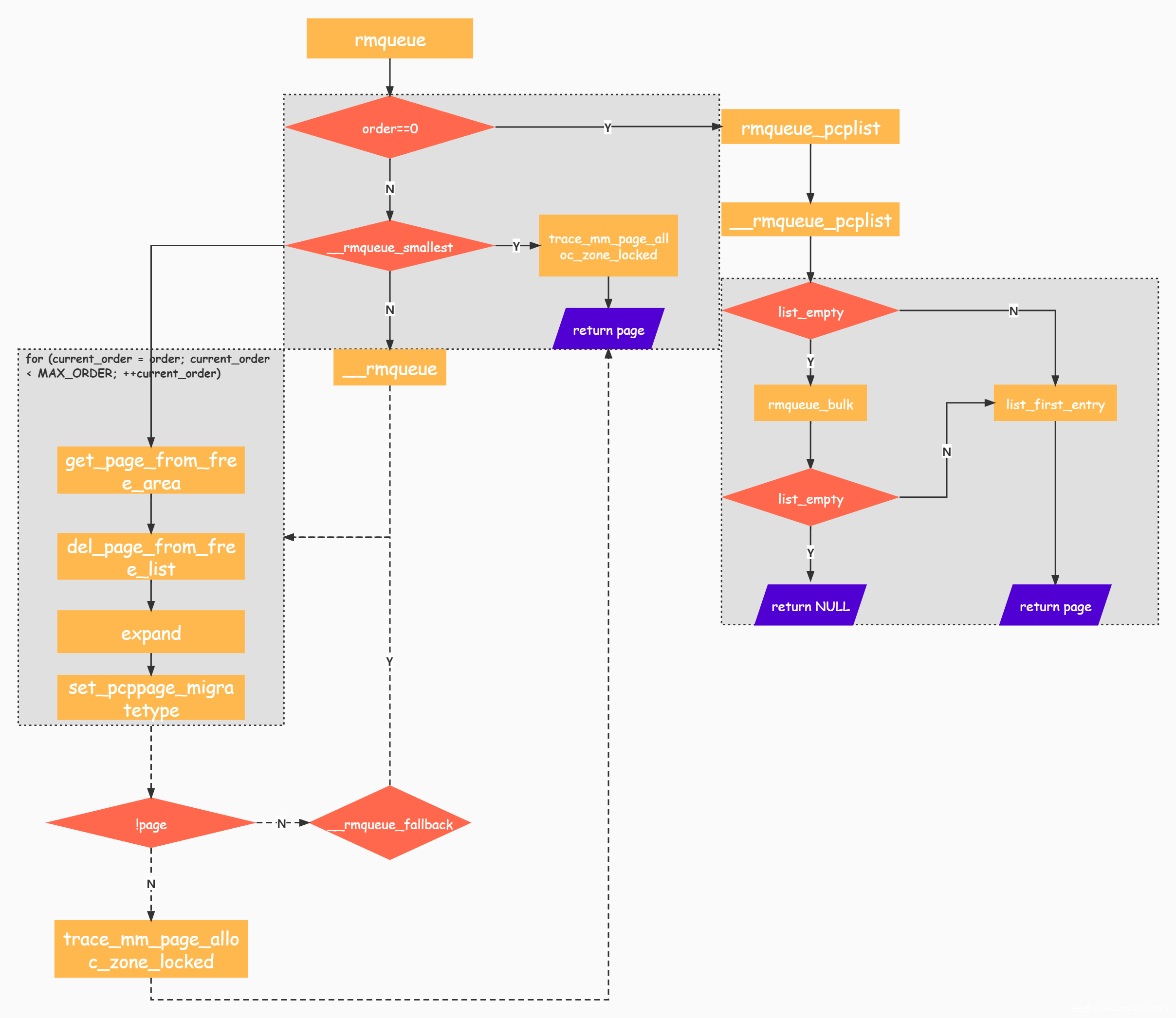
/*
* Allocate a page from the given zone. Use pcplists for order-0 allocations.
*/
static inline
struct page *rmqueue(struct zone *preferred_zone,
struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
gfp_t gfp_flags, unsigned int alloc_flags,
int migratetype)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct page *page;
if (likely(order == 0)) {
/*
* MIGRATE_MOVABLE pcplist could have the pages on CMA area and
* we need to skip it when CMA area isn't allowed.
*/
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CMA) || alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA ||
migratetype != MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {
page = rmqueue_pcplist(preferred_zone, zone, gfp_flags,
migratetype, alloc_flags);
goto out;
}
}
/*
* We most definitely don't want callers attempting to
* allocate greater than order-1 page units with __GFP_NOFAIL.
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE((gfp_flags & __GFP_NOFAIL) && (order > 1));
spin_lock_irqsave(&zone->lock, flags);
do {
page = NULL;
/*
* order-0 request can reach here when the pcplist is skipped
* due to non-CMA allocation context. HIGHATOMIC area is
* reserved for high-order atomic allocation, so order-0
* request should skip it.
*/
if (order > 0 && alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER) {
page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC);
if (page)
trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);
}
if (!page)
page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags);
} while (page && check_new_pages(page, order));
spin_unlock(&zone->lock);
if (!page)
goto failed;
__mod_zone_freepage_state(zone, -(1 << order),
get_pcppage_migratetype(page));
__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1 << order);
zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone);
local_irq_restore(flags);
out:
/* Separate test+clear to avoid unnecessary atomics */
if (test_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags)) {
clear_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);
wakeup_kswapd(zone, 0, 0, zone_idx(zone));
}
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page && bad_range(zone, page), page);
return page;
failed:
local_irq_restore(flags);
return NULL;
}
如果是分配单页,则执行rmqueue_pcplist:
/* Lock and remove page from the per-cpu list */
static struct page *rmqueue_pcplist(struct zone *preferred_zone,
struct zone *zone, gfp_t gfp_flags,
int migratetype, unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp;
struct list_head *list;
struct page *page;
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
pcp = &this_cpu_ptr(zone->pageset)->pcp;
list = &pcp->lists[migratetype];
page = __rmqueue_pcplist(zone, migratetype, alloc_flags, pcp, list);
if (page) {
__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1);
zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone);
}
local_irq_restore(flags);
return page;
}
该函数从per_cpu_pageset中分配单页,在0x01.2中介绍Zone时,其结构体含有一pageset字段:
struct zone {
......
struct per_cpu_pageset __percpu *pageset;
......
}
该结构体定义如下:
enum migratetype {
MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE,
MIGRATE_MOVABLE,
MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE,
MIGRATE_PCPTYPES, /* the number of types on the pcp lists */
MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC = MIGRATE_PCPTYPES,
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
/*
* MIGRATE_CMA migration type is designed to mimic the way
* ZONE_MOVABLE works. Only movable pages can be allocated
* from MIGRATE_CMA pageblocks and page allocator never
* implicitly change migration type of MIGRATE_CMA pageblock.
*
* The way to use it is to change migratetype of a range of
* pageblocks to MIGRATE_CMA which can be done by
* __free_pageblock_cma() function. What is important though
* is that a range of pageblocks must be aligned to
* MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES should biggest page be bigger then
* a single pageblock.
*/
MIGRATE_CMA,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION
MIGRATE_ISOLATE, /* can't allocate from here */
#endif
MIGRATE_TYPES
};
......
struct per_cpu_pages {
int count; /* number of pages in the list */
int high; /* high watermark, emptying needed */
int batch; /* chunk size for buddy add/remove */
/* Lists of pages, one per migrate type stored on the pcp-lists */
struct list_head lists[MIGRATE_PCPTYPES];
};
struct per_cpu_pageset {
struct per_cpu_pages pcp;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
s8 expire;
u16 vm_numa_stat_diff[NR_VM_NUMA_STAT_ITEMS];
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
s8 stat_threshold;
s8 vm_stat_diff[NR_VM_ZONE_STAT_ITEMS];
#endif
};
此函数核心功能由__rmqueue_pcplist实现:
/* Remove page from the per-cpu list, caller must protect the list */
static struct page *__rmqueue_pcplist(struct zone *zone, int migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp,
struct list_head *list)
{
struct page *page;
do {
if (list_empty(list)) {
pcp->count += rmqueue_bulk(zone, 0,
READ_ONCE(pcp->batch), list,
migratetype, alloc_flags);
if (unlikely(list_empty(list)))
return NULL;
}
page = list_first_entry(list, struct page, lru);
list_del(&page->lru);
pcp->count--;
} while (check_new_pcp(page));
return page;
}
首先判断list是否为空——如果为空,则调用rmqueue_bulk(该函数核心为__rmqueue,暂不作展开)分配Page;如果不为空,则分配一页。
如果order大于0,首先执行__rmqueue_smallest函数:
/*
* Go through the free lists for the given migratetype and remove
* the smallest available page from the freelists
*/
static __always_inline
struct page *__rmqueue_smallest(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
int migratetype)
{
unsigned int current_order;
struct free_area *area;
struct page *page;
/* Find a page of the appropriate size in the preferred list */
for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER; ++current_order) {
area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);
page = get_page_from_free_area(area, migratetype);
if (!page)
continue;
del_page_from_free_list(page, zone, current_order);
expand(zone, page, order, current_order, migratetype);
set_pcppage_migratetype(page, migratetype);
return page;
}
return NULL;
}
get_page_from_free_area函数是对list_first_entry_or_null宏的包装(MIGRATE_TYPES定义已在上文给出,不再赘述):
struct free_area {
struct list_head free_list[MIGRATE_TYPES];
unsigned long nr_free;
};
static inline struct page *get_page_from_free_area(struct free_area *area,
int migratetype)
{
return list_first_entry_or_null(&area->free_list[migratetype],
struct page, lru);
}
list_first_entry_or_null宏同上文提及的list_first_entry一样,于/include/linux/list.h文件中定义:
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
......
/**
* list_first_entry_or_null - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note that if the list is empty, it returns NULL.
*/
#define list_first_entry_or_null(ptr, type, member) ({ \
struct list_head *head__ = (ptr); \
struct list_head *pos__ = READ_ONCE(head__->next); \
pos__ != head__ ? list_entry(pos__, type, member) : NULL; \
})
而container_of宏定义位于/include/linux/kernel.h文件
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
void *__mptr = (void *)(ptr); \
BUILD_BUG_ON_MSG(!__same_type(*(ptr), ((type *)0)->member) && \
!__same_type(*(ptr), void), \
"pointer type mismatch in container_of()"); \
((type *)(__mptr - offsetof(type, member))); })
分配成功,将其从free_area中删除并减少nr_free计数:
static inline void del_page_from_free_list(struct page *page, struct zone *zone,
unsigned int order)
{
/* clear reported state and update reported page count */
if (page_reported(page))
__ClearPageReported(page);
list_del(&page->lru);
__ClearPageBuddy(page);
set_page_private(page, 0);
zone->free_area[order].nr_free--;
}
list_del宏展开如下:
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, next);
}
......
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{
if (!__list_del_entry_valid(entry))
return;
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
/**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
set_page_private(page, 0)函数将page的private字段设为0:
static inline void set_page_private(struct page *page, unsigned long private)
{
page->private = private;
}
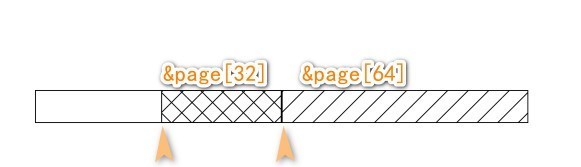
假设我们要申请32(2^5=32)个连续Page块——order为5,而free_area[5]与free_area[6]中都没有这样的块,那么就 要从free_area[7]中申请。这时传递给expand函数的low与high参数分别为5与7:
static inline void expand(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,
int low, int high, int migratetype)
{
unsigned long size = 1 << high;
while (high > low) {
high--;
size >>= 1;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(bad_range(zone, &page[size]), &page[size]);
/*
* Mark as guard pages (or page), that will allow to
* merge back to allocator when buddy will be freed.
* Corresponding page table entries will not be touched,
* pages will stay not present in virtual address space
*/
if (set_page_guard(zone, &page[size], high, migratetype))
continue;
add_to_free_list(&page[size], zone, high, migratetype);
set_buddy_order(&page[size], high);
}
}
那么剩下96个连续Page块先分割出一64个连续Page块,后分割出一32个连续Page块,并将其分别插入对应free_area中:
static inline void set_buddy_order(struct page *page, unsigned int order)
{
set_page_private(page, order);
__SetPageBuddy(page);
}
......
/* Used for pages not on another list */
static inline void add_to_free_list(struct page *page, struct zone *zone,
unsigned int order, int migratetype)
{
struct free_area *area = &zone->free_area[order];
list_add(&page->lru, &area->free_list[migratetype]);
area->nr_free++;
}
set_pcppage_migratetype将index字段设置为迁移类型:
static inline void set_pcppage_migratetype(struct page *page, int migratetype)
{
page->index = migratetype;
}
__rmqueue_smallest分配失败则调用__rmqueue函数进行分配:
/*
* Do the hard work of removing an element from the buddy allocator.
* Call me with the zone->lock already held.
*/
static __always_inline struct page *
__rmqueue(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order, int migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
struct page *page;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CMA)) {
/*
* Balance movable allocations between regular and CMA areas by
* allocating from CMA when over half of the zone's free memory
* is in the CMA area.
*/
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA &&
zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES) >
zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES) / 2) {
page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);
if (page)
goto out;
}
}
retry:
page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, migratetype);
if (unlikely(!page)) {
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA)
page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);
if (!page && __rmqueue_fallback(zone, order, migratetype,
alloc_flags))
goto retry;
}
out:
if (page)
trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);
return page;
}
若未启用CONFIG_CMA选项,该函数会再次调用__rmqueue_smallest——分配成功则返回,分配失败调用__rmqueue_fallback,该函数从指定类型的备用类型中获取Page并移动到该类型freelist中:
/*
* Try finding a free buddy page on the fallback list and put it on the free
* list of requested migratetype, possibly along with other pages from the same
* block, depending on fragmentation avoidance heuristics. Returns true if
* fallback was found so that __rmqueue_smallest() can grab it.
*
* The use of signed ints for order and current_order is a deliberate
* deviation from the rest of this file, to make the for loop
* condition simpler.
*/
static __always_inline bool
__rmqueue_fallback(struct zone *zone, int order, int start_migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
struct free_area *area;
int current_order;
int min_order = order;
struct page *page;
int fallback_mt;
bool can_steal;
/*
* Do not steal pages from freelists belonging to other pageblocks
* i.e. orders < pageblock_order. If there are no local zones free,
* the zonelists will be reiterated without ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT.
*/
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT)
min_order = pageblock_order;
/*
* Find the largest available free page in the other list. This roughly
* approximates finding the pageblock with the most free pages, which
* would be too costly to do exactly.
*/
for (current_order = MAX_ORDER - 1; current_order >= min_order;
--current_order) {
area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);
fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,
start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);
if (fallback_mt == -1)
continue;
/*
* We cannot steal all free pages from the pageblock and the
* requested migratetype is movable. In that case it's better to
* steal and split the smallest available page instead of the
* largest available page, because even if the next movable
* allocation falls back into a different pageblock than this
* one, it won't cause permanent fragmentation.
*/
if (!can_steal && start_migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE
&& current_order > order)
goto find_smallest;
goto do_steal;
}
return false;
find_smallest:
for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER;
current_order++) {
area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);
fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,
start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);
if (fallback_mt != -1)
break;
}
/*
* This should not happen - we already found a suitable fallback
* when looking for the largest page.
*/
VM_BUG_ON(current_order == MAX_ORDER);
do_steal:
page = get_page_from_free_area(area, fallback_mt);
steal_suitable_fallback(zone, page, alloc_flags, start_migratetype,
can_steal);
trace_mm_page_alloc_extfrag(page, order, current_order,
start_migratetype, fallback_mt);
return true;
}
从MAX_ORDER - 1开始到min_order循环调用find_suitable_fallback:
/*
* Check whether there is a suitable fallback freepage with requested order.
* If only_stealable is true, this function returns fallback_mt only if
* we can steal other freepages all together. This would help to reduce
* fragmentation due to mixed migratetype pages in one pageblock.
*/
int find_suitable_fallback(struct free_area *area, unsigned int order,
int migratetype, bool only_stealable, bool *can_steal)
{
int i;
int fallback_mt;
if (area->nr_free == 0)
return -1;
*can_steal = false;
for (i = 0;; i++) {
fallback_mt = fallbacks[migratetype][i];
if (fallback_mt == MIGRATE_TYPES)
break;
if (free_area_empty(area, fallback_mt))
continue;
if (can_steal_fallback(order, migratetype))
*can_steal = true;
if (!only_stealable)
return fallback_mt;
if (*can_steal)
return fallback_mt;
}
return -1;
}
首先检查该区域内是否存在可用Page,若不为0则进入循环。fallbacks数组定义了各类型可使用的备用类型,以MIGRATE_TYPES作为结束:
/*
* This array describes the order lists are fallen back to when
* the free lists for the desirable migrate type are depleted
*/
static int fallbacks[MIGRATE_TYPES][3] = {
[MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },
[MIGRATE_MOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },
[MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE] = { MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
[MIGRATE_CMA] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION
[MIGRATE_ISOLATE] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
};
free_area_empty检查备用类型是否为空,为空则进入下一备用类型。can_steal_fallback判断是否可以Steal:
static bool can_steal_fallback(unsigned int order, int start_mt)
{
/*
* Leaving this order check is intended, although there is
* relaxed order check in next check. The reason is that
* we can actually steal whole pageblock if this condition met,
* but, below check doesn't guarantee it and that is just heuristic
* so could be changed anytime.
*/
if (order >= pageblock_order)
return true;
if (order >= pageblock_order / 2 ||
start_mt == MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE ||
start_mt == MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE ||
page_group_by_mobility_disabled)
return true;
return false;
}
如果从备用类型中找到可以Steal的Page,先执行get_page_from_free_area,之后执行steal_suitable_fallback函数:
/*
* This function implements actual steal behaviour. If order is large enough,
* we can steal whole pageblock. If not, we first move freepages in this
* pageblock to our migratetype and determine how many already-allocated pages
* are there in the pageblock with a compatible migratetype. If at least half
* of pages are free or compatible, we can change migratetype of the pageblock
* itself, so pages freed in the future will be put on the correct free list.
*/
static void steal_suitable_fallback(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,
unsigned int alloc_flags, int start_type, bool whole_block)
{
unsigned int current_order = buddy_order(page);
int free_pages, movable_pages, alike_pages;
int old_block_type;
old_block_type = get_pageblock_migratetype(page);
/*
* This can happen due to races and we want to prevent broken
* highatomic accounting.
*/
if (is_migrate_highatomic(old_block_type))
goto single_page;
/* Take ownership for orders >= pageblock_order */
if (current_order >= pageblock_order) {
change_pageblock_range(page, current_order, start_type);
goto single_page;
}
/*
* Boost watermarks to increase reclaim pressure to reduce the
* likelihood of future fallbacks. Wake kswapd now as the node
* may be balanced overall and kswapd will not wake naturally.
*/
if (boost_watermark(zone) && (alloc_flags & ALLOC_KSWAPD))
set_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);
/* We are not allowed to try stealing from the whole block */
if (!whole_block)
goto single_page;
free_pages = move_freepages_block(zone, page, start_type,
&movable_pages);
/*
* Determine how many pages are compatible with our allocation.
* For movable allocation, it's the number of movable pages which
* we just obtained. For other types it's a bit more tricky.
*/
if (start_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {
alike_pages = movable_pages;
} else {
/*
* If we are falling back a RECLAIMABLE or UNMOVABLE allocation
* to MOVABLE pageblock, consider all non-movable pages as
* compatible. If it's UNMOVABLE falling back to RECLAIMABLE or
* vice versa, be conservative since we can't distinguish the
* exact migratetype of non-movable pages.
*/
if (old_block_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)
alike_pages = pageblock_nr_pages
- (free_pages + movable_pages);
else
alike_pages = 0;
}
/* moving whole block can fail due to zone boundary conditions */
if (!free_pages)
goto single_page;
/*
* If a sufficient number of pages in the block are either free or of
* comparable migratability as our allocation, claim the whole block.
*/
if (free_pages + alike_pages >= (1 << (pageblock_order-1)) ||
page_group_by_mobility_disabled)
set_pageblock_migratetype(page, start_type);
return;
single_page:
move_to_free_list(page, zone, current_order, start_type);
}
该函数会检查是否移动单页,如果是直接调用move_to_free_list:
static inline void move_to_free_list(struct page *page, struct zone *zone,
unsigned int order, int migratetype)
{
struct free_area *area = &zone->free_area[order];
list_move_tail(&page->lru, &area->free_list[migratetype]);
}
list_move_tail相关定义如下:
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
if (!__list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
return;
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
}
......
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
......
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
如果是移动Block,则调用move_freepages_block:
int move_freepages_block(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,
int migratetype, int *num_movable)
{
unsigned long start_pfn, end_pfn;
struct page *start_page, *end_page;
if (num_movable)
*num_movable = 0;
start_pfn = page_to_pfn(page);
start_pfn = start_pfn & ~(pageblock_nr_pages-1);
start_page = pfn_to_page(start_pfn);
end_page = start_page + pageblock_nr_pages - 1;
end_pfn = start_pfn + pageblock_nr_pages - 1;
/* Do not cross zone boundaries */
if (!zone_spans_pfn(zone, start_pfn))
start_page = page;
if (!zone_spans_pfn(zone, end_pfn))
return 0;
return move_freepages(zone, start_page, end_page, migratetype,
num_movable);
}
该函数计算完起始与终止Page,PFN之后,调用move_freepages函数进行移动:
/*
* Move the free pages in a range to the freelist tail of the requested type.
* Note that start_page and end_pages are not aligned on a pageblock
* boundary. If alignment is required, use move_freepages_block()
*/
static int move_freepages(struct zone *zone,
struct page *start_page, struct page *end_page,
int migratetype, int *num_movable)
{
struct page *page;
unsigned int order;
int pages_moved = 0;
for (page = start_page; page <= end_page;) {
if (!pfn_valid_within(page_to_pfn(page))) {
page++;
continue;
}
if (!PageBuddy(page)) {
/*
* We assume that pages that could be isolated for
* migration are movable. But we don't actually try
* isolating, as that would be expensive.
*/
if (num_movable &&
(PageLRU(page) || __PageMovable(page)))
(*num_movable)++;
page++;
continue;
}
/* Make sure we are not inadvertently changing nodes */
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page_to_nid(page) != zone_to_nid(zone), page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page_zone(page) != zone, page);
order = buddy_order(page);
move_to_free_list(page, zone, order, migratetype);
page += 1 << order;
pages_moved += 1 << order;
}
return pages_moved;
}
综上,__rmqueue_fallback返回True以后会再次执行__rmqueue_smallest进行分配。
至此,本文已分析完伙伴系统fastpath部分——get_page_from_freelist函数,后续文章会继续分析__alloc_pages_slowpath,free_pages等函数及Slab分配器。
参阅链接
- Linux内核(5.4.81)——内存管理模块源码分析
- Linux内核5.13版本内存管理模块源码分析
- Translation lookaside buffer
- Linux内核高端内存
- Linux物理内存页面分配
- gfp_mask转换成对应的zone和migratetype
- Linux内存管理笔记(二十)————zonelist初始化
- Linux中的物理内存管理 [二]
- Linux Kernel vs. Memory Fragmentation (Part I)
- 描述系统上cpu和memory的状态:node_states
- Linux内存子系统——分配物理页面(alloc_pages)
- Linux内存管理(六): 分配物理内存alloc_pages
- 从备用类型中steal page










发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录